Since 1959, DeLoach Industries, Inc. has been a trusted leader in manufacturing water, wastewater, and odor control solutions and air emission control systems. Recognized as one of the oldest and most respected manufacturers in the U.S., we specialize in providing reliable solutions that help municipalities and industrial facilities manage odors, meet regulatory standards, and maintain safe working and community environments.
Read More
Topics:
odor control,
water treatment,
Biological Odor Control Scrubber,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Industrial water treatment,
Water Treatment Technologies,
Municipal Odor Control,
Industrial air emissions
If you’ve been following the news, you know a growing problem with PFAS (per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances) exists.
PFAS, a group of synthetic chemicals in a wide range of products, is causing a growing concern. Despite their widespread use, some PFAS compounds have been found to degrade into potentially harmful byproducts like PFAS-methyl tetrahydrofuran. What's more alarming is that these chemicals have infiltrated our drinking water sources, even in areas with high water tables. This is why it's crucial to understand effective methods for removing PFAS from water. What should you do if you suspect that there’s a problem with your water? Check the source of the water, test it, and treat it if necessary.
Follow these steps to remove PFAS from drinking water.
Test Your Water
Although knowing how to remove contaminants is essential, it’s even more important to understand how to test your water for contamination. A water test kit can help you determine whether there are contaminants in your water and whether they are at a dangerous level. You can purchase water test kits at grocery stores, hardware stores, and online retailers. Generally, these kits come with the standard set of tests for a home water filtration system, but they also often include tests for specific contaminants. Use these tests to determine whether your water is safe to drink. If your water contains contaminants, remove them from your water source. This can be done by digging a more bottomless well, installing a water filtration system, or getting a water purification system. If your water does not contain contaminants, you don’t need to do anything except continue drinking your water.
