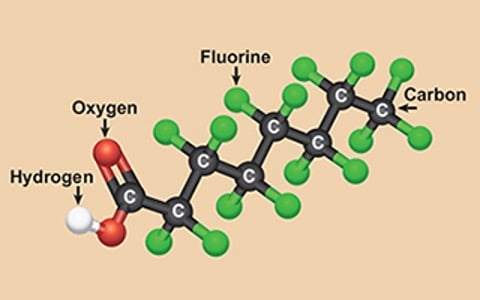
I will explore the potential risks of exposure to two members of a family of man-made chemicals called PFAS.
These chemicals are PFOA and PFOS, "poly-fluoroalkyl substances."
I will discuss the sources of PFOA and PFOS. These include leaching from industrial sites, the use of consumer products, and food and water contamination.
I will also discuss the exposure pathways of PFOA and PFOS. I will examine the regulations and guidelines for the use of these chemicals. I will also investigate their impact on the environment and various industries.
I will guide long-term human health effects.
This guide covers the potential risks of pfo's and pfoa's. It explains their sources and exposure pathways. It also looks at regulations and guidelines for their usage and impact on the environment and industries.

Introduction to PFOA and PFOS
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
FDA,
Safe drinking water,
wastewater,
Global,
RO system,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Drinking Water,
PFA's,
DeLoach Industries,
Cosmetics,
make-up,
water process system,
removing PFAS & PFOS,
pfas exposure,
health effects of pfas,
nonstick cookware,
wastewater treatment system,
water treatment standards,
PFOS,
safe drinking water act,
pfoa regulations,
the environmental protection agency,
drinking water standards,
adverse health effects,
water resistant clothing,
environmental safety
If you’ve been following the news, you know a growing problem with PFAS (per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances) exists.
PFAS, a group of synthetic chemicals in a wide range of products, is causing a growing concern. Despite their widespread use, some PFAS compounds have been found to degrade into potentially harmful byproducts like PFAS-methyl tetrahydrofuran. What's more alarming is that these chemicals have infiltrated our drinking water sources, even in areas with high water tables. This is why it's crucial to understand effective methods for removing PFAS from water. What should you do if you suspect that there’s a problem with your water? Check the source of the water, test it, and treat it if necessary.
Follow these steps to remove PFAS from drinking water.
Test Your Water
Although knowing how to remove contaminants is essential, it’s even more important to understand how to test your water for contamination. A water test kit can help you determine whether there are contaminants in your water and whether they are at a dangerous level. You can purchase water test kits at grocery stores, hardware stores, and online retailers. Generally, these kits come with the standard set of tests for a home water filtration system, but they also often include tests for specific contaminants. Use these tests to determine whether your water is safe to drink. If your water contains contaminants, remove them from your water source. This can be done by digging a more bottomless well, installing a water filtration system, or getting a water purification system. If your water does not contain contaminants, you don’t need to do anything except continue drinking your water.
Check the Source
Understanding the source of your water is a crucial step in addressing contamination. Whether you have a well or a water treatment system, knowing where your water comes from can provide valuable insights. By tracing the water's journey from the source, you can determine if contamination occurs upstream. This knowledge is essential for well owners, who might overlook the significance of understanding their water source. If you find contamination at the source, you can address it immediately, such as reducing the distance between the source and your dwelling or seeking alternative, uncontaminated sources.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
Chemical Odor,
Safe drinking water,
RO system,
filters,
Filter Media,
residential well water systems,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
backwash,
Carbon Filter,
Micron Filter,
Drinking Water,
Clean Water,
Contaminated Water,
Water Source,
Sediment Filter,
PFA's,
Water Test,
Water Test Kit
In recent years, PFOA and PFOS, commonly known as "forever chemicals," have raised concerns among municipalities, food and beverage industries, and commercial facilities in the USA and around the globe. These synthetic chemicals, which never break down and pose significant health risks, have been detected in water, food supplies, and even bottled purified water. As new EPA regulations take effect in 2024, industries are searching for effective and cost-efficient methods to remove these hazardous substances from their water supply. Fortunately, advanced water purification technologies such as microfiltration, ultrafiltration, and reverse osmosis can address these challenges.
