I will explore the potential risks of exposure to two members of a family of man-made chemicals called PFAS.
These chemicals are PFOA and PFOS, "poly-fluoroalkyl substances."
I will discuss the sources of PFOA and PFOS. These include leaching from industrial sites, the use of consumer products, and food and water contamination.
I will also discuss the exposure pathways of PFOA and PFOS. I will examine the regulations and guidelines for the use of these chemicals. I will also investigate their impact on the environment and various industries.
I will guide long-term human health effects.
This guide covers the potential risks of pfo's and pfoa's. It explains their sources and exposure pathways. It also looks at regulations and guidelines for their usage and impact on the environment and industries.

Introduction to PFOA and PFOS
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
FDA,
Safe drinking water,
wastewater,
Global,
RO system,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Drinking Water,
PFA's,
DeLoach Industries,
Cosmetics,
make-up,
water process system,
removing PFAS & PFOS,
pfas exposure,
health effects of pfas,
nonstick cookware,
wastewater treatment system,
water treatment standards,
PFOS,
safe drinking water act,
pfoa regulations,
the environmental protection agency,
drinking water standards,
adverse health effects,
water resistant clothing,
environmental safety
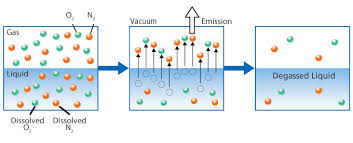
Requires an application commonly referred to as either “Degasification” or "Decarbonation" and it requires the use of a piece of water treatment equipment called either a “degasifier” or a “decarbonator”.
Both of these are similar in nature and are designed for Carbon Dioxide (CO2) removal from the incoming water. A properly designed decarbonator can remove 99.99% of the free carbon dioxide gas that is present in the water stream. One of the primary reasons for utilizing a decarbonator or degasifier for the removal of carbon dioxide gas is the raise the pH of the water without the need to add caustic. resulting in high-purity water.
The other reason is the remove the CO2 prior to treating the water with Ion Exchange which utilizes Anion or Cation resins to reduce the regeneration cycles for the resin beds. High concentrations of CO2 consume the ion charge within the resins and require more frequent regeneration cycles. The difference between anion and cation resins is that one is positively charged (anion) and the other is negatively charged (cation), cation resins, attract positive ions with their negative charge.
The term decarbonation describes the process of the removal of suspended gas or the conversion of carbonic acids into free Carbon Dioxide. Carbonic Acid (H2CO3) is stable at normal ambient anhydrous conditions. However, Carbonic Acid decomposes when not stable and in the presence of any water molecules to form carbon dioxide (CO2). The Carbonic acid breaks down when present in water and it is converted to a gas based upon certain conditions. It is common to have CO2 present in water requiring a decarbonation process when utilizing certain types of water filtration such as membrane filtration with reverse osmosis or it can be present when the need to adjust pH is required. When removing (CO2) the process is often referred to as “Decarbonation”, when removing (H2S) Hydrogen Sulfide the process is often referred to as “Degasification”.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
aeration,
iron oxidation,
water treatment,
water plant,
bicarbonate,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
dissolved gases,
De-Aeration,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
oxygen,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
gases,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier
The Basics of Water Decarbonation
and the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2). The need to remove (CO2) is essential in most Aquaculture, Municipal, Industrial, and Food & Beverage Processes To understand you must familiarize yourself with Henry’s Law.
Henry's Law defines the method and proportional relationship between the amount of a gas in a solution in relation to the gas's partial pressure in the atmosphere. Often you will see and hear various terms like degasification, decarbonation, aeration, and even air stripping when discussing the removal of dissolved gases and other convertible elements from water. Understanding the impacts that Carbon Dioxide (CO2) can have on both equipment and aquatic life provides the basic reasons why the need to decarbonate water, exists. Carbon Dioxide (CO2) can exist naturally in the raw water supply or be the result of ph control and balance. In either case, the process called Decarbonation or Degasification provides the most cost-effective and efficient manner to reduce or tally remove (CO2) from the water. In addition to Carbon Dioxide (CO2), water can contain a variety of other contaminants that may impact the removal efficiency of the Carbon Dioxide. A variety of elements as well as dissolved gases such as oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide (CO2). A full analytical review of the water chemistry is required to properly design and size the “Water Treatment” process.
