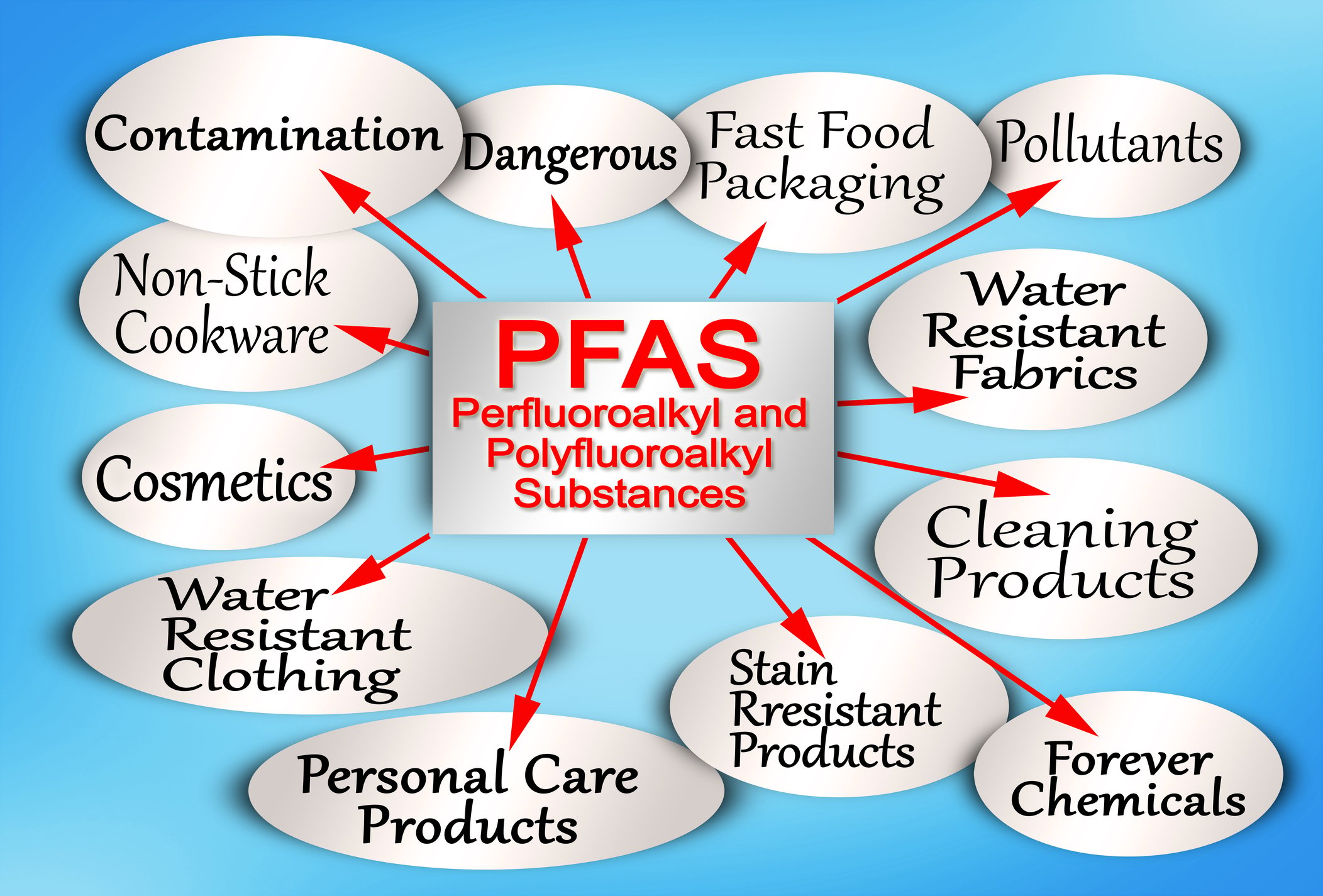
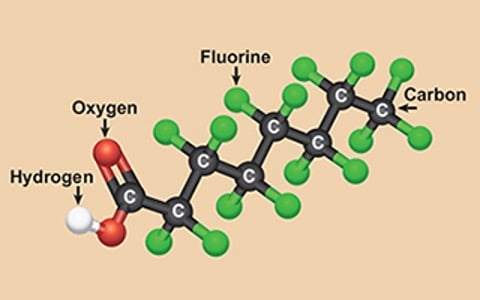
I will explore the potential risks of exposure to two members of a family of man-made chemicals called PFAS.
These chemicals are PFOA and PFOS, "poly-fluoroalkyl substances."
I will discuss the sources of PFOA and PFOS. These include leaching from industrial sites, the use of consumer products, and food and water contamination.
