Basics of water decarbonation for dissolved organic carbon.
The water treatment industry continues to develop and evolve. Over the past two decades, there have been many new developments in technology and even more refinement in existing technologies such as "Degasification". The evolution and advancement of water treatment have been driven by the constantly increasing demand from an increase in population that demand cost-effective solutions and recognition to improve safety with the implementation of NSF 61 standards.
All human cultures on our planet share a single commonality: the dependency on water to survive.
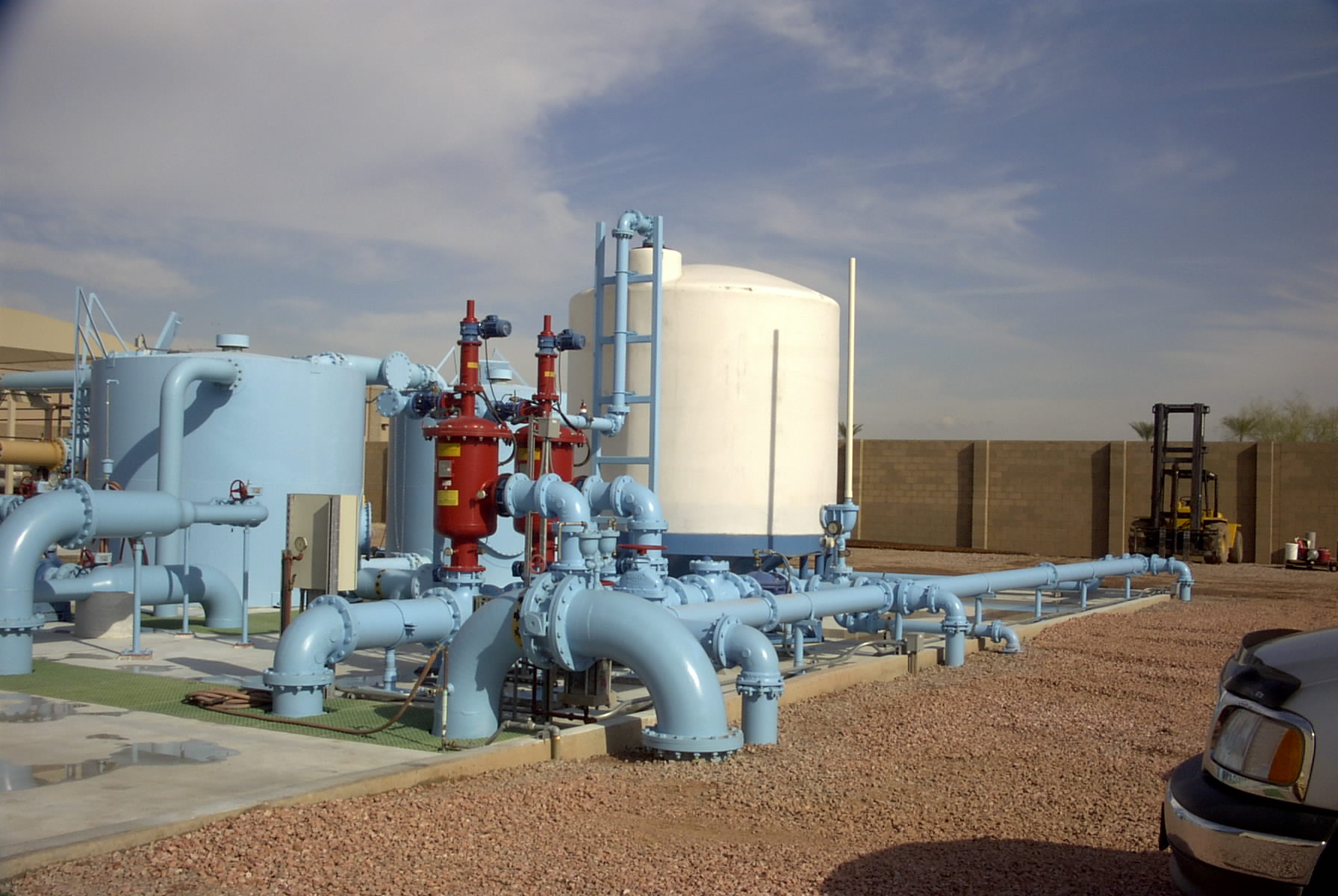
Many existing technologies, such as "Degasification," have evolved with higher efficiency to meet the demand changes and provide safety to consumers and the systems. Degasification refers to the removal of dissolved gases from liquids, and the science to degasify water is based upon a chemistry equation known as "Henry's Law". The "proportionality factor" is called Henry's law constant" and was developed by William Henry in the early 19th century. Henry's Law states that "the amount of dissolved gas is proportional to its partial pressure in the gas." The most "cost" effective method to perform degasification is with the packed vertical tower called a "Degasifier” or “Decarbonator.”
