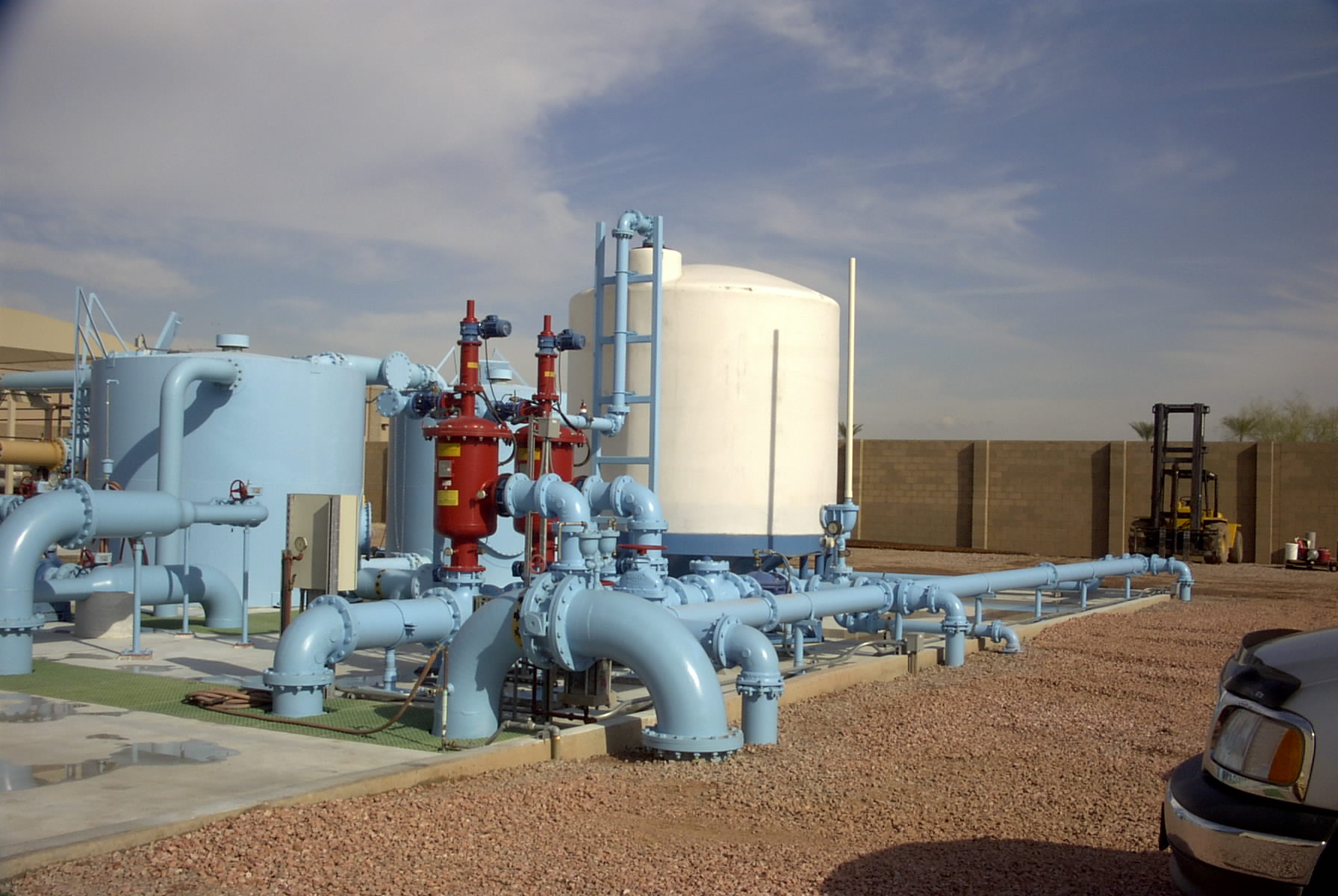
In the production and purification of water for industry
there are many types of different processes available to remove harmful minerals and gases from the water stream but the most effective process and most cost-effective from both a capital investment and operational cost is a “Forced Draft Degasification System” (Degasifier).
Degasification is used in a wide range of water processes for industrial and municipal applications which extend from the production of chemicals to the production of semiconductors and in all applications the need to remove contaminants from the water and dissolved gases is key to achieving the end results needed in the industrial water process. Water from the ground often contains elements such as calcium carbonate, manganese, iron, salts, hydrogen sulfide, and sulfur just to name a few of the basic contaminants and these naturally occurring elements can cause serious damage and consequences to process equipment such as boiler systems, piping, membranes, and cation and anion exchange resins used in the demineralization process.
Calcium carbonate can dissolve in water under certain pH ranges forming carbonic acid and releasing carbon dioxide (CO2) gases. These gases are not only very corrosive to equipment like boiler feed systems and boiler tubes but also attack the actual resin beds found in cation and anion softening and demineralization system causing an increase in regeneration and chemical consumption and resin bed replacement.
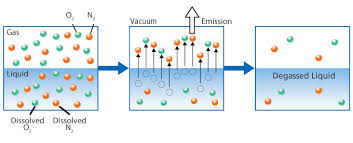
By incorporating a Force Draft Degasification system you can remove dissolved gasses
like CO2 and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) to as low as 99.999% and improve the cation and anion system performance, extend the resin bed life, and lower the operating cost of the water treatment process.
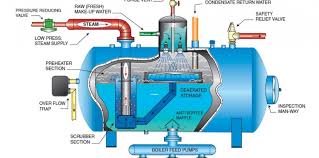
Quite often Forced Draft Degasification is utilized “post” treatment to also remove newly formed dissolved gases prior to entering the boiler feed system to prevent corrosion damage within the tubes and feed system and pumps. These gases are easily removed with the forced draft degasifier at a much lower cost than chemical additives or liquid cell degasification that requires higher capital cost and much higher operating cost.