Water demineralization is also called deionization and is a process known as “Ion Exchange.”
In simple terms, water demineralization is “Water Purification.” The process involves removing dissolved ionic mineral solids from a feed-water process, typically for “Industrial” water applications. Still, it can also be utilized to remove dissolved solids from a water process for “Aquaculture,” “Food and Beverage,” and the “Municipal” markets.
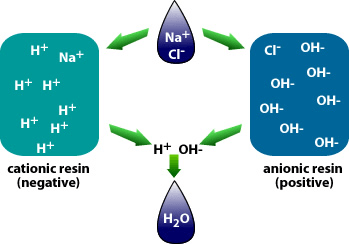
Why is demineralization utilized? It can remove dissolved solids to near distilled water quality at a much lower capital and operational cost than other treatment processes such as membrane softening (Reverse Osmosis). Demineralization applies the science known as “Ion Exchange,” which attracts negative and positive charged ions and allows either to attach themselves to a negative ion depending on their respective current negative or positive charge during what is known as a resin cycle. In other technical articles, we will explore and go into more specific details on the science of the ion exchange process. Water that has dissolved salts and minerals has ions, either negatively charged ions known as “Anions” or positively charged ions known as “Cations.” To treat the water and remove these contaminants, the ions in the water are attracted to counter-ions, which have a negative charge. In a demineralization treatment process, there are pressure vessels that hold resin beads which are typically made of plastic. The beads are made from a plastic material with an ionic functional group that allows them to hold and maintain an electrostatic electrical charge. Some of these resin groups are negatively charged, referred to as “Anion” resins, while others hold a positive charge and are called “Cations” resins.
There are different applications to apply Ion exchange technologies, which is why you will often hear different terminology interchanged like deionization and demineralization. The raw water quality and the specific application will dictate the type of ion exchange process needed. For example, if the water contains a high level of hardness, the water will most likely contain Ca2+ or Mg2+ dissolved solids possessing a positive charge. To replace these hard ions, it is typical to utilize a resin bed with a salt ion like Na+. As the water passes over the resin bead material within the pressure vessel. The hard ions are replaced with the salt ion; therefore, all the hardness within the water is removed. However, the water will now contain a higher concentration of sodium ions, and this must be considered during the evaluation and selection process of the type of resin material to utilize for the specific application. If the water application requires high purity and the removal of as many solids as possible, then the term or process selected is referred to as demineralization.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
water distribution system,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
media packing,
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
RO system,
H2S Degasifier,
Aquaculture,
degassed water,
Co2 ph,
removal of CO2 from water,
Deagasification,
decarbonation of water,
hydrogen ion,
particulate matter,
municipal water systems,
industrial facilities,
automated control systems,
Ion exchange,
cations,
anions
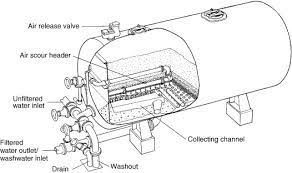
Industrial water systems use water filters to reduce the level of solids in water from:
- Industrial
- Semiconductor
- Manufacturing
- Refining
- Oil and Natural Gas Production Processes
The wastewater may contain harmful chemicals to humans, plants, or animals. Three types of filters are commonly used in industrial settings:
Gravity filters, pressure filters, and constructed wetlands. Pressure filters have two variations: multimedia and higher-pressure micron or cartridge filters. Constructed wetlands or natural filters are not often utilized in industrial processes. Based on the requirements to obtain environmental permits and safeguard the ecosystem.
There are many benefits to pressure filtering systems in industrial wastewater. Pressure filters can remove particles down to 0.3 microns in size. They don't clog up as quickly as other filter types, and it's much faster than other types of filtration methods.
Pressure filtering is also very cost-effective because it uses less energy than other methods. Look no further if you're looking for a high-quality industrial water filter that cuts down on operating costs!
Pressure Filters (Multimedia type) are often used in industrial settings to filter particulates down to 15 microns in size.