I will also discuss the exposure pathways of PFOA and PFOS. I will examine the regulations and guidelines for the use of these chemicals. I will also investigate their impact on the environment and various industries.
I will guide long-term human health effects.
This guide covers the potential risks of pfo's and pfoa's. It explains their sources and exposure pathways. It also looks at regulations and guidelines for their usage and impact on the environment and industries.

Introduction to PFOA and PFOS
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
FDA,
Safe drinking water,
wastewater,
Global,
RO system,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Drinking Water,
PFA's,
DeLoach Industries,
Cosmetics,
make-up,
water process system,
removing PFAS & PFOS,
pfas exposure,
health effects of pfas,
nonstick cookware,
wastewater treatment system,
water treatment standards,
PFOS,
safe drinking water act,
pfoa regulations,
the environmental protection agency,
drinking water standards,
adverse health effects,
water resistant clothing,
environmental safety
Water is essential for life, but not all water is safe to drink.
Contaminants like perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS), collectively known as PFAS, have been a growing concern in our water supply. Fortunately, there's a remarkable solution that often goes unnoticed: carbon absorption filters. Here, we'll explore the technology behind carbon absorption filters, how they effectively trap PFAS and their numerous benefits in water treatment.
Understanding Carbon Absorption Technology
Before delving into how carbon filters combat PFAS, let’s review the fundamentals of carbon absorption technology. Activated carbon, the hero in this story, is an incredibly porous material with a vast surface area, typically derived from sources like coconut shells, wood, or coal. This porous structure is what makes activated carbon ideal for trapping contaminants.
1. Activated Carbon's Structure: Think of activated carbon like a sponge, but not just any ordinary sponge – it's a super sponge! At a microscopic level, it's filled with tiny pores and holes, creating a vast and intricate network. Imagine walking through a maze with endless twists and turns – that's what the structure of activated carbon looks like. And why does this matter? Because all those nooks and crannies provide a massive surface area. It's like having a big, open field instead of a cramped room. This extra space is perfect for grabbing onto molecules, kind of like how Velcro sticks to fabric. This process is called adsorption, where molecules stick to the surface of the carbon rather than getting soaked up inside like a regular sponge.
2. Adsorption vs. Absorption: Let's clear up some confusion between two similar-sounding words. Absorption is like when a sponge soaks up water – it goes inside the sponge. But adsorption is different; it's all about what happens on the surface. Imagine you're playing with magnets. When they attract and stick together, that's like adsorption. Activated carbon is a magnet for contaminants. It doesn't suck them in like a vacuum; instead, it attracts them and sticks them onto its surface, where they stay put. So, while absorption is about taking things in, adsorption is about grabbing onto things on the outside.
3. Adsorbent Specificity: One of the remarkable features of activated carbon is its remarkable versatility and ability to adsorb a wide range of contaminants, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which are harmful chemicals emitted from products like paints and cleaning supplies, chlorine, commonly found in water disinfection processes, and, most importantly, PFAS, notorious for their widespread presence in water sources and resistance to degradation, making activated carbon an indispensable tool in combating environmental pollution.
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
Safe drinking water,
municipal water systems,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Drinking Water,
DeLoach Industries,
carbon filters,
removing PFAS & PFOS,
pfas exposure,
health effects of pfas,
exposure to pfas,
water treatment standards,
PFOS,
drinking water standards,
forever chemicals,
water purification systems,
carbon absorption
In recent years, PFOA and PFOS, commonly known as "forever chemicals," have raised concerns among municipalities, food and beverage industries, and commercial facilities in the USA and around the globe. These synthetic chemicals, which never break down and pose significant health risks, have been detected in water, food supplies, and even bottled purified water. As new EPA regulations take effect in 2024, industries are searching for effective and cost-efficient methods to remove these hazardous substances from their water supply. Fortunately, advanced water purification technologies such as microfiltration, ultrafiltration, and reverse osmosis can address these challenges.
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
advanced treatment solutions,
Safe drinking water,
RO system,
municipal water systems,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Drinking Water,
DeLoach Industries,
reverse osmosis,
water process system,
removing PFAS & PFOS,
pfas exposure,
health effects of pfas,
exposure to pfas,
water treatment standards,
PFOS,
safe drinking water act,
the environmental protection agency,
drinking water standards,
forever chemicals,
water purification systems,
microfiltration and ultrafiltration,
potable water,
membrane technology,
types of membranes,
flat sheet,
spirally wound
PFOA and PFOS are man-made chemicals used in various products to simplify life.
Forever chemicals, also known as synthetic chemicals called PFAS, have gained recognition. Scientists created these chemicals to make products resistant to water, stains, and sticking. The United States initially utilized them in the 1950s.
