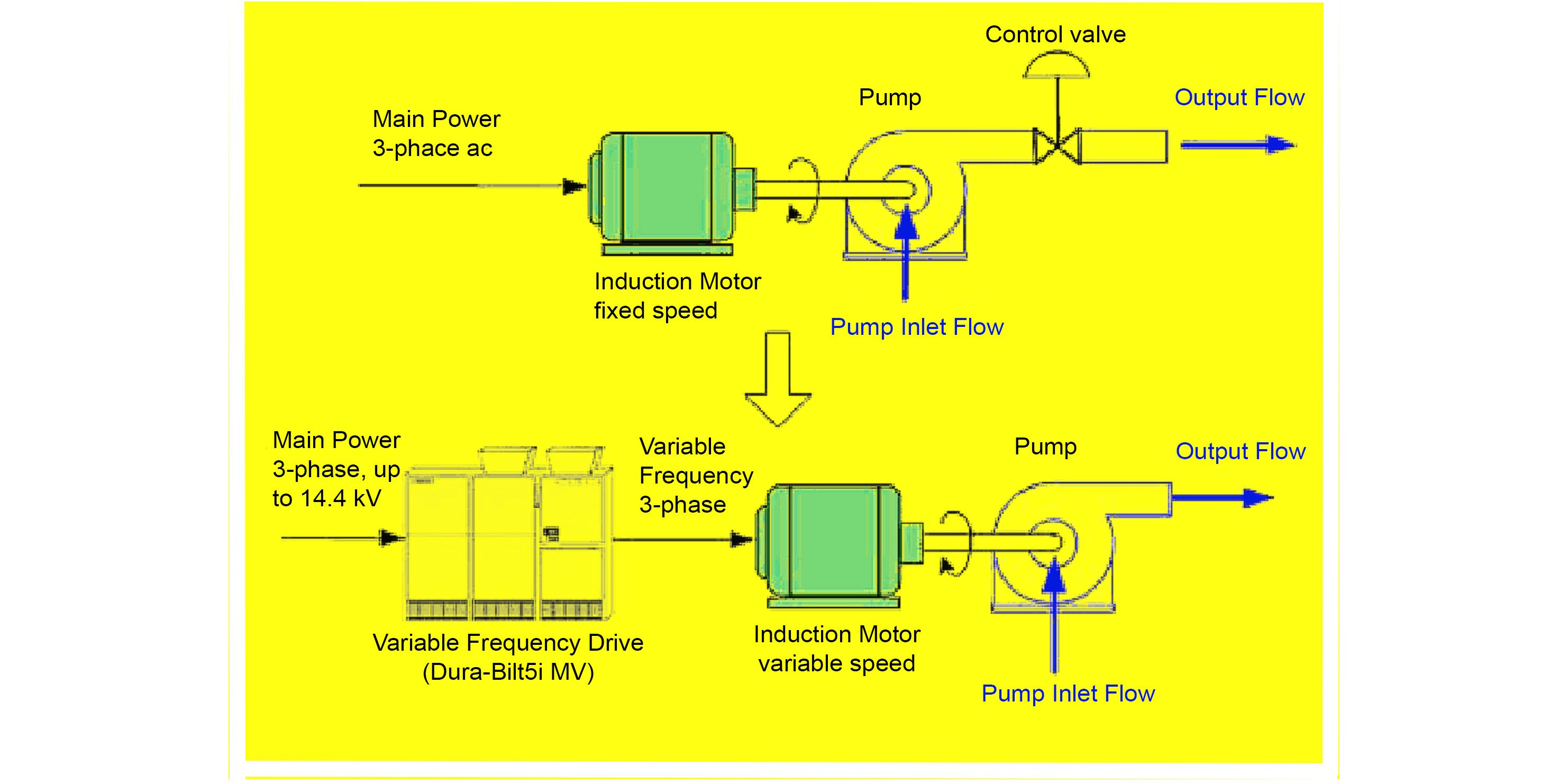
In an industrial environment, electric motors are used for a variety of applications.
These often include pumping water or other fluids, transporting material on conveyors or lifts, or providing motive force to moving parts of a mechanical device. The electric motor dominates the field whenever something needs to move. Regardless of the end user, all these motors will have one thing in common, a motor controller.
A motor controller is a device with the means to turn the motor on and off, provide circuit protection, and serve as a disconnecting means to render the circuit safe during maintenance. Traditionally, this is done with a direct-on-line (DOL) motor starter. A DOL starter installation consists of a branch breaker combined with a DOL motor starter and overload module. In a typical DOL motor starter installation, the branch breaker will serve as short circuit protection, as well as a means of electrical disconnect. The motor starter unit is essentially a large relay with a magnetic coil and high-power contacts held apart by springs. When the motor is called to run, the magnetic coil is energized, pulling in the contacts and bridging the line side to the load side terminals, allowing power to flow. Once the motor starter has contact, electrical power flows out through an overload disconnect module, and then to the electric motor. The DOL motor starter is a well-proven design that is familiar to almost anyone in the industrial space and is still what is found in a majority of applications.