Degasification and decarbonation are essential processes in water treatment that play a crucial role in improving water quality.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
gases,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier,
co2 dissolved in water,
degassed water,
decarbonation of water,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
hydrogen sulfide molar mass,
DeLoach Industries,
carbon filters,
removing hydrogen sulfide in water,
hydrogen sulfide gas,
dissolved oxygen
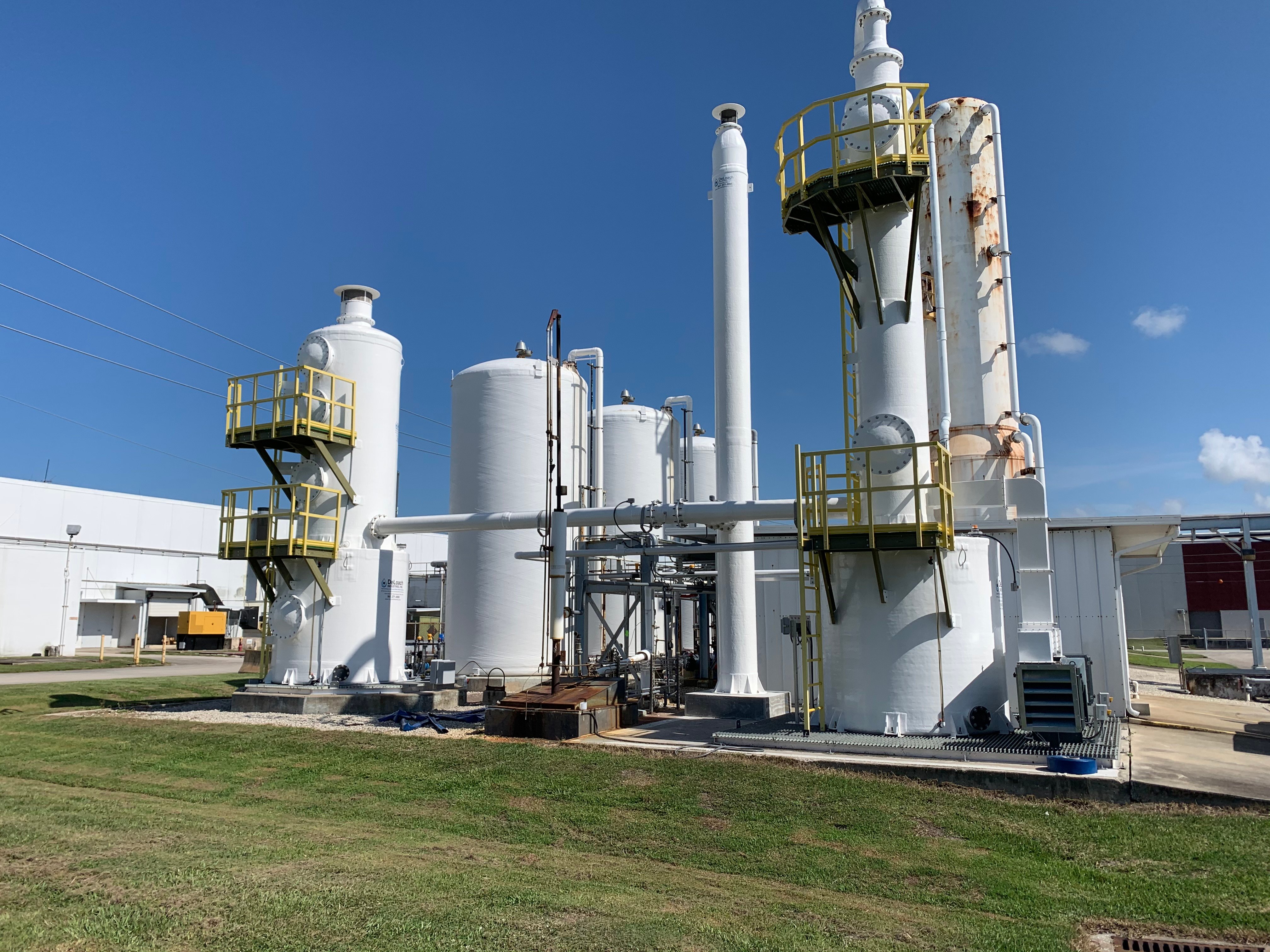
Requires an application commonly referred to as either “Degasification” or "Decarbonation" and it requires the use of a piece of water treatment equipment called either a “degasifier” or a “decarbonator”.
