The EPA and other world health organizations have sounded the alarm on the dangers and health impacts of being exposed to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs & PFOAs) also known as the forever chemicals.
In response, federal and state regulators are adopting new water quality guidelines and laws to address these contaminants in our drinking water systems and groundwater pollution. It's a pervasive issue, as PFASs can be found in various types and over 4,700 different variations, each with at least three polyfluorinated carbon atoms.
With more than 10,000 types of PFASs introduced into products, it's no wonder that the quality of drinking water in the USA and other countries has been compromised. But what exactly are PFASs? These are fluorinated substances that contain at least one fully fluorinated methyl or methylene carbon atom. While they do not contain atoms like hydrogen, chlorine, bromine, or iodine, any chemical with a perfluorinated (CF3) or perfluorinated (CF2) component falls under the PFAS category. However, there are a few exceptions.
PFASs can be further classified into subgroups such as surfactants, perfluorosulfonic acids, perfluorooctane sulfonic acids, perfluorocarboxylic acids, and perfluorooctanoic acids (commonly referred to as PFOSs and PFOAs). These persistent organic pollutants, also known as "forever chemicals," pose a significant challenge due to their resistance to environmental degradation. As a result, they are found in humans, animals, and water supplies across the USA.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
NSF/ANSI 61,
Decarbonation,
Safe drinking water,
ansi61,
Co2 ph,
CO2 in water,
Deagasification,
hydrogen ion,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.
Water demineralization is also called deionization and is a process known as “Ion Exchange.”
In simple terms, water demineralization is “Water Purification.” The process involves removing dissolved ionic mineral solids from a feed-water process, typically for “Industrial” water applications. Still, it can also be utilized to remove dissolved solids from a water process for “Aquaculture,” “Food and Beverage,” and the “Municipal” markets.
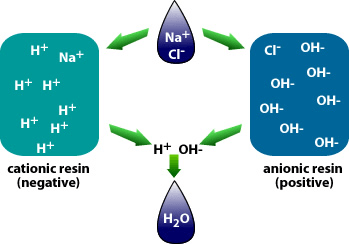
Why is demineralization utilized? It can remove dissolved solids to near distilled water quality at a much lower capital and operational cost than other treatment processes such as membrane softening (Reverse Osmosis). Demineralization applies the science known as “Ion Exchange,” which attracts negative and positive charged ions and allows either to attach themselves to a negative ion depending on their respective current negative or positive charge during what is known as a resin cycle. In other technical articles, we will explore and go into more specific details on the science of the ion exchange process. Water that has dissolved salts and minerals has ions, either negatively charged ions known as “Anions” or positively charged ions known as “Cations.” To treat the water and remove these contaminants, the ions in the water are attracted to counter-ions, which have a negative charge. In a demineralization treatment process, there are pressure vessels that hold resin beads which are typically made of plastic. The beads are made from a plastic material with an ionic functional group that allows them to hold and maintain an electrostatic electrical charge. Some of these resin groups are negatively charged, referred to as “Anion” resins, while others hold a positive charge and are called “Cations” resins.
There are different applications to apply Ion exchange technologies, which is why you will often hear different terminology interchanged like deionization and demineralization. The raw water quality and the specific application will dictate the type of ion exchange process needed. For example, if the water contains a high level of hardness, the water will most likely contain Ca2+ or Mg2+ dissolved solids possessing a positive charge. To replace these hard ions, it is typical to utilize a resin bed with a salt ion like Na+. As the water passes over the resin bead material within the pressure vessel. The hard ions are replaced with the salt ion; therefore, all the hardness within the water is removed. However, the water will now contain a higher concentration of sodium ions, and this must be considered during the evaluation and selection process of the type of resin material to utilize for the specific application. If the water application requires high purity and the removal of as many solids as possible, then the term or process selected is referred to as demineralization.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
water distribution system,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
media packing,
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
RO system,
H2S Degasifier,
Aquaculture,
degassed water,
Co2 ph,
removal of CO2 from water,
Deagasification,
decarbonation of water,
hydrogen ion,
particulate matter,
municipal water systems,
industrial facilities,
automated control systems,
Ion exchange,
cations,
anions
The importance of removing Carbon Dioxide in the water!
Carbon dioxide exists naturally in nature as free CO2 and can be found in many water sources from lakes, streams, or other surface water bodies. Carbon dioxide occurs naturally in small amounts (about 0.04 percent) in the Earth's atmosphere. Monitoring CO2 levels in your water can be done through test kits or monitoring systems. When monitoring CO2 levels, it is important to note the concentration at which the monitoring needs to occur. Industrial level ion exchange systems should be monitored at a concentration typically 15–20 times greater than required for drinking water quality. Ion exchange systems used for high purity water production should be monitored at a concentration typically 40–50 times greater than what is required for drinking water quality. Due to carbon dioxide’s abundance and its role as the primary driver of climate change, there are concerns about increasing concentrations of this gas in the atmosphere. To reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, people can reduce the amount of carbon dioxide released during energy production by using renewable energy sources and energy efficiency. Carbon dioxide can be captured and stored underground with carbon sequestration technologies.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
carbon dioxide,
CO2 in water,
excess co2,
hydrogen ion