They're also very cost-effective due to their energy; pressure filters utilize much less energy than other filtration methods. Pressure filters can include multimedia, a mixture of gravel and sand, multimedia, gravel, sand, and anthracite, or multimedia, which combines gravel, sand, greensand, and anthracite filter media. The variations are dependent on the applications and the need.
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
water treatment,
water plant,
media packing,
ION Exchange Resin,
RO system,
Pressure filter,
Sand filters,
Filter Media,
industrial facilities,
green sand,
Gravity Filters,
Constructed Wetlands
A Biological Odor Control Scrubber Is Just One Of Many Different Types Of Available Technologies to treat air emissions that may contain harmful gases.
This class of equipment commonly falls into a category referred to as “Odor Control Scrubbers” and they are utilized to remove dangerous or noxious odors from an air stream. The Biological Odor Control System has gained popularity among many end users such as municipal operators due to the reduced operating cost and more simplistic operating requirements. A typical chemical odor control scrubber often requires two or more chemical additives and more instrumentation is required to maintain system performance. With the additional chemicals required and instrumentation comes the need for more hands-on maintenance, calibration, and safety requirements which increases the operating costs and workload of the operator.
A Biological Odor Control System relies on active bacteria cultures that recirculate within a water stream and flow across a random packed media bed that is beneficial to the bacteria culture.
During the process of metabolizing harmful gases such as Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) the biological odor control system requires only the addition of Caustic to control and balance the pH and additional water makeup to replace what has been consumed through evaporation or during the blowdown process to eliminate solids. There are several different types of odor control and chemical wet scrubbers, industrial air scrubbers on the market today and each provides a solution for the treatment of noxious or corrosive gases and odors in the industry. And even though Biological scrubbers are commonly utilized in municipal applications for the treatment of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gases that were produced by a water or wastewater treatment process there are times when a Biological Scrubber does not provide the best solution for treatment. When there are wide or rapidly changing concentrations in the ppm (parts per million) level then a Biological Scrubber will have difficulties balancing and acclimating fast enough to prevent a breakthrough. As an example, In water treatment, there is a treatment process referred to as “degasification” which strips the hydrogen sulfide gas from the water, and then the concentrated H2S gas is exhausted from the tower through an exhaust port. When the concentration rises above 1 ppm for hydrogen sulfide gas then the levels become both noxious to the surroundings as well as corrosive. Many times, the levels range from 3-7 PPM in concentration with Hydrogen Sulfide and pose a serious health threat, noxious odor, and corrosive environment demanding capture and treatment. When utilizing an Odor Control Scrubber such as a Biological Scrubber the gases are pulled or pushed through an air duct system that is connected to the Biological Scrubber inlet or suction side of the blower. The same process is utilized when treating Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) gases that were captured at a wastewater treatment process. These gases may have been generated from a source such as the wastewater treatment plant, lift station, or master head-works facility. When captured the gases are also conveyed in a similar manner to the Biological Odor Control Tower for treatment.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
degasification,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
media packing,
caustic,
wastewater,
gases,
H2S Degasifier,
Ammonia,
air emissions
Basics of water decarbonation for dissolved organic carbon.
The water treatment industry continues to develop and evolve. Over the past two decades, there have been many new developments in technology and even more refinement in existing technologies such as "Degasification". The evolution and advancement of water treatment have been driven by the constantly increasing demand from an increase in population that demand cost-effective solutions and recognition to improve safety with the implementation of NSF 61 standards.
All human cultures on our planet share a single commonality: the dependency on water to survive.