Both of these are similar in nature and are designed for Carbon Dioxide (CO2) removal from the incoming water. A properly designed decarbonator can remove 99.99% of the free carbon dioxide gas that is present in the water stream. One of the primary reasons for utilizing a decarbonator or degasifier for the removal of carbon dioxide gas is the raise the pH of the water without the need to add caustic. resulting in high-purity water.
The other reason is the remove the CO2 prior to treating the water with Ion Exchange which utilizes Anion or Cation resins to reduce the regeneration cycles for the resin beds. High concentrations of CO2 consume the ion charge within the resins and require more frequent regeneration cycles. The difference between anion and cation resins is that one is positively charged (anion) and the other is negatively charged (cation), cation resins, attract positive ions with their negative charge.
The term decarbonation describes the process of the removal of suspended gas or the conversion of carbonic acids into free Carbon Dioxide. Carbonic Acid (H2CO3) is stable at normal ambient anhydrous conditions. However, Carbonic Acid decomposes when not stable and in the presence of any water molecules to form carbon dioxide (CO2). The Carbonic acid breaks down when present in water and it is converted to a gas based upon certain conditions. It is common to have CO2 present in water requiring a decarbonation process when utilizing certain types of water filtration such as membrane filtration with reverse osmosis or it can be present when the need to adjust pH is required. When removing (CO2) the process is often referred to as “Decarbonation”, when removing (H2S) Hydrogen Sulfide the process is often referred to as “Degasification”.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
aeration,
iron oxidation,
water treatment,
water plant,
bicarbonate,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
dissolved gases,
De-Aeration,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
oxygen,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
gases,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier
The Basics of Water Decarbonation
and the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2). The need to remove (CO2) is essential in most Aquaculture, Municipal, Industrial, and Food & Beverage Processes To understand you must familiarize yourself with Henry’s Law.
Henry's Law defines the method and proportional relationship between the amount of a gas in a solution in relation to the gas's partial pressure in the atmosphere. Often you will see and hear various terms like degasification, decarbonation, aeration, and even air stripping when discussing the removal of dissolved gases and other convertible elements from water. Understanding the impacts that Carbon Dioxide (CO2) can have on both equipment and aquatic life provides the basic reasons why the need to decarbonate water, exists. Carbon Dioxide (CO2) can exist naturally in the raw water supply or be the result of ph control and balance. In either case, the process called Decarbonation or Degasification provides the most cost-effective and efficient manner to reduce or tally remove (CO2) from the water. In addition to Carbon Dioxide (CO2), water can contain a variety of other contaminants that may impact the removal efficiency of the Carbon Dioxide. A variety of elements as well as dissolved gases such as oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide (CO2). A full analytical review of the water chemistry is required to properly design and size the “Water Treatment” process.
Breaking the bonds in water releases a dissolved gas
such as carbon dioxide (CO2) you must change the conditions of the vapor pressure surrounding the gas and allow the gas to be removed. There are many variables to consider when designing or calculating the “means and methods” of the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2). When I refer to the means and methods. I am referring to the design of a decarbonator and its components. The means equals the size and type (Hydraulic load) of the decarbonator and the “method” equals the additional variables such as the cubic foot of airflow (CFM) and “Ratio” of the air to water to accomplish the proportional condition needed to remove the carbon dioxide (CO2).
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
aeration,
iron oxidation,
water treatment,
water plant,
bicarbonate,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
dissolved gases,
De-Aeration,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
oxygen,
degasifier,
gases,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier,
removal of CO2 from water
Odor control in a manufacturing facility is essential.
It prevents potential health risks and discomfort caused by the spread of chemicals, vapors, and fumes. Additionally, excessive vapors can hinder the efficiency of exhaust and natural ventilation systems.
One effective solution for addressing odor issues is the installation of an Odor Control Scrubber Tower. These towers are part of the ventilation system in manufacturing plants and chemical processing facilities.
Odor control scrubbers help to remove noxious fumes and odors from exhaust and air streams. This is an effective way to improve air quality. This process involves utilizing an activated carbon filter and an ionic air filter
Key Considerations for Installing an Odor Control Scrubber Tower:
Health and Safety of Workers:
Industrial environments pose risks of exposure to hazardous fumes and gases for workers. Unhealthy odors emitted in high concentrations can jeopardize their well-being and safety. In some cases, these gases may even be combustible, adding an extra level of danger.