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
advanced treatment solutions,
Safe drinking water,
RO system,
municipal water systems,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Drinking Water,
DeLoach Industries,
reverse osmosis,
water process system,
removing PFAS & PFOS,
pfas exposure,
health effects of pfas,
exposure to pfas,
water treatment standards,
PFOS,
safe drinking water act,
the environmental protection agency,
drinking water standards,
forever chemicals,
water purification systems,
microfiltration and ultrafiltration,
potable water,
membrane technology,
types of membranes,
flat sheet,
spirally wound
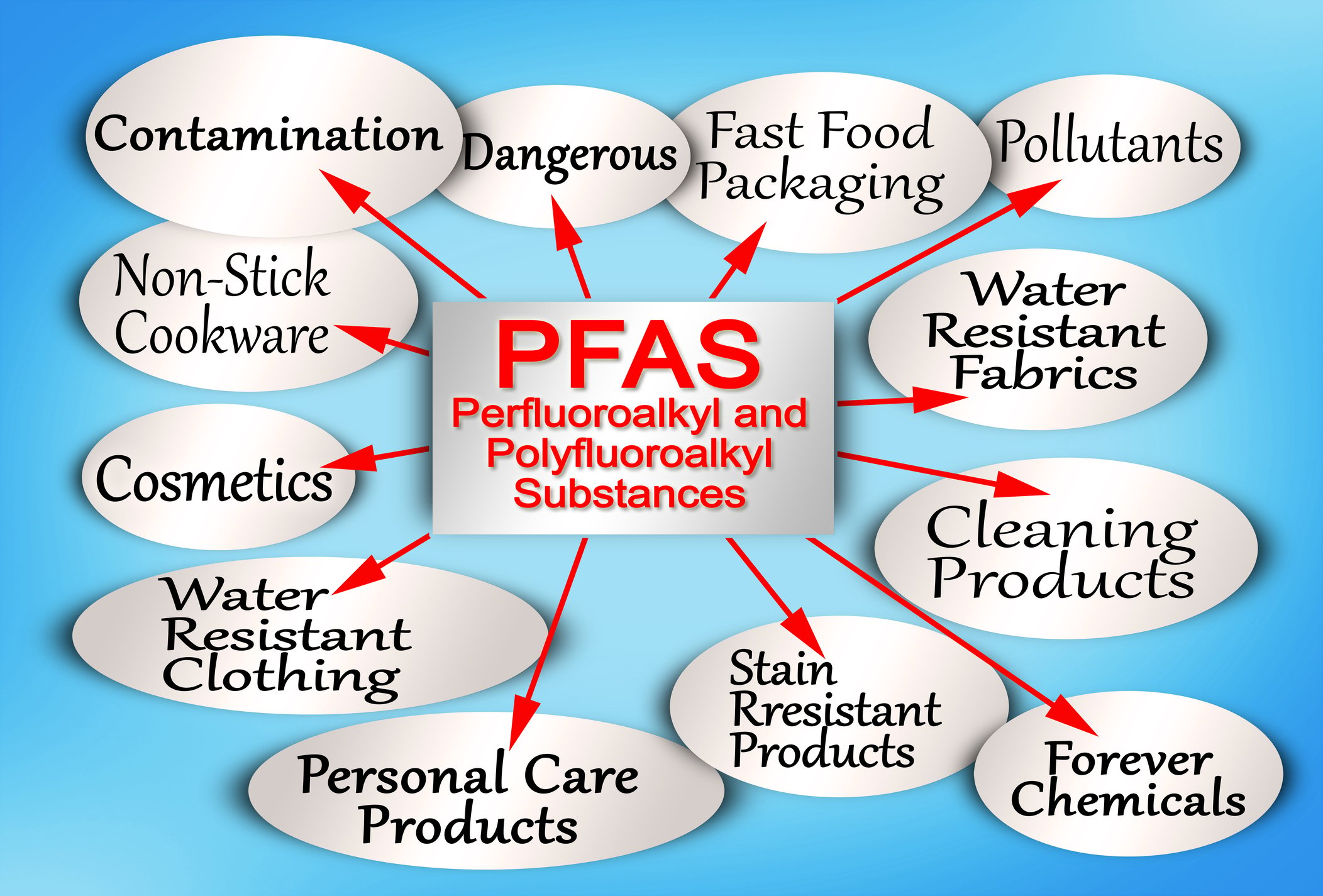
PFOA and PFOS are man-made chemicals used in various products to simplify life.