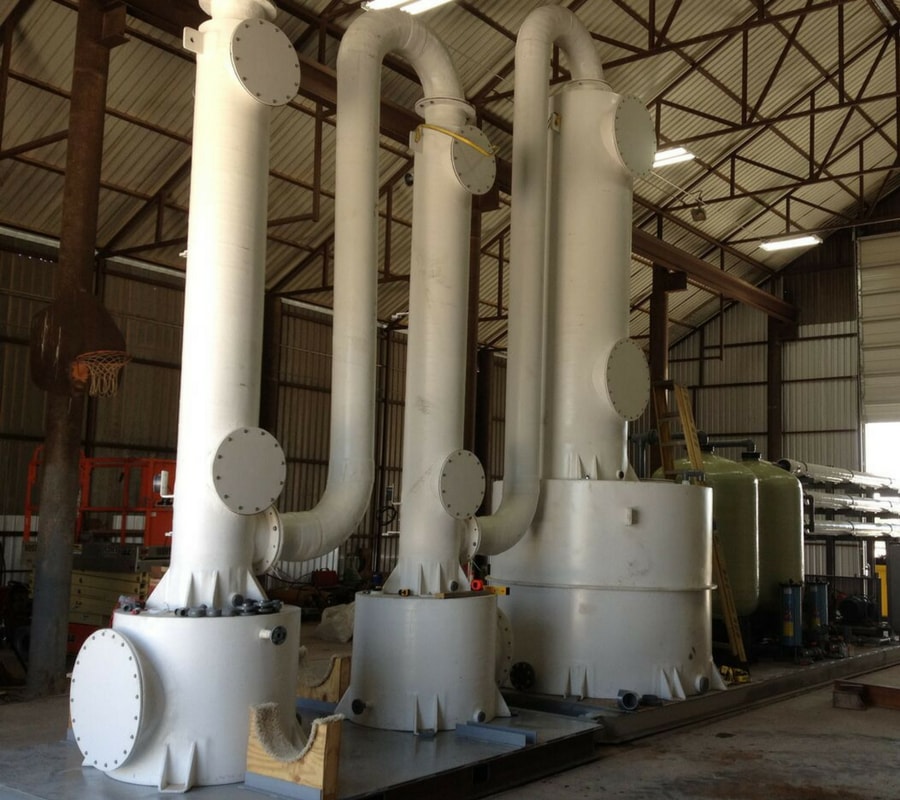
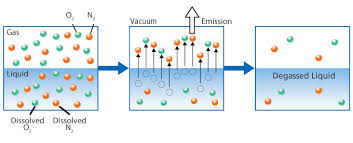
Many existing technologies, such as "Degasification," have evolved with higher efficiency to meet the demand changes and provide safety to consumers and the systems. Degasification refers to the removal of dissolved gases from liquids, and the science to degasify water is based upon a chemistry equation known as "Henry's Law". The "proportionality factor" is called Henry's law constant" and was developed by William Henry in the early 19th century. Henry's Law states that "the amount of dissolved gas is proportional to its partial pressure in the gas." The most "cost" effective method to perform degasification is with the packed vertical tower called a "Degasifier” or “Decarbonator.”
The key words in this previous sentence for owners, operators, and engineers to focus on is "the most cost-effective" as there is no other process more cost-effective at removing dissolved gases at the lowest cost than using a Degasifier or decarbonator. The process of degasification is simple enough to understand. Water is pumped to the top of a vertically constructed tower, where it first enters the tower through some type of distribution system at the same time, there is a cross-current air flowing up from the bottom by a blower located at the bottom of the tower, and the air encounters the water and is exhausted at the top of the tower through an exhaust port. There are various types of distribution systems, and we will explore these in later discussions. Once the water enters the top of the tower and passes through the distribution system, it then travels by gravity downward. The next thing the water encounters is some type of media packing. There are various forms of media packing offered in the degasification industry, and each type can offer higher performance or have the ability to deter fouling. The selection of the type, size, and volume is where the “experience, engineering, and understanding of each application” comes into play.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
About DeLoach Industries,
water plant,
NSF/ANSI 61,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
media packing,
pH levels,
scaling,
caustic,
Decarbonation,
Safe drinking water,
dissolved gases,
carbon dioxide,
decarbonator,
boiler system,
degasifier,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier,
Dissolved organic Carbon,
co2 dissolved in water
In the production and purification of water for industry
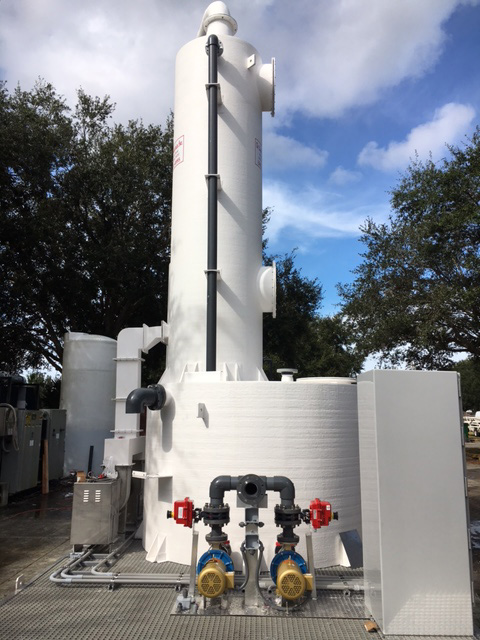
there are many types of different processes available to remove harmful minerals and gases from the water stream but the most effective process and most cost-effective from both a capital investment and operational cost is a “Forced Draft Degasification System” (Degasifier).