Check the Source
Understanding the source of your water is a crucial step in addressing contamination. Whether you have a well or a water treatment system, knowing where your water comes from can provide valuable insights. By tracing the water's journey from the source, you can determine if contamination occurs upstream. This knowledge is essential for well owners, who might overlook the significance of understanding their water source. If you find contamination at the source, you can address it immediately, such as reducing the distance between the source and your dwelling or seeking alternative, uncontaminated sources.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
Chemical Odor,
Safe drinking water,
RO system,
filters,
Filter Media,
residential well water systems,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
backwash,
Carbon Filter,
Micron Filter,
Drinking Water,
Clean Water,
Contaminated Water,
Water Source,
Sediment Filter,
PFA's,
Water Test,
Water Test Kit
Odor control in a manufacturing facility is essential.
It prevents potential health risks and discomfort caused by the spread of chemicals, vapors, and fumes. Additionally, excessive vapors can hinder the efficiency of exhaust and natural ventilation systems.
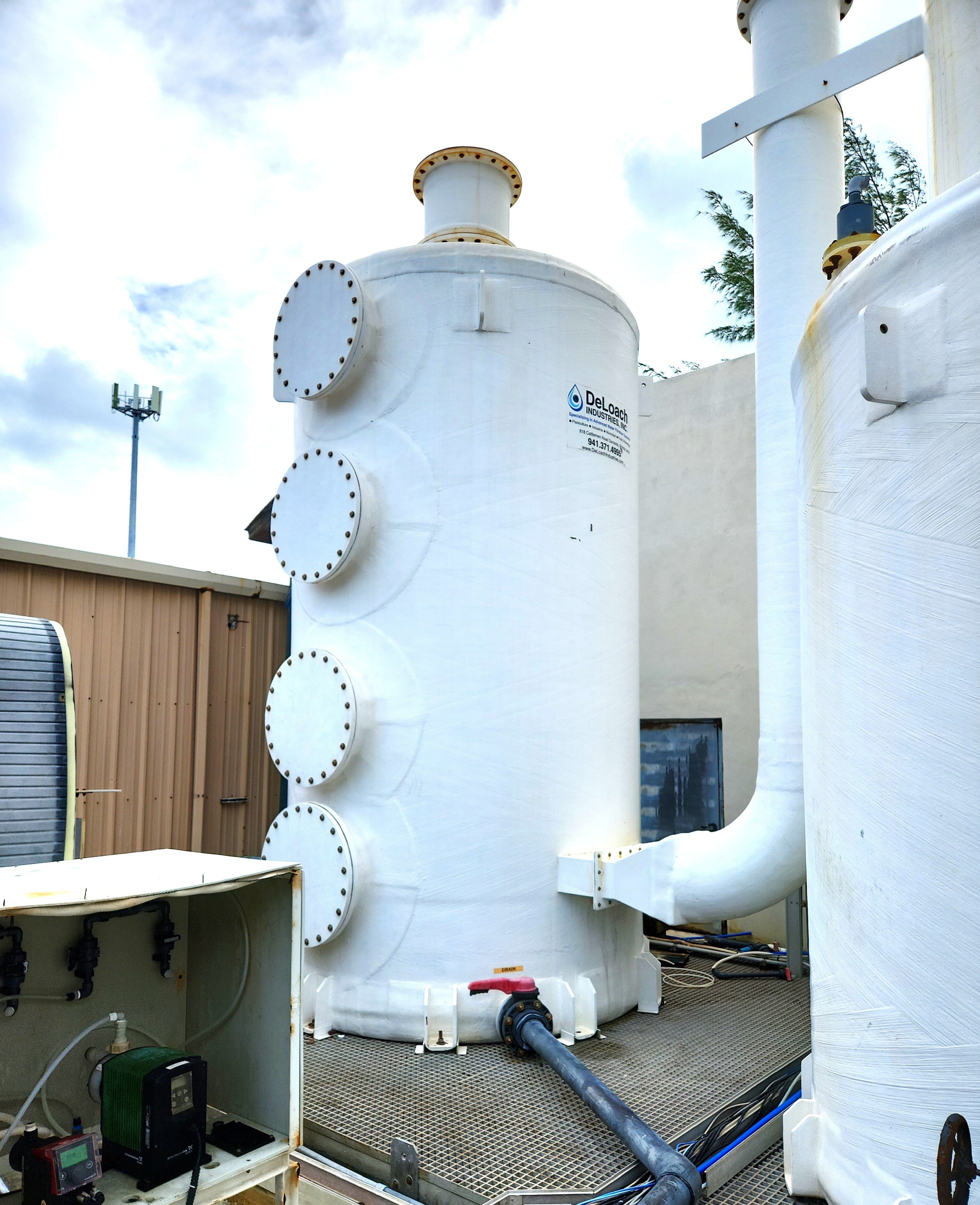
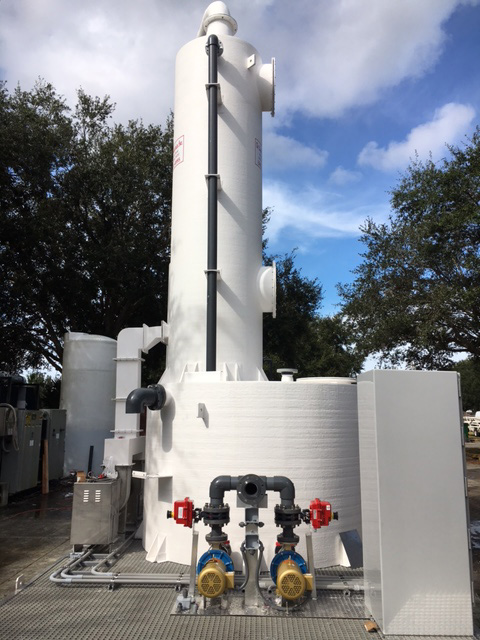
One effective solution for addressing odor issues is the installation of an Odor Control Scrubber Tower. These towers are part of the ventilation system in manufacturing plants and chemical processing facilities.
Odor control scrubbers help to remove noxious fumes and odors from exhaust and air streams. This is an effective way to improve air quality. This process involves utilizing an activated carbon filter and an ionic air filter
Key Considerations for Installing an Odor Control Scrubber Tower:
Health and Safety of Workers:
Industrial environments pose risks of exposure to hazardous fumes and gases for workers. Unhealthy odors emitted in high concentrations can jeopardize their well-being and safety. In some cases, these gases may even be combustible, adding an extra level of danger.