Forever chemicals, also known as synthetic chemicals called PFAS, have gained recognition. Scientists created these chemicals to make products resistant to water, stains, and sticking. The United States initially utilized them in the 1950s.
DuPont introduced Teflon in the 1950s to help Americans have nonstick cookware and make their lives easier. Americans and people from other countries liked this new improvement and soon used these substances in many different products.
These chemicals are resistant to water and lipids, so they don't break down and last a long time in the environment.
Over time, companies have used these chemicals in manufacturing various products, such as firefighting foam, food packaging, and cosmetics. As a result, these chemicals have entered the air, water, soil, and food production. They discontinued the use of PFAS and their other compounds in the mid-1970s.
People believe that contamination has affected more than 7000 metric tons of Fluorochemicals. PFOAs and PFOS, which can cause various health problems, have exposed many Americans and people in the USA.
PFOA chemicals contaminated 1% of public drinking water supply systems in 2016. The EPA did not regulate safe levels of PFOA and PFOS in drinking water systems for many years.
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
advanced treatment solutions,
pH levels,
Safe drinking water,
RO system,
particulate matter,
Filter Media,
municipal water systems,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Drinking Water,
Clean Water,
PFA's,
DeLoach Industries,
nylon,
Cosmetics,
reverse osmosis,
water process system,
removing PFAS & PFOS,
pfas exposure,
health effects of pfas,
exposure to pfas,
nonstick cookware,
food packaging,
water treatment standards,
PFOS,
safe drinking water act,
pfoa regulations,
the environmental protection agency,
drinking water standards,
water resistant clothing,
environmental safety,
forever chemicals
If you’ve been reading the news lately, you know nanoparticles are not so great. In everything from cosmetics to water filters, nanoparticles have been shown to cause various health problems. But what exactly are nanoparticles, and how can you protect yourself from their harmful effects? Let’s answer these questions and more with this quick guide on removing nanoparticles from your drinking water.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
About DeLoach Industries,
water plant,
safety,
Safe drinking water,
Global,
distillation,
RO membrane,
RO system,
particulate matter,
filters,
municipal water systems,
residential well water systems,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Drinking Water,
Clean Water,
Water Test,
Water Test Kit,
DeLoach Industries,
technology,
minerals,
temperature,
nanoparticles,
Cosmetics,
Nano,
make-up,
organ function,
contaminants,
pressure filters,
reverse osmosis,
carbon filters,
UV filters,
activated carbon
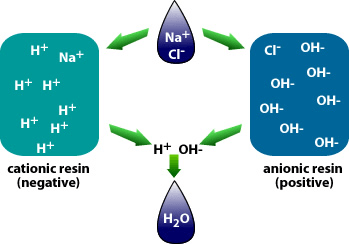
Water demineralization is also called deionization and is a process known as “Ion Exchange.”
In simple terms, water demineralization is “Water Purification.” The process involves removing dissolved ionic mineral solids from a feed-water process, typically for “Industrial” water applications. Still, it can also be utilized to remove dissolved solids from a water process for “Aquaculture,” “Food and Beverage,” and the “Municipal” markets.