Degasification is used in a wide range of water processes for industrial and municipal applications which extend from the production of chemicals to the production of semiconductors and in all applications the need to remove contaminants from the water and dissolved gases is key to achieving the end results needed in the industrial water process. Water from the ground often contains elements such as calcium carbonate, manganese, iron, salts, hydrogen sulfide, and sulfur just to name a few of the basic contaminants and these naturally occurring elements can cause serious damage and consequences to process equipment such as boiler systems, piping, membranes, and cation and anion exchange resins used in the demineralization process.
Calcium carbonate can dissolve in water under certain pH ranges forming carbonic acid and releasing carbon dioxide (CO2) gases. These gases are not only very corrosive to equipment like boiler feed systems and boiler tubes but also attack the actual resin beds found in cation and anion softening and demineralization system causing an increase in regeneration and chemical consumption and resin bed replacement.
By incorporating a Force Draft Degasification system you can remove dissolved gasses
like CO2 and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) to as low as 99.999% and improve the cation and anion system performance, extend the resin bed life, and lower the operating cost of the water treatment process.
Quite often Forced Draft Degasification is utilized “post” treatment to also remove newly formed dissolved gases prior to entering the boiler feed system to prevent corrosion damage within the tubes and feed system and pumps. These gases are easily removed with the forced draft degasifier at a much lower cost than chemical additives or liquid cell degasification that requires higher capital cost and much higher operating cost.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
iron oxidation,
water treatment,
water distribution system,
aluminum,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
calcium carbonate,
media packing,
pH levels,
Langilier index (LSI),
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
dissolved gases,
feed water,
De-Aeration,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier
Avoid problems with calcium chlorite and corrosive gasses with your odor control scrubber.
When planning or designing an odor control system, one should pay close attention to several key variables that can cause havoc on a chemical odor control scrubber when trying to treat hydrogen sulfide or ammonia gases. The need for odor control occurs in many different forms. It is essential to understand the process that is creating the odorous or corrosive gas and the need for odor control & air emissions treatment.
First, begin to identify
all the potential obstacles that may creep up later after the chemical odor or corrosive gas control system goes online, like acid or caustic consumption. For example, chemical odor control systems designed for water treatment for the municipal industry are typically needed and attached to a degasification or decarbonation process, often needed to treat hydrogen sulfide (H2S). However, designers often may not pay close enough attention to the type of water process available for “make-up” water for the chemical scrubber. The addition of caustic can create scaling or fouling. This unknown variable of the makeup water quality can lead to a complete tower shutdown if the chemical scrubber distribution and media bed scales or fouls. The most commonly used chemicals for a hydrogen sulfide (H2S) scrubber are either chlorine in the form of sodium hypochlorite or caustic in the form of caustic soda. Both of these chemicals are common to a water treatment facility and are already in place to adjust and control pH.
