Hydrogen Sulfide Chemical Formula and the Molar Mass of H2S.
H2S is a naturally occurring chemical compound created in nature with the decay of organic material. Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with a molecular formula comprised of (2) hydrogen atoms and (1) one sulfur atom. The formula is displayed as H2S. The gas is a colorless hydride, often known as the “Rotten egg gas.” This gas is very dangerous as it is poisonous and toxic to all life forms. It is also very corrosive and flammable. The H2S molar mass is 34.1 g/mol, with a melting point of -76 F (-60 C) and a melting point of –115.6F or (-82C).
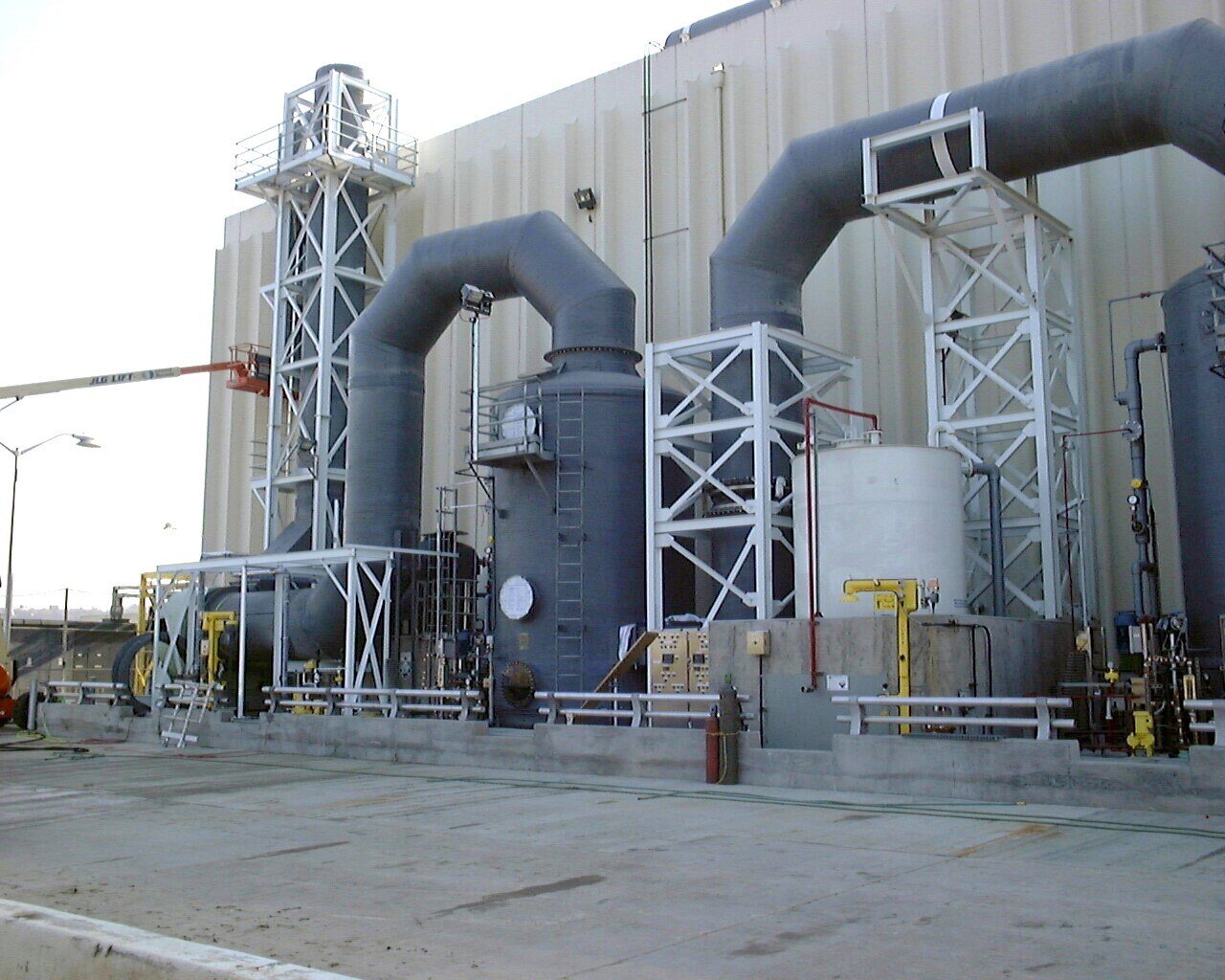
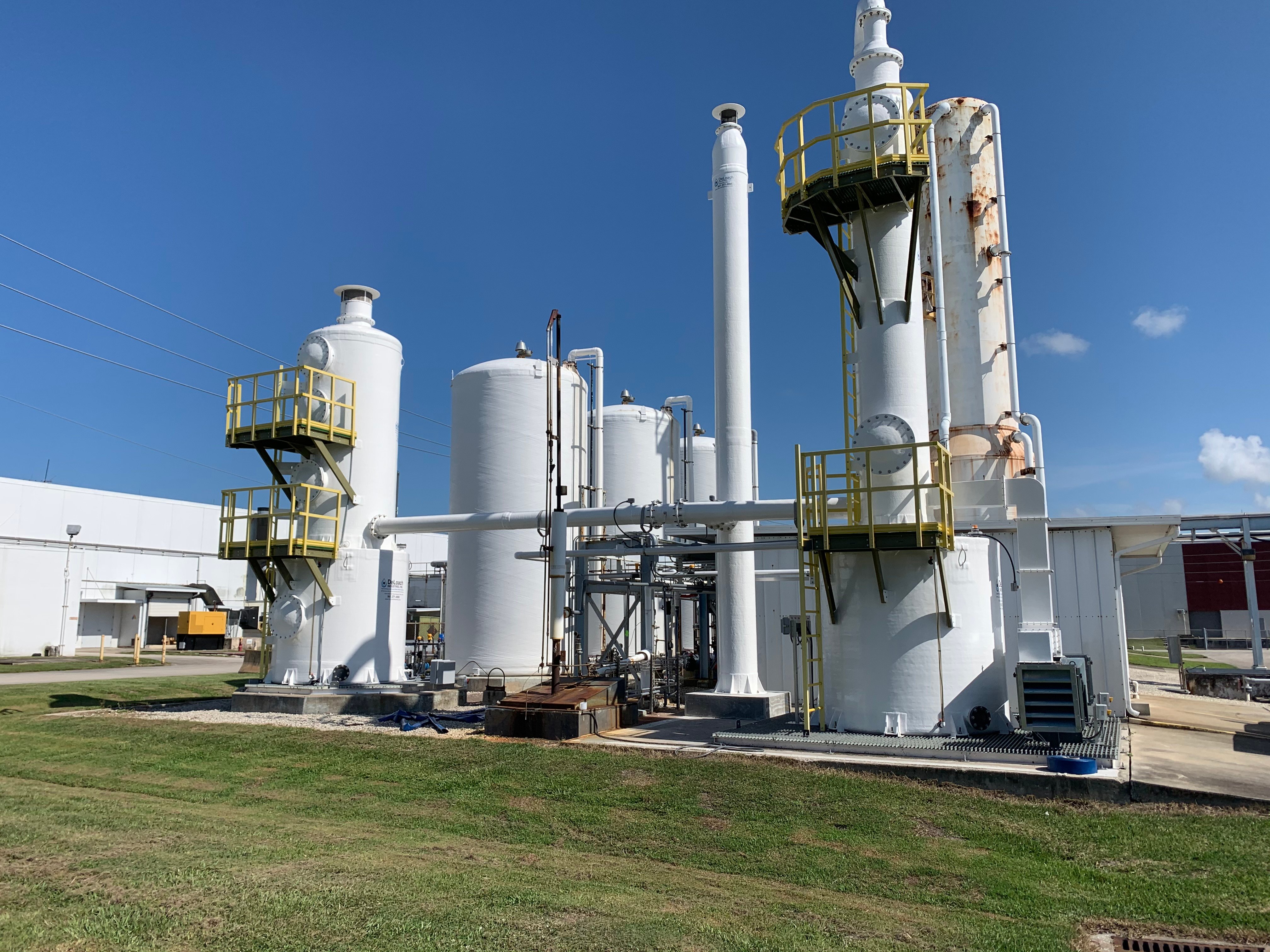
Hydrogen sulfide gas is also created more often from a byproduct of a manufacturing process or the removal of water or wastewater treatment systems. In wastewater, as organic material decays, H2S is released, captured, and treated to protect human lives, reduce corrosion, H2S gas exposure, and H2S gas poisoning, H2S presence and reduce odor complaints. H2S gas is produced during manufacturing operations at refineries, pulp mills, and mining. These high levels of H2S are released during manufacturing. They must be captured and neutralized to protect human life from unwanted health effects such as pulmonary edemaand prevent excessive corrosion to your system. You cannot even smell gas at higher concentrations, and it is not distinguishable as “rotten egg gas,” which makes it even more dangerous and drives the need for hydrogen sulfide scrubbers equipment, fume scrubbers, or odor control scrubbers.
According to the “Agency for Toxic Substance & Disease Registry,” those who work within certain industries are exposed daily to higher levels of hydrogen sulfide gas than the normal public. Because the gas is also heavier than air, it will settle into lower places like manholes, tanks, and basements, and it will travel across the ground filling in low-level areas. To protect the public, OSHA (occupational safety and health administration) has set guidelines and rules known as “Permissible Exposure Limits” (PEL). A PEL is a legal limit a worker may be exposed to a chemical substance. The PEL limit for hydrogen sulfide is ten parts per million (10 ppm) over eight hours.