Odor control scrubber towers remove gases from the contaminated air, ensuring a safe working environment. These towers reduce the risk of health issues such as nausea, headaches, allergy symptoms, eye irritation, and loss of consciousness. This helps maintain worker productivity and prevents sickness caused by toxic fumes and gases.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
odor control,
water treatment,
water distribution system,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
safety,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
caustic,
Safe drinking water,
wastewater,
gases,
Biological Odor Control Scrubber,
Biological odor control,
what is a scrubber,
municipal water systems,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Clean Water,
Industrial Odor Control
In many water treatment and chemical processes,
it is a requirement to keep track of the pH of the water or product stream. In DeLoach Industries equipment such as degasification systems, or odor control scrubbers, pH measurement is critical to control the chemical reactions happening within the treatment system. PH is an indication of the acidic vs alkaline nature of the fluid. An acidic fluid will have a greater concentration of H+ hydrogen ions, while an alkaline fluid will have a greater concentration of OH- hydroxide ions. This electrochemical nature is used in the construction, reading, and maintenance of electronic pH probes.
PH probes are generally glass and will contain a reference element, and a sensing element. When the pH probe is immersed in the fluid to be measured, the electrical potential difference between the sensing element and the reference element is amplified by electronics and the resulting voltage is used in a calculation to determine pH from differential electron potential. As a pH probe remains in service, ion exchange will slowly change the electrical potential of the sensing element, the reference element, or both. This happens because the hydrogen ions are small enough to travel through the glass sensor body and cause reference potential shifts over time. This is normal behavior for all pH probes and is the reason why pH probes must be periodically calibrated.
Calibration is a process where a pH probe is immersed in a series of standardized stable pH solutions called “buffers”. The standard set of buffers includes a pH 4.0 acidic buffer, a pH 7.0 neutral buffer, and a pH 10.0 alkaline buffer. These buffer solutions are chemically designed to hold a stable pH and are used as a reference for the internal calculations that are done by the pH amplifier or transmitter that interprets the reading taken by the pH probe. As the reference voltage vs actual pH for a mature probe changes, the known buffer solution provides a benchmark for the calculation. Each pH instrumentation manufacturer will have a slightly different method for performing a calibration, but in general, the system will have you step through the buffer solutions while an automated routine makes note of the expected voltage vs calibration voltage at each step. The computation algorithm will use this drift information to re-scale the calculation to re-establish accuracy.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
pH levels of water,
iron oxidation,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
Alkalinity,
ION Exchange Resin,
carbon dioxide,
gases,
RO system,
Aqua Farming
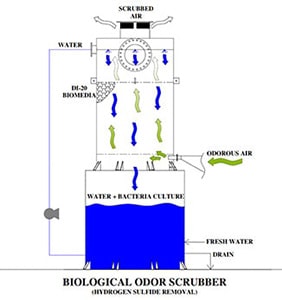
A Biological Odor Control Scrubber Is Just One Of Many Different Types Of Available Technologies to treat air emissions that may contain harmful gases.
This class of equipment commonly falls into a category referred to as “Odor Control Scrubbers” and they are utilized to remove dangerous or noxious odors from an air stream. The Biological Odor Control System has gained popularity among many end users such as municipal operators due to the reduced operating cost and more simplistic operating requirements. A typical chemical odor control scrubber often requires two or more chemical additives and more instrumentation is required to maintain system performance. With the additional chemicals required and instrumentation comes the need for more hands-on maintenance, calibration, and safety requirements which increases the operating costs and workload of the operator.
A Biological Odor Control System relies on active bacteria cultures that recirculate within a water stream and flow across a random packed media bed that is beneficial to the bacteria culture.