The makeup water plays a significant role in the operation of a chemical scrubber.
When water containing high hardness levels is used as the source for the makeup water, your chemical scrubber can become fouled, and scaling can occur in a matter of hours, depending on the alkalinity and salts within the water. Solidification can occur from the scaling when combining sodium hypochlorite and raw feed water at specific pH ranges and these ranges are usually the range needed to achieve peak performance. Calcium chloride will form, and your chemical odor control scrubber will become a solid chunk of calcium chlorite making, making the ability for water or air to pass freely through the media packing next to impossible. No matter what type of media packing is utilized in the odor control or gas scrubber, it can foul and scale if the water chemistry is incorrect. Trust me when I say “been there and done that”! I have seen operators who have allowed a chemical scrubber to become out of balance with pH control and completely solidify the tower column to the degree that neither air nor water passage is possible. The problem can still occur with ammonia scrubbers but are different with different sets of parameters.
Read More
Topics:
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
calcium carbonate,
media packing,
pH levels,
Alkalinity,
Langilier index (LSI),
scaling,
chlorine,
caustic,
ION Exchange Resin,
Safe drinking water,
dissolved gases,
De-Aeration,
carbon dioxide,
oxygen,
degasifier,
gases,
H2S Degasifier,
calcium chlorite
The water treatment industry has developed and evolved over the years to continue to find new ways to produce degassed water,
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
safety,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
media packing,
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
wastewater,
Global,
carbon dioxide,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
gases,
RO membrane,
H2S Degasifier,
degassed water
Many types of water treatment systems depend on some type of media to provide the best performance required as it relates to water treatment and waste water treatment. For use in reverse osmosis there is a reliance on membranes which act as filters to separate the solids from the water. For ion exchange there are “resins” whether AION or CATION the resins works to treat hard and corrosive water. Degasification and decarbonation towers both require an internal media and sometimes this is referred to as “Random Packing” or “Loose Fill Media” and in this process the media acts like a traffic cop directing traffic.
In this case it directs the water on its way down and through a towers internals where it is constantly reshaping the water droplets over and over again forcing gas molecules to come to the surface edge of the water where they are removed. Carbon filters also require a media which is of course “Carbon”. The carbon media acts like a sponge absorbing the contaminants that you wish to remove from the water until it is saturated and must be replaced or regenerated. Even sand filters or pressure filters require a media.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
water treatment,
water plant,
media packing,
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
feed water,
wastewater,
decarbonator,
gases,
RO membrane
Understanding De-Aeration and Decarbonation in Water Treatment Systems
De-Aeration and decarbonation are two essential processes used to remove carbon dioxide (CO2) and dissolved oxygen (O2) from water streams, particularly in boiler-feed water systems. While both processes share the goal of eliminating CO2, they differ in their approach to removing oxygen. A De-Aeration system focuses on removing both CO2 and O2, while a decarbonation system primarily targets the removal of CO2. Let's delve deeper into these processes to understand their mechanisms and benefits.
In a De-Aeration system, steam is introduced at the bottom of the tower. The inlet feed water is heated to near saturation temperature, minimizing pressure drop and venting limits. This ensures optimal thermal operating efficiency of the tower. The steam acts as a carrier gas, stripping both CO2 and O2 from the water as it rises through the tower. The tower is equipped with an internal distribution system and media packing to enhance the removal of dissolved gases. By the time the water reaches the top of the tower, it has undergone significant de-aeration, resulting in reduced CO2 and O2 levels. This purified water is then ready for entry into the boiler, ensuring efficient and reliable steam generation.
Read More
Topics:
media packing,
Decarbonation,
De-Aeration,
carbon dioxide,
oxygen,
steam,
decarbonator
Maintaining Water Quality: Key to Effective Chemical Odor Control Treatment Systems
Read More
Topics:
odor control,
calcium carbonate,
Chemical Odor,
media packing,
Langilier index (LSI),
scaling,
chlorine,
caustic