Why is demineralization utilized? It can remove dissolved solids to near distilled water quality at a much lower capital and operational cost than other treatment processes such as membrane softening (Reverse Osmosis). Demineralization applies the science known as “Ion Exchange,” which attracts negative and positive charged ions and allows either to attach themselves to a negative ion depending on their respective current negative or positive charge during what is known as a resin cycle. In other technical articles, we will explore and go into more specific details on the science of the ion exchange process. Water that has dissolved salts and minerals has ions, either negatively charged ions known as “Anions” or positively charged ions known as “Cations.” To treat the water and remove these contaminants, the ions in the water are attracted to counter-ions, which have a negative charge. In a demineralization treatment process, there are pressure vessels that hold resin beads which are typically made of plastic. The beads are made from a plastic material with an ionic functional group that allows them to hold and maintain an electrostatic electrical charge. Some of these resin groups are negatively charged, referred to as “Anion” resins, while others hold a positive charge and are called “Cations” resins.
There are different applications to apply Ion exchange technologies, which is why you will often hear different terminology interchanged like deionization and demineralization. The raw water quality and the specific application will dictate the type of ion exchange process needed. For example, if the water contains a high level of hardness, the water will most likely contain Ca2+ or Mg2+ dissolved solids possessing a positive charge. To replace these hard ions, it is typical to utilize a resin bed with a salt ion like Na+. As the water passes over the resin bead material within the pressure vessel. The hard ions are replaced with the salt ion; therefore, all the hardness within the water is removed. However, the water will now contain a higher concentration of sodium ions, and this must be considered during the evaluation and selection process of the type of resin material to utilize for the specific application. If the water application requires high purity and the removal of as many solids as possible, then the term or process selected is referred to as demineralization.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
water distribution system,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
media packing,
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
RO system,
H2S Degasifier,
Aquaculture,
degassed water,
Co2 ph,
removal of CO2 from water,
Deagasification,
decarbonation of water,
hydrogen ion,
particulate matter,
municipal water systems,
industrial facilities,
automated control systems,
Ion exchange,
cations,
anions
Industrial water systems use water filters to reduce the level of solids in water from:
- Industrial
- Semiconductor
- Manufacturing
- Refining
- Oil and Natural Gas Production Processes
The wastewater may contain harmful chemicals to humans, plants, or animals. Three types of filters are commonly used in industrial settings:
Gravity filters, pressure filters, and constructed wetlands. Pressure filters have two variations: multimedia and higher-pressure micron or cartridge filters. Constructed wetlands or natural filters are not often utilized in industrial processes. Based on the requirements to obtain environmental permits and safeguard the ecosystem.
There are many benefits to pressure filtering systems in industrial wastewater. Pressure filters can remove particles down to 0.3 microns in size. They don't clog up as quickly as other filter types, and it's much faster than other types of filtration methods.
Pressure filtering is also very cost-effective because it uses less energy than other methods. Look no further if you're looking for a high-quality industrial water filter that cuts down on operating costs!
Pressure Filters (Multimedia type) are often used in industrial settings to filter particulates down to 15 microns in size.
They're also very cost-effective due to their energy; pressure filters utilize much less energy than other filtration methods. Pressure filters can include multimedia, a mixture of gravel and sand, multimedia, gravel, sand, and anthracite, or multimedia, which combines gravel, sand, greensand, and anthracite filter media. The variations are dependent on the applications and the need.
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
water treatment,
water plant,
media packing,
ION Exchange Resin,
RO system,
Pressure filter,
Sand filters,
Filter Media,
industrial facilities,
green sand,
Gravity Filters,
Constructed Wetlands
Per- and polyfluorinated substances (PFAS), known as "forever chemicals," have long been utilized in various consumer products due to their exceptional properties.