Breaking the bonds in water releases a dissolved gas
such as carbon dioxide (CO2) you must change the conditions of the vapor pressure surrounding the gas and allow the gas to be removed. There are many variables to consider when designing or calculating the “means and methods” of the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2). When I refer to the means and methods. I am referring to the design of a decarbonator and its components. The means equals the size and type (Hydraulic load) of the decarbonator and the “method” equals the additional variables such as the cubic foot of airflow (CFM) and “Ratio” of the air to water to accomplish the proportional condition needed to remove the carbon dioxide (CO2).
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
aeration,
iron oxidation,
water treatment,
water plant,
bicarbonate,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
dissolved gases,
De-Aeration,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
oxygen,
degasifier,
gases,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier,
removal of CO2 from water
One of the most pressing issues that we face today is the phenomenon of red tide.
Red tide is algae bloom that can cause serious harm to marine life and humans.
In this article, I will explore what red tide is, what causes it, and its impact on Florida. Most importantly, the role of wastewater treatment in helping to prevent it.
What is Red Tide?
Red tide is a natural phenomenon that occurs when certain species of algae grow out of control. These algae produce toxins that harm marine life and humans. The term "red tide" comes from the reddish-brown color that the water takes on when the algae bloom. The bloom can happen in any part of the world in warm, coastal waters.
What Causes Red Tide?
Various factors cause these harmful algae to bloom.
- Changes in water temperature
- Nutrient pollution
- Ocean currents
The most common cause is nutrient pollution. Nutrient pollution occurs when excess nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus enter the water. These nutrients can come from agricultural runoff, sewage from residential drain fields, inefficient wastewater treatment plants, septic tanks, and fertilizer.
Red Tide Blooms in Florida - History and Impact.
Florida has a long history of deadly algae blooms. The state experiences red tide almost every year, lasting for months.
It devastates the state's marine life, including fish, sea turtles, and dolphins. The algae produce toxins that can kill these animals. The dead fish can wash up on shore, causing beachgoers an unpleasant odor and an eyesore.
How Do These Microscopic Algae Affect Marine Life?
It affects marine life in a variety of ways. The algae's toxins can cause respiratory problems and neurological issues.
With most coastal outbreaks, the loss of marine life is significant. It produces toxins and decreases oxygen levels, another contributing factor to marine animal fatalities. Red tide disrupts the entire ecosystem and has been increasing in both frequencies of outbreaks as well as areas impacted.
How Does Red Tide Impact Humans?
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water treatment,
wastewater,
DeLoach Industries,
water process system,
red tide,
wastewater treatment plants,
red tide in florida,
wastewater treatment system,
cause of red tide,
water temperature,
marine life,
wastewater treatment infrastructure,
benefits of wastewater treatment,
water treatment standards
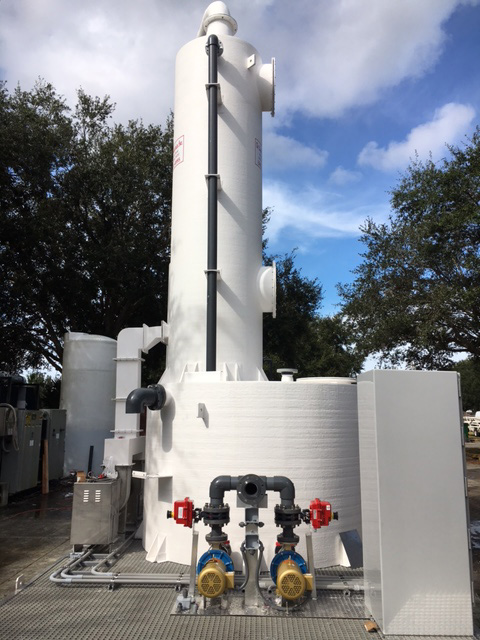
Odor control in a manufacturing facility is essential.
It prevents potential health risks and discomfort caused by the spread of chemicals, vapors, and fumes. Additionally, excessive vapors can hinder the efficiency of exhaust and natural ventilation systems.
One effective solution for addressing odor issues is the installation of an Odor Control Scrubber Tower. These towers are part of the ventilation system in manufacturing plants and chemical processing facilities.
Odor control scrubbers help to remove noxious fumes and odors from exhaust and air streams. This is an effective way to improve air quality. This process involves utilizing an activated carbon filter and an ionic air filter
Key Considerations for Installing an Odor Control Scrubber Tower:
Health and Safety of Workers:
Industrial environments pose risks of exposure to hazardous fumes and gases for workers. Unhealthy odors emitted in high concentrations can jeopardize their well-being and safety. In some cases, these gases may even be combustible, adding an extra level of danger.