DuPont introduced Teflon in the 1950s to help Americans have nonstick cookware and make their lives easier. Americans and people from other countries liked this new improvement and soon used these substances in many different products.
These chemicals are resistant to water and lipids, so they don't break down and last a long time in the environment.
Over time, companies have used these chemicals in manufacturing various products, such as firefighting foam, food packaging, and cosmetics. As a result, these chemicals have entered the air, water, soil, and food production. They discontinued the use of PFAS and their other compounds in the mid-1970s.
People believe that contamination has affected more than 7000 metric tons of Fluorochemicals. PFOAs and PFOS, which can cause various health problems, have exposed many Americans and people in the USA.
PFOA chemicals contaminated 1% of public drinking water supply systems in 2016. The EPA did not regulate safe levels of PFOA and PFOS in drinking water systems for many years.
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
advanced treatment solutions,
pH levels,
Safe drinking water,
RO system,
particulate matter,
Filter Media,
municipal water systems,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Drinking Water,
Clean Water,
PFA's,
DeLoach Industries,
nylon,
Cosmetics,
reverse osmosis,
water process system,
removing PFAS & PFOS,
pfas exposure,
health effects of pfas,
exposure to pfas,
nonstick cookware,
food packaging,
water treatment standards,
PFOS,
safe drinking water act,
pfoa regulations,
the environmental protection agency,
drinking water standards,
water resistant clothing,
environmental safety,
forever chemicals
In modern industrial water treatment, advancements in technology and processes have revolutionized the way contaminants are removed from water.
This blog explores the integration of NSF/ANSI 61 certified systems, artificial intelligence in water treatment, and cutting-edge processes such as decarbonation and degasification. We'll also discuss the key differences between forced draft and induced draft degasification towers, helping you make informed decisions while designing your Industrial Water Treatment System.
-
NSF/ANSI 61-Certified Water Treatment Systems: To ensure the safety and quality of water treatment equipment, NSF/ANSI 61 certification has become a crucial standard. This certification verifies that materials and components used in water treatment systems comply with health and safety requirements. When selecting a water treatment solution, opting for NSF/ANSI 61 certified systems guarantees peace of mind and adherence to the highest industry standards.
-
Harnessing Artificial Intelligence in Water Treatment: Artificial intelligence (AI) has penetrated various industries, and water treatment is no exception. Integrating AI into water treatment processes allows for more efficient and optimized operations. AI-driven systems can monitor water quality in real-time, predict system failures, optimize chemical dosing, and reduce energy consumption. By leveraging AI technologies, water treatment facilities can enhance their overall performance and streamline resource utilization.
-
Decarbonation and Degasification Systems: Decarbonation and degasification are essential processes in industrial water treatment, particularly in pH levels in water and the ability to control removing the contaminants. These processes target the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other dissolved gases from water to improve its quality. Two key systems used for this purpose are the decarbonator and aeration system.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
NSF/ANSI 61,
Chemical Odor,
Decarbonation,
Safe drinking water,
De-Aeration,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
degassed water,
ansi61,
nsf/ansi61,
Deagasification,
decarbonation of water,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Drinking Water,
Industrial Odor Control,
DeLoach Industries,
contaminants,
process system,
safe drinking water act,
drinking water standards,
environmental safety,
air emissions,
Forced Draft,
Induced Draft
Per- and polyfluorinated substances (PFAS), known as "forever chemicals," have long been utilized in various consumer products due to their exceptional properties.
However, the challenge lies in effectively treating or eliminating PFAS once they enter the environment or water supply. This blog will focus on the technological advancements in removing PFAS and perfluorooctanoic acids (PFOAs) from water sources. By exploring different treatment methods, such as activated carbon absorption, ion exchange resins, and reverse osmosis, and simply avoiding PFOA and PFOS, we can better understand the available options for mitigating these persistent chemicals in water.
Activated Carbon Absorption
One of the earliest technologies employed for PFAS removal is activated carbon absorption. This method involves the use of specially treated carbon materials that effectively adsorb PFAS compounds from water sources. The activated carbon's large surface area and porous structure allow it to trap and retain PFAS molecules. This technology has proven effective in removing PFAS, including PFOAs, from drinking water and environmental sources. However, periodic treatment and regeneration of the activated carbon are necessary to maintain its efficacy.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
iron oxidation,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
ION Exchange Resin,
Safe drinking water,
wastewater,
degasifier,
RO system,
Deagasification,
PFA's,
technology,
contaminants,
reverse osmosis,
carbon filters,
activated carbon,
removing PFAS & PFOS,
pfas exposure,
health effects of pfas,
nonstick cookware,
wastewater treatment systems,
PFOS,
pfoa regulations,
drinking water standards,
water resistant clothing,
environmental safety