However, the challenge lies in effectively treating or eliminating PFAS once they enter the environment or water supply. This blog will focus on the technological advancements in removing PFAS and perfluorooctanoic acids (PFOAs) from water sources. By exploring different treatment methods, such as activated carbon absorption, ion exchange resins, and reverse osmosis, and simply avoiding PFOA and PFOS, we can better understand the available options for mitigating these persistent chemicals in water.
Activated Carbon Absorption
One of the earliest technologies employed for PFAS removal is activated carbon absorption. This method involves the use of specially treated carbon materials that effectively adsorb PFAS compounds from water sources. The activated carbon's large surface area and porous structure allow it to trap and retain PFAS molecules. This technology has proven effective in removing PFAS, including PFOAs, from drinking water and environmental sources. However, periodic treatment and regeneration of the activated carbon are necessary to maintain its efficacy.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
iron oxidation,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
ION Exchange Resin,
Safe drinking water,
wastewater,
degasifier,
RO system,
Deagasification,
PFA's,
technology,
contaminants,
reverse osmosis,
carbon filters,
activated carbon,
removing PFAS & PFOS,
pfas exposure,
health effects of pfas,
nonstick cookware,
wastewater treatment systems,
PFOS,
pfoa regulations,
drinking water standards,
water resistant clothing,
environmental safety
In many water treatment and chemical processes,
it is a requirement to keep track of the pH of the water or product stream. In DeLoach Industries equipment such as degasification systems, or odor control scrubbers, pH measurement is critical to control the chemical reactions happening within the treatment system. PH is an indication of the acidic vs alkaline nature of the fluid. An acidic fluid will have a greater concentration of H+ hydrogen ions, while an alkaline fluid will have a greater concentration of OH- hydroxide ions. This electrochemical nature is used in the construction, reading, and maintenance of electronic pH probes.
PH probes are generally glass and will contain a reference element, and a sensing element. When the pH probe is immersed in the fluid to be measured, the electrical potential difference between the sensing element and the reference element is amplified by electronics and the resulting voltage is used in a calculation to determine pH from differential electron potential. As a pH probe remains in service, ion exchange will slowly change the electrical potential of the sensing element, the reference element, or both. This happens because the hydrogen ions are small enough to travel through the glass sensor body and cause reference potential shifts over time. This is normal behavior for all pH probes and is the reason why pH probes must be periodically calibrated.
Calibration is a process where a pH probe is immersed in a series of standardized stable pH solutions called “buffers”. The standard set of buffers includes a pH 4.0 acidic buffer, a pH 7.0 neutral buffer, and a pH 10.0 alkaline buffer. These buffer solutions are chemically designed to hold a stable pH and are used as a reference for the internal calculations that are done by the pH amplifier or transmitter that interprets the reading taken by the pH probe. As the reference voltage vs actual pH for a mature probe changes, the known buffer solution provides a benchmark for the calculation. Each pH instrumentation manufacturer will have a slightly different method for performing a calibration, but in general, the system will have you step through the buffer solutions while an automated routine makes note of the expected voltage vs calibration voltage at each step. The computation algorithm will use this drift information to re-scale the calculation to re-establish accuracy.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
pH levels of water,
iron oxidation,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
Alkalinity,
ION Exchange Resin,
carbon dioxide,
gases,
RO system,
Aqua Farming
DeLoach Industries made history in 1977 at the City of Cape Coral Florida water treatment plant with its large scale “degasification towers” connected to what was to become the first municipal water treatment facility in the United States to deploy the use of reverse osmosis on a large-scale production municipal treatment plant.
The Cape Coral water treatment plant for came online in 1977 and produced 3 million gallons of water per day (GPD) or 11.35 liters of purified and treated water utilizing the “reverse osmosis” process. By 1985 the plant had expanded as it kept up with growth to produce 15 million gallons per day making it at the time the world’s largest “reverse osmosis” water treatment plant facility.
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
Alkalinity,
scaling,
chlorine,
caustic,
Decarbonation,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
RO membrane,
RO system,
H2S Degasifier