Odor control scrubber towers remove gases from the contaminated air, ensuring a safe working environment. These towers reduce the risk of health issues such as nausea, headaches, allergy symptoms, eye irritation, and loss of consciousness. This helps maintain worker productivity and prevents sickness caused by toxic fumes and gases.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
odor control,
water treatment,
water distribution system,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
safety,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
caustic,
Safe drinking water,
wastewater,
gases,
Biological Odor Control Scrubber,
Biological odor control,
what is a scrubber,
municipal water systems,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Clean Water,
Industrial Odor Control
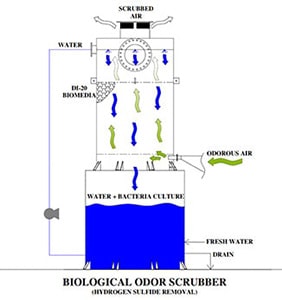
A Biological Odor Control Scrubber Is Just One Of Many Different Types Of Available Technologies to treat air emissions that may contain harmful gases.
This class of equipment commonly falls into a category referred to as “Odor Control Scrubbers” and they are utilized to remove dangerous or noxious odors from an air stream. The Biological Odor Control System has gained popularity among many end users such as municipal operators due to the reduced operating cost and more simplistic operating requirements. A typical chemical odor control scrubber often requires two or more chemical additives and more instrumentation is required to maintain system performance. With the additional chemicals required and instrumentation comes the need for more hands-on maintenance, calibration, and safety requirements which increases the operating costs and workload of the operator.
A Biological Odor Control System relies on active bacteria cultures that recirculate within a water stream and flow across a random packed media bed that is beneficial to the bacteria culture.
During the process of metabolizing harmful gases such as Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) the biological odor control system requires only the addition of Caustic to control and balance the pH and additional water makeup to replace what has been consumed through evaporation or during the blowdown process to eliminate solids. There are several different types of odor control and chemical wet scrubbers, industrial air scrubbers on the market today and each provides a solution for the treatment of noxious or corrosive gases and odors in the industry. And even though Biological scrubbers are commonly utilized in municipal applications for the treatment of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gases that were produced by a water or wastewater treatment process there are times when a Biological Scrubber does not provide the best solution for treatment. When there are wide or rapidly changing concentrations in the ppm (parts per million) level then a Biological Scrubber will have difficulties balancing and acclimating fast enough to prevent a breakthrough. As an example, In water treatment, there is a treatment process referred to as “degasification” which strips the hydrogen sulfide gas from the water, and then the concentrated H2S gas is exhausted from the tower through an exhaust port. When the concentration rises above 1 ppm for hydrogen sulfide gas then the levels become both noxious to the surroundings as well as corrosive. Many times, the levels range from 3-7 PPM in concentration with Hydrogen Sulfide and pose a serious health threat, noxious odor, and corrosive environment demanding capture and treatment. When utilizing an Odor Control Scrubber such as a Biological Scrubber the gases are pulled or pushed through an air duct system that is connected to the Biological Scrubber inlet or suction side of the blower. The same process is utilized when treating Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) gases that were captured at a wastewater treatment process. These gases may have been generated from a source such as the wastewater treatment plant, lift station, or master head-works facility. When captured the gases are also conveyed in a similar manner to the Biological Odor Control Tower for treatment.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
degasification,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
media packing,
caustic,
wastewater,
gases,
H2S Degasifier,
Ammonia,
air emissions
The need for pH control with water degasification and decarbonation in water treatment includes almost every industry and includes;
The need for pH control with water degasification and decarbonation in water treatment includes almost every industry and including; Aquaculture, food, and beverage, industrial, municipal, and even pisciculture. In some water treatment applications, harmful gases such as Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) are removed, while in other applications, Carbon Dioxide (CO2) or a combination of both. In addition, there's a host of other organic and inorganic elements found in water, both naturally occurring and