During the process of metabolizing harmful gases such as Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) the biological odor control system requires only the addition of Caustic to control and balance the pH and additional water makeup to replace what has been consumed through evaporation or during the blowdown process to eliminate solids. There are several different types of odor control and chemical wet scrubbers, industrial air scrubbers on the market today and each provides a solution for the treatment of noxious or corrosive gases and odors in the industry. And even though Biological scrubbers are commonly utilized in municipal applications for the treatment of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gases that were produced by a water or wastewater treatment process there are times when a Biological Scrubber does not provide the best solution for treatment. When there are wide or rapidly changing concentrations in the ppm (parts per million) level then a Biological Scrubber will have difficulties balancing and acclimating fast enough to prevent a breakthrough. As an example, In water treatment, there is a treatment process referred to as “degasification” which strips the hydrogen sulfide gas from the water, and then the concentrated H2S gas is exhausted from the tower through an exhaust port. When the concentration rises above 1 ppm for hydrogen sulfide gas then the levels become both noxious to the surroundings as well as corrosive. Many times, the levels range from 3-7 PPM in concentration with Hydrogen Sulfide and pose a serious health threat, noxious odor, and corrosive environment demanding capture and treatment. When utilizing an Odor Control Scrubber such as a Biological Scrubber the gases are pulled or pushed through an air duct system that is connected to the Biological Scrubber inlet or suction side of the blower. The same process is utilized when treating Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) gases that were captured at a wastewater treatment process. These gases may have been generated from a source such as the wastewater treatment plant, lift station, or master head-works facility. When captured the gases are also conveyed in a similar manner to the Biological Odor Control Tower for treatment.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
degasification,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
media packing,
caustic,
wastewater,
gases,
H2S Degasifier,
Ammonia,
air emissions
The need for pH control with water degasification and decarbonation in water treatment includes almost every industry and includes;
The need for pH control with water degasification and decarbonation in water treatment includes almost every industry and including; Aquaculture, food, and beverage, industrial, municipal, and even pisciculture. In some water treatment applications, harmful gases such as Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) are removed, while in other applications, Carbon Dioxide (CO2) or a combination of both. In addition, there's a host of other organic and inorganic elements found in water, both naturally occurring and manmade, that require removal during some part of the water treatment process.
In almost every application of degasification or decarbonation, you will hear or see the term pH used either by need or by the result. If, as an example, the water treatment application requires the removal of Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) to be removed either as “free” gas or requires the conversion of Sulfides into (H2S) gas. You will often also see the need to adjust the pH of the water chemistry to maximize both the removal and the conversion to increase the efficiency of the equipment being utilized to remove the hydrogen sulfide, such as a degasification tower or commonly called a degasifier.
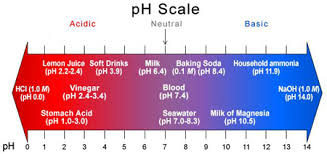
So, what is pH?
Water pH is a term used to describe whether or not the water is “acidic” or “basic.” pH ranges in water can be from 0-14. 0 is the most acidic, and 14 is at the far end and is the most basic, leaving “7” as the neutral state. A pH of 7 is neither acidic nor basic. So, what causes pH to be acidic? In nature, the most common cause of a low acidic pH in water is Carbon Dioxide (CO2) which occurs naturally when photosynthesis, decomposition, or respiration occurs in nature. The increase in CO2 causes an increase in ions, producing a lower pH in a simplified explanation.
How does pH play such a significant role in degasification and decarbonation?
As mentioned above in the example of the removal of certain harmful elements such as sulfides, sulfates, and free H2S hydrogen sulfide gases, to maximize the removal from water utilizing a degasification tower, it is essential to maintain as close to a pH of 5 as possible. When the pH rises above 5, the ability to convert and strip the free H2S gas from the water diminishes. When a degasification tower operates within this specific range and if it has been designed with the higher efficient distribution systems such as the ones utilized by DeLoach Industries, removal efficiencies of 99.999%- 100% can be achieved. If the pH rises to seven or above, the removal process becomes much more complex, and typically, you will have much lower results. The pH adjustment during the water treatment process is typically accomplished by adding commercially available acid, such as “sulphuric acid,” one of the most common in the municipal and food and beverage industry.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
gases,
H2S Degasifier,
Aqua Farming,
Fish Farming,
Aquaculture
Optimizing Water Quality and Enhancing Efficiency.
To enhance and balance the water quality in aquaculture and pisciculture operations, the industry is recognizing the benefits of utilizing a type of water treatment called “Forced Draft Degasification” to remove CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) and H2S (Hydrogen Sulfide) gases and oxidize other elements such as Iron or Magnesium.
Removing these elements from the water process improves the quality of the water and aids in the balancing of the pH without the need for additional chemicals. This also reduces the risk of unnecessary and preventable loss of life to your aqua farming project. Keeping the ph at the proper level will enable a good healthy environment and will prevent further problems that may occur due to the ph is not kept in a stable state.