Odor control scrubber towers remove gases from the contaminated air, ensuring a safe working environment. These towers reduce the risk of health issues such as nausea, headaches, allergy symptoms, eye irritation, and loss of consciousness. This helps maintain worker productivity and prevents sickness caused by toxic fumes and gases.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
odor control,
water treatment,
water distribution system,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
safety,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
caustic,
Safe drinking water,
wastewater,
gases,
Biological Odor Control Scrubber,
Biological odor control,
what is a scrubber,
municipal water systems,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Clean Water,
Industrial Odor Control
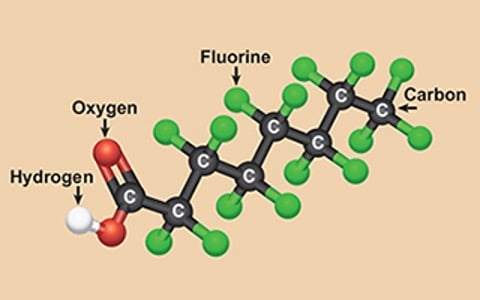
Per- and polyfluorinated substances (PFAS), known as "forever chemicals," have long been utilized in various consumer products due to their exceptional properties.
However, the challenge lies in effectively treating or eliminating PFAS once they enter the environment or water supply. This blog will focus on the technological advancements in removing PFAS and perfluorooctanoic acids (PFOAs) from water sources. By exploring different treatment methods, such as activated carbon absorption, ion exchange resins, and reverse osmosis, and simply avoiding PFOA and PFOS, we can better understand the available options for mitigating these persistent chemicals in water.
Activated Carbon Absorption
One of the earliest technologies employed for PFAS removal is activated carbon absorption. This method involves the use of specially treated carbon materials that effectively adsorb PFAS compounds from water sources. The activated carbon's large surface area and porous structure allow it to trap and retain PFAS molecules. This technology has proven effective in removing PFAS, including PFOAs, from drinking water and environmental sources. However, periodic treatment and regeneration of the activated carbon are necessary to maintain its efficacy.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
iron oxidation,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
ION Exchange Resin,
Safe drinking water,
wastewater,
degasifier,
RO system,
Deagasification,
PFA's,
technology,
contaminants,
reverse osmosis,
carbon filters,
activated carbon,
removing PFAS & PFOS,
pfas exposure,
health effects of pfas,
nonstick cookware,
wastewater treatment systems,
PFOS,
pfoa regulations,
drinking water standards,
water resistant clothing,
environmental safety
In water treatment systems it is often important to measure the rate at which water is flowing through the system. Data from flow measurement devices can be used to control chemical dosing, set pump speeds, control filter loading rates, inform maintenance programs, and other tasks necessary for the operation of a water treatment facility or on key components such as Degasification and Decarbonation systems or Biological Odor Control Systems. As with most types of instrumentation, there is an array of technologies that can be used for the task, each one with various strengths and optimal applications. For modern electronically controlled systems, the most common types of flow sensors used are axial turbine flowmeters, paddlewheel flowmeters, differential pressure/orifice plate flow transducers, and magnetic flowmeters. This article will briefly discuss the technology and features of each of these types.