The key words in this previous sentence for owners, operators, and engineers to focus on is "the most cost-effective" as there is no other process more cost-effective at removing dissolved gases at the lowest cost than using a Degasifier or decarbonator. The process of degasification is simple enough to understand. Water is pumped to the top of a vertically constructed tower, where it first enters the tower through some type of distribution system at the same time, there is a cross-current air flowing up from the bottom by a blower located at the bottom of the tower, and the air encounters the water and is exhausted at the top of the tower through an exhaust port. There are various types of distribution systems, and we will explore these in later discussions. Once the water enters the top of the tower and passes through the distribution system, it then travels by gravity downward. The next thing the water encounters is some type of media packing. There are various forms of media packing offered in the degasification industry, and each type can offer higher performance or have the ability to deter fouling. The selection of the type, size, and volume is where the “experience, engineering, and understanding of each application” comes into play.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
About DeLoach Industries,
water plant,
NSF/ANSI 61,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
media packing,
pH levels,
scaling,
caustic,
Decarbonation,
Safe drinking water,
dissolved gases,
carbon dioxide,
decarbonator,
boiler system,
degasifier,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier,
Dissolved organic Carbon,
co2 dissolved in water
In the United States manufacturing industry, an astonishing 400 million gallons of water per day (MGD) is consumed to generate steam.
Out of this amount, approximately 60 MGD is sent to blow-down drains, while another 300 MGD is used for direct injection of steam. The common denominator in all of these processes is the need for purified and treated water. Without proper treatment, manufacturers would face frequent shutdowns and increased capital expenditure, significantly impacting their cost of goods. One effective method of water treatment to protect boilers is through degasification and deaeration.
Degasification towers play a crucial role in removing harmful gases such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S), carbon dioxide (CO2), and often dissolved oxygen (DO). The elimination of these corrosive gases is vital for enhancing the lifespan and efficiency of boiler systems. If these gases are allowed to remain in the boiler feed water, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), it can lead to disastrous consequences, including higher operating costs and reduced system longevity. Carbon dioxide (CO2) can convert into carbonic acid, creating a corrosive environment for the boiler and other critical components. In cases where an ion exchange process is implemented prior to the boiler, the presence of carbon dioxide (CO2) can drastically increase regeneration costs as the resins are consumed. By removing carbon dioxide (CO2), the life of the resin is extended, and the pH of the water is elevated, reducing the need for additional chemicals and further lowering operating costs.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
degasification,
iron oxidation,
water treatment,
water distribution system,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
feed water,
De-Aeration,
steam generation,
steam generating boilers,
carbon dioxide,
steam,
decarbonator,
boiler system,
degasifier,
gases,
RO membrane,
carbonic acid,
RO system,
H2S Degasifier,
Boiler feed water
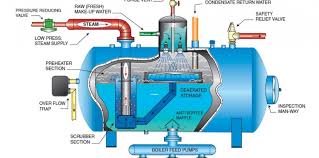
The operation of steam-generating boilers and the process of removing dissolved gases from the feed water is of utmost importance.
Deaeration is essential in the boiler system process.
Deaeration involves removing oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from the water. Removing oxygen and carbon dioxide from the water before it enters the boiler system is essential. This prevents corrosion of the boiler system components and reduces costly maintenance and repairs to your system.
Oxygen and carbon dioxide can corrode and destroy metal components of the boiler system.
Corrosion can be costly to repair or replace. This is due to oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) not being removed from the water.
In order to avoid unwanted corrosion, it is necessary to treat the water before it enters the boiler system. This can be achieved through different techniques, including deaeration, chemical treatment, or mechanical filtration.
The deaeration process typically requires a deaerator. This device combines heat and vacuum to remove dissolved gases from water. The deaerator reduces the amount of dissolved solids in the water.This can improve the efficiency of the boiler system. Neglecting regular maintenance and inspection of the boiler can lead to severe corrosion damage and operational issues.
Read More
Topics:
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
feed water,
De-Aeration,
steam generating boilers,
carbon dioxide,
oxygen,
steam,
decarbonator,
boiler system