If you’ve been following the news, you know a growing problem with PFAS (per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances) exists.
PFAS, a group of synthetic chemicals in a wide range of products, is causing a growing concern. Despite their widespread use, some PFAS compounds have been found to degrade into potentially harmful byproducts like PFAS-methyl tetrahydrofuran. What's more alarming is that these chemicals have infiltrated our drinking water sources, even in areas with high water tables. This is why it's crucial to understand effective methods for removing PFAS from water. What should you do if you suspect that there’s a problem with your water? Check the source of the water, test it, and treat it if necessary.
Follow these steps to remove PFAS from drinking water.
Test Your Water
Although knowing how to remove contaminants is essential, it’s even more important to understand how to test your water for contamination. A water test kit can help you determine whether there are contaminants in your water and whether they are at a dangerous level. You can purchase water test kits at grocery stores, hardware stores, and online retailers. Generally, these kits come with the standard set of tests for a home water filtration system, but they also often include tests for specific contaminants. Use these tests to determine whether your water is safe to drink. If your water contains contaminants, remove them from your water source. This can be done by digging a more bottomless well, installing a water filtration system, or getting a water purification system. If your water does not contain contaminants, you don’t need to do anything except continue drinking your water.
Check the Source
Understanding the source of your water is a crucial step in addressing contamination. Whether you have a well or a water treatment system, knowing where your water comes from can provide valuable insights. By tracing the water's journey from the source, you can determine if contamination occurs upstream. This knowledge is essential for well owners, who might overlook the significance of understanding their water source. If you find contamination at the source, you can address it immediately, such as reducing the distance between the source and your dwelling or seeking alternative, uncontaminated sources.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
Chemical Odor,
Safe drinking water,
RO system,
filters,
Filter Media,
residential well water systems,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
backwash,
Carbon Filter,
Micron Filter,
Drinking Water,
Clean Water,
Contaminated Water,
Water Source,
Sediment Filter,
PFA's,
Water Test,
Water Test Kit
PFOA and PFOS are man-made chemicals used in various products to simplify life.
Forever chemicals, also known as synthetic chemicals called PFAS, have gained recognition. Scientists created these chemicals to make products resistant to water, stains, and sticking. The United States initially utilized them in the 1950s.
DuPont introduced Teflon in the 1950s to help Americans have nonstick cookware and make their lives easier. Americans and people from other countries liked this new improvement and soon used these substances in many different products.
These chemicals are resistant to water and lipids, so they don't break down and last a long time in the environment.
Over time, companies have used these chemicals in manufacturing various products, such as firefighting foam, food packaging, and cosmetics. As a result, these chemicals have entered the air, water, soil, and food production. They discontinued the use of PFAS and their other compounds in the mid-1970s.
People believe that contamination has affected more than 7000 metric tons of Fluorochemicals. PFOAs and PFOS, which can cause various health problems, have exposed many Americans and people in the USA.
PFOA chemicals contaminated 1% of public drinking water supply systems in 2016. The EPA did not regulate safe levels of PFOA and PFOS in drinking water systems for many years.
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
advanced treatment solutions,
pH levels,
Safe drinking water,
RO system,
particulate matter,
Filter Media,
municipal water systems,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Drinking Water,
Clean Water,
PFA's,
DeLoach Industries,
nylon,
Cosmetics,
reverse osmosis,
water process system,
removing PFAS & PFOS,
pfas exposure,
health effects of pfas,
exposure to pfas,
nonstick cookware,
food packaging,
water treatment standards,
PFOS,
safe drinking water act,
pfoa regulations,
the environmental protection agency,
drinking water standards,
water resistant clothing,
environmental safety,
forever chemicals
Industrial water systems use water filters to reduce the level of solids in water from:
- Industrial
- Semiconductor
- Manufacturing
- Refining
- Oil and Natural Gas Production Processes
The wastewater may contain harmful chemicals to humans, plants, or animals. Three types of filters are commonly used in industrial settings:
Gravity filters, pressure filters, and constructed wetlands. Pressure filters have two variations: multimedia and higher-pressure micron or cartridge filters. Constructed wetlands or natural filters are not often utilized in industrial processes. Based on the requirements to obtain environmental permits and safeguard the ecosystem.
There are many benefits to pressure filtering systems in industrial wastewater. Pressure filters can remove particles down to 0.3 microns in size. They don't clog up as quickly as other filter types, and it's much faster than other types of filtration methods.
Pressure filtering is also very cost-effective because it uses less energy than other methods. Look no further if you're looking for a high-quality industrial water filter that cuts down on operating costs!