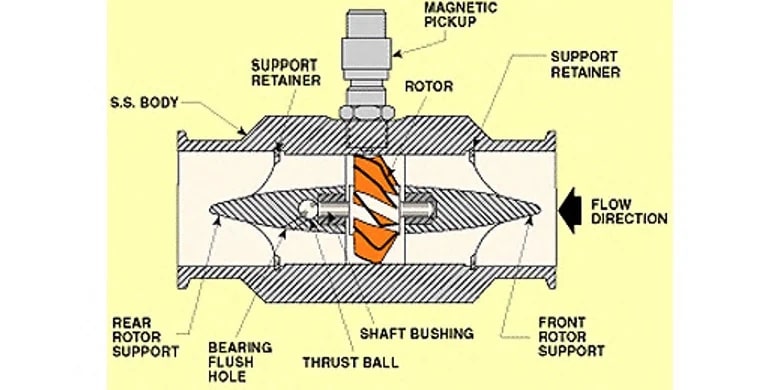
A turbine flow meter,
consists of a tube that contains supports to hold a multi-bladed metal turbine in the center. The turbine is designed to have close clearance to the walls of the tubing such that nearly all of the water is made to flow through the turbine blades as it travels through the pipe. The turbine is supported on finely finished bearings so that the turbine will spin freely even under very low flows. As the turbine spins, a magnetic pickup located outside of the flowmeter housing is used to sense the tips of the turbine blade spinning past the pickup. An amplifier/transmitter is then used to amplify the pulses and either transmit them directly or convert the pulse frequency into an analog signal that is then sent to a programmable controller for further use elsewhere in the system. One advantage of a turbine flowmeter is that the electronics are separated from the fluid path. The magnetic pickup is the only electronic component, and it is installed outside of the turbine housing, reading the presence of the turbine blade tips through the wall of the sensor body. In clean water applications, this can be advantageous because the magnetic pickup can be replaced if needed without removing the turbine from service. However, the turbine itself covers most of the pipe area and creates back pressure in the system, requiring increased pumping energy to move a given amount of water. In Industrial Water Treatment or Filtration Treatment, turbines can also easily become fouled or jammed if they are used to measure water or other fluids with entrained solids, algae or bacteria cultures which cause significant accumulation, or corrosive chemical components that can degrade the turbine bearings.
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
About DeLoach Industries,
water plant,
pumps,
Alkalinity,
Safe drinking water,
wastewater,
Recycling,
pharmaceutical water,
Aqua Farming,
Aquaculture,
Pipe Size,
municipal water systems,
industrial facilities,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
actuated valves,
pump controls,
Drinking Water,
Clean Water,
Water Test,
Water Test Kit,
DeLoach Industries,
civil engineers
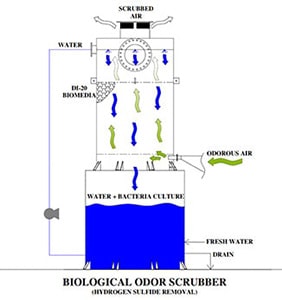
A Biological Odor Control Scrubber Is Just One Of Many Different Types Of Available Technologies to treat air emissions that may contain harmful gases.
This class of equipment commonly falls into a category referred to as “Odor Control Scrubbers” and they are utilized to remove dangerous or noxious odors from an air stream. The Biological Odor Control System has gained popularity among many end users such as municipal operators due to the reduced operating cost and more simplistic operating requirements. A typical chemical odor control scrubber often requires two or more chemical additives and more instrumentation is required to maintain system performance. With the additional chemicals required and instrumentation comes the need for more hands-on maintenance, calibration, and safety requirements which increases the operating costs and workload of the operator.
A Biological Odor Control System relies on active bacteria cultures that recirculate within a water stream and flow across a random packed media bed that is beneficial to the bacteria culture.
During the process of metabolizing harmful gases such as Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) the biological odor control system requires only the addition of Caustic to control and balance the pH and additional water makeup to replace what has been consumed through evaporation or during the blowdown process to eliminate solids. There are several different types of odor control and chemical wet scrubbers, industrial air scrubbers on the market today and each provides a solution for the treatment of noxious or corrosive gases and odors in the industry. And even though Biological scrubbers are commonly utilized in municipal applications for the treatment of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gases that were produced by a water or wastewater treatment process there are times when a Biological Scrubber does not provide the best solution for treatment. When there are wide or rapidly changing concentrations in the ppm (parts per million) level then a Biological Scrubber will have difficulties balancing and acclimating fast enough to prevent a breakthrough. As an example, In water treatment, there is a treatment process referred to as “degasification” which strips the hydrogen sulfide gas from the water, and then the concentrated H2S gas is exhausted from the tower through an exhaust port. When the concentration rises above 1 ppm for hydrogen sulfide gas then the levels become both noxious to the surroundings as well as corrosive. Many times, the levels range from 3-7 PPM in concentration with Hydrogen Sulfide and pose a serious health threat, noxious odor, and corrosive environment demanding capture and treatment. When utilizing an Odor Control Scrubber such as a Biological Scrubber the gases are pulled or pushed through an air duct system that is connected to the Biological Scrubber inlet or suction side of the blower. The same process is utilized when treating Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) gases that were captured at a wastewater treatment process. These gases may have been generated from a source such as the wastewater treatment plant, lift station, or master head-works facility. When captured the gases are also conveyed in a similar manner to the Biological Odor Control Tower for treatment.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
degasification,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
media packing,
caustic,
wastewater,
gases,
H2S Degasifier,
Ammonia,
air emissions
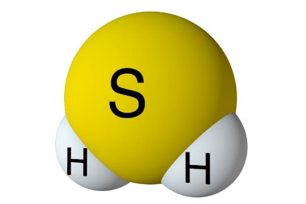
Hydrogen Sulfide Chemical Formula and the Molar Mass of H2S.