Read More
Topics:
De-Aeration,
carbon dioxide,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
gases,
H2S Degasifier,
Aqua Farming,
Fish Farming,
Aquaculture,
Pisciculture
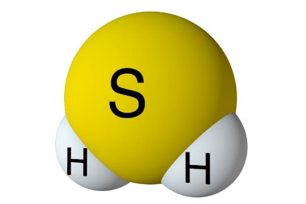
Hydrogen Sulfide Chemical Formula and the Molar Mass of H2S.
H2S is a naturally occurring chemical compound created in nature with the decay of organic material. Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with a molecular formula comprised of (2) hydrogen atoms and (1) one sulfur atom. The formula is displayed as H2S. The gas is a colorless hydride, often known as the “Rotten egg gas.” This gas is very dangerous as it is poisonous and toxic to all life forms. It is also very corrosive and flammable. The H2S molar mass is 34.1 g/mol, with a melting point of -76 F (-60 C) and a melting point of –115.6F or (-82C).
Hydrogen sulfide gas is also created more often from a byproduct of a manufacturing process or the removal of water or wastewater treatment systems. In wastewater, as organic material decays, H2S is released, captured, and treated to protect human lives, reduce corrosion, H2S gas exposure, and H2S gas poisoning, H2S presence and reduce odor complaints. H2S gas is produced during manufacturing operations at refineries, pulp mills, and mining. These high levels of H2S are released during manufacturing. They must be captured and neutralized to protect human life from unwanted health effects such as pulmonary edemaand prevent excessive corrosion to your system. You cannot even smell gas at higher concentrations, and it is not distinguishable as “rotten egg gas,” which makes it even more dangerous and drives the need for hydrogen sulfide scrubbers equipment, fume scrubbers, or odor control scrubbers.
According to the “Agency for Toxic Substance & Disease Registry,” those who work within certain industries are exposed daily to higher levels of hydrogen sulfide gas than the normal public. Because the gas is also heavier than air, it will settle into lower places like manholes, tanks, and basements, and it will travel across the ground filling in low-level areas. To protect the public, OSHA (occupational safety and health administration) has set guidelines and rules known as “Permissible Exposure Limits” (PEL). A PEL is a legal limit a worker may be exposed to a chemical substance. The PEL limit for hydrogen sulfide is ten parts per million (10 ppm) over eight hours.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
degasification,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
dissolved gases,
wastewater,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
gases,
H2S Degasifier,
Hydrogen Sulfide Chemical Formula,
Molar mass,
Hydrogen Sulfide formula,
molar mass h2s,
hydrogen sulfide molar mass,
hydrogen sulfide gas
Water Treatment
When planning and designing a man made on land aquaculture or pisciculture facility.
The most important key element is the quality of the water. For operations developing in Florida or the Caribbean it is important to remember that water quality varies in Florida and other states in the US and typically requires some type of water treatment. For fresh and salt water land based farms that utilize tanks located inside of a building the water needs to be treated and pure from any naturally occurring contaminants such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S), iron (Fe+), and even carbon dioxide (CO2).
The most cost effective way to treat incoming water for aquaculture farming and remove hydrogen sulfide, iron, and lower carbon dioxide is the use of a “degasification” tower. A degasification tower or degasifier is a piece of process equipment. Degasifiers can also be referred to as a “decarbonator” or “air stripper” or even “aeration tower”. The degasification tower is a vertical column designed to remove certain types of contaminants by “stripping” the molecules of converted gases and expelling them from the water as a gas. The science is based upon “Henry’s Law” and it relies upon the disproportionate varying vapor pressures of gases.
If the incoming raw water contains levels of sulfides or hydrogen sulfide gases it is recommended to remove the hydrogen sulfide to improve the water quality and reduce the risk of the development and formation of bacteria that can thrive on the Sulfur. In addition hydrogen sulfide is corrosive and will cause harm to other components within the process if left untreated. It is important to adjust the pH of the raw feed water prior to degasification to ensure full conversion of the sulfides into hydrogen sulfide gas (H2S) to enable the degasification process to perform and remove up to 99.99% of the harmful contaminants without adding additional chemicals. This saves money and improves quality of the product!
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
Alkalinity,
Decarbonation,
Caribbean,
carbon dioxide,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
gases,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier,
Aqua Farming,
Fish Farming,
Aquaculture,
Pisciculture