Pressure Filters (Multimedia type) are often used in industrial settings to filter particulates down to 15 microns in size.
They're also very cost-effective due to their energy; pressure filters utilize much less energy than other filtration methods. Pressure filters can include multimedia, a mixture of gravel and sand, multimedia, gravel, sand, and anthracite, or multimedia, which combines gravel, sand, greensand, and anthracite filter media. The variations are dependent on the applications and the need.
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
water treatment,
water plant,
media packing,
ION Exchange Resin,
RO system,
Pressure filter,
Sand filters,
Filter Media,
industrial facilities,
green sand,
Gravity Filters,
Constructed Wetlands
In water treatment, it is often required to remove small particulate matter from the raw water.
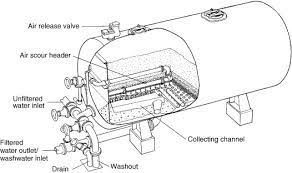
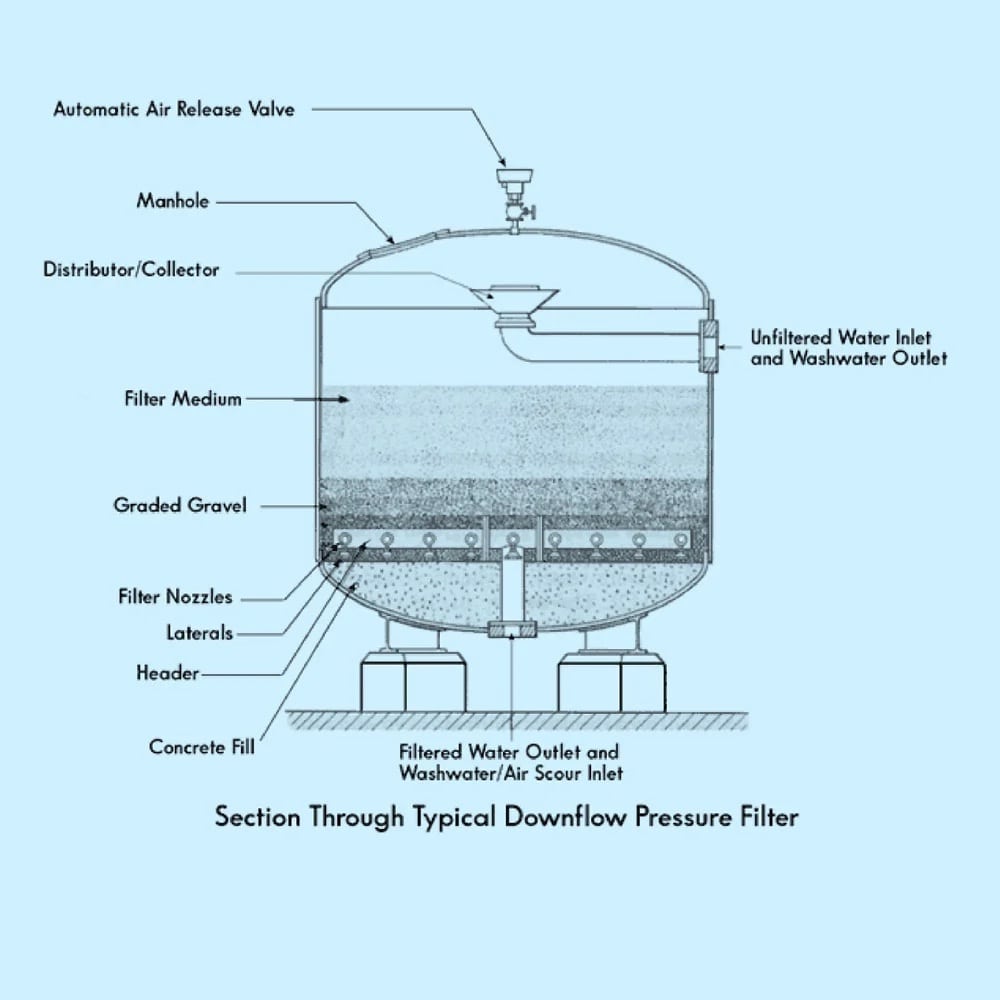
One of the most cost-effective ways to accomplish this is with a pressure filter. Sometimes referred to as “sand filters,” a pressure filter consists of a rigid filter vessel capable of withstanding internal pressure, combined with pipework to distribute and collect water and one or multiple types of filter media. Pressure filters are commonly used in municipal water systems, industrial facilities, residential well water systems, and swimming pools. Typical pressure filter construction is shown below:
At the top of the filter vessel, a distributor is used to break up and distribute the water flow so that there are no concentrated flow jets that stir up the media bed. Inflow distributors are usually oriented to direct flow at the top of the vessel to disperse the flow further. Below the distributor is the primary filter bed. The filter bed contains fine-grained media, most often sand, including crushed anthracite coal, activated charcoal, garnet, or other granular bulk products. The media bed is the thickest layer in the filter vessel and is the region that does the actual filtering of the water or other fluid. Below the media bed will be one or more support layers. These will usually be larger-sized gravel that is chosen to support the filter bed while allowing high flow through the support layer and into the outflow header. The outflow header can take several forms but is often composed of a large central pipe with multiple smaller pipes or “laterals” attached. The laterals are slotted or perforated. This allows the pressurized water to flow into the laterals and out through the outflow header into the downstream components of the water treatment system.
Read More
Topics:
particulate matter,
filters,
Pressure filter,
Sand filters,
Filter Media,
municipal water systems,
industrial facilities,
residential well water systems,
greensand,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
backwash,
automated control systems,
actuated valves,
pump controls
Ammonia (AM) is a common water pollutant that significantly impacts the water process industry.
It is not just polluting water bodies but also aqua wells and humidifiers. Generally, AM is produced from human sweat and urine and created from synthetic ammonia in industrial processes.
Ammonia has three types of amines – primary, secondary, and tertiary – all are toxic for humans and aquatic life.
- Primary Amine has two carbon and one nitrogen atom, also called methylamine or CHNH2.
- Secondary Amine has two nitrogen atoms with no carbon atom between them, also called Dimethylamine or CH2(NH)CH3.
- Tertiary Amine has three nitrogen atoms with no carbon atoms between them; thus, it’s called Trimethylamine or CH3C(NH)CH3.
In natural conditions, primary Amide bacteria produce Amide under high-temperature conditions. In an aqueous solution and soil environments with high pH levels (>6).
Primary amide can form by the dehydrogenation of nitriles, such as acetonitrile, which are further oxidized to form acetic acid.
Primary amide form by alkaline hydrolysis of nitro compounds such as 2-nitrophenol.
Process systems often need to recognize when the Degasification or Decarbonation system is failing or underperforming.
Read More
Topics:
Decarbonation,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
Amine,
Ammonia,
Deagasification,
Filter Media,
distribution system,
blower motor,
process system,
frequent inspections
Water treatment towers and storage tanks are high places that require special precautions when entering. While the majority of people who enter these locations for work can be trusted, there are some hazards that make it more important than usual to follow safety procedures.
These locations can get very hot and humid, and can also be filled with harmful chemicals and microorganisms that can cause serious health issues if inhaled or absorbed through the skin. Therefore, the general standard for workplace safety is much higher when entering locations like these.
Make sure you have read and understood the following information about safety when entering a water treatment plant. It will help you understand how to stay safe and protect yourself from harm when entering a water treatment plant. normal installation, maintenance, or even emergency repairs, it is often required to enter into a water treatment tower (degasifier, air stripper, decarbonator, or clear well/ storage tank). When this occurs, full safety protocols should be followed at all times, in accordance with OSHA regulations. A tower or tank B classification is a "Confined Space" location. For more information visit the OSHA confined space regulations page.
In addition, there are other safety risks that an operator or technician can be exposed to while inside these types of closed locations. The risk can come from fumes of hydrogen sulfide (H2S), chlorine from an injection line, or a lack of oxygen O2. A proper confined space permit should be prepared and only technicians with proper training and certifications should enter into these types of confined spaces.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
safety,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
media packing,
scaling,
caustic,
Safe drinking water,
dissolved gases,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
gases,
Ammonia,
what is a scrubber,
Hydrogen Sulfide formula,
Deagasification,
Filter Media,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Drinking Water,
Clean Water,
Contaminated Water,
OSHA
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
pH levels of water,
aeration,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
fiberglass,
About DeLoach Industries,
fabrication,
biological scrubber,
Chemical Odor,
media packing,
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
De-Aeration,
decarbonator,
boiler system,
distillation,
degasifier,
RO system,
H2S Degasifier,
Fish Farming,
Aquaculture,
Pisciculture,
Biological Odor Control Scrubber,
Biological odor control,
removal of CO2 from water,
Deagasification,
decarbonation of water,
Sand filters,
Filter Media,
municipal water systems,
greensand,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Drinking Water