H2S is a naturally occurring chemical compound created in nature with the decay of organic material. Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with a molecular formula comprised of (2) hydrogen atoms and (1) one sulfur atom. The formula is displayed as H2S. The gas is a colorless hydride, often known as the “Rotten egg gas.” This gas is very dangerous as it is poisonous and toxic to all life forms. It is also very corrosive and flammable. The H2S molar mass is 34.1 g/mol, with a melting point of -76 F (-60 C) and a melting point of –115.6F or (-82C).
Hydrogen sulfide gas is also created more often from a byproduct of a manufacturing process or the removal of water or wastewater treatment systems. In wastewater, as organic material decays, H2S is released, captured, and treated to protect human lives, reduce corrosion, H2S gas exposure, and H2S gas poisoning, H2S presence and reduce odor complaints. H2S gas is produced during manufacturing operations at refineries, pulp mills, and mining. These high levels of H2S are released during manufacturing. They must be captured and neutralized to protect human life from unwanted health effects such as pulmonary edemaand prevent excessive corrosion to your system. You cannot even smell gas at higher concentrations, and it is not distinguishable as “rotten egg gas,” which makes it even more dangerous and drives the need for hydrogen sulfide scrubbers equipment, fume scrubbers, or odor control scrubbers.
According to the “Agency for Toxic Substance & Disease Registry,” those who work within certain industries are exposed daily to higher levels of hydrogen sulfide gas than the normal public. Because the gas is also heavier than air, it will settle into lower places like manholes, tanks, and basements, and it will travel across the ground filling in low-level areas. To protect the public, OSHA (occupational safety and health administration) has set guidelines and rules known as “Permissible Exposure Limits” (PEL). A PEL is a legal limit a worker may be exposed to a chemical substance. The PEL limit for hydrogen sulfide is ten parts per million (10 ppm) over eight hours.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
degasification,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
dissolved gases,
wastewater,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
gases,
H2S Degasifier,
Hydrogen Sulfide Chemical Formula,
Molar mass,
Hydrogen Sulfide formula,
molar mass h2s,
hydrogen sulfide molar mass,
hydrogen sulfide gas
In the production and purification of water for industry
there are many types of different processes available to remove harmful minerals and gases from the water stream but the most effective process and most cost-effective from both a capital investment and operational cost is a “Forced Draft Degasification System” (Degasifier).
Degasification is used in a wide range of water processes for industrial and municipal applications which extend from the production of chemicals to the production of semiconductors and in all applications the need to remove contaminants from the water and dissolved gases is key to achieving the end results needed in the industrial water process. Water from the ground often contains elements such as calcium carbonate, manganese, iron, salts, hydrogen sulfide, and sulfur just to name a few of the basic contaminants and these naturally occurring elements can cause serious damage and consequences to process equipment such as boiler systems, piping, membranes, and cation and anion exchange resins used in the demineralization process.
Calcium carbonate can dissolve in water under certain pH ranges forming carbonic acid and releasing carbon dioxide (CO2) gases. These gases are not only very corrosive to equipment like boiler feed systems and boiler tubes but also attack the actual resin beds found in cation and anion softening and demineralization system causing an increase in regeneration and chemical consumption and resin bed replacement.
By incorporating a Force Draft Degasification system you can remove dissolved gasses
like CO2 and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) to as low as 99.999% and improve the cation and anion system performance, extend the resin bed life, and lower the operating cost of the water treatment process.
Quite often Forced Draft Degasification is utilized “post” treatment to also remove newly formed dissolved gases prior to entering the boiler feed system to prevent corrosion damage within the tubes and feed system and pumps. These gases are easily removed with the forced draft degasifier at a much lower cost than chemical additives or liquid cell degasification that requires higher capital cost and much higher operating cost.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
iron oxidation,
water treatment,
water distribution system,
aluminum,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
calcium carbonate,
media packing,
pH levels,
Langilier index (LSI),
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
dissolved gases,
feed water,
De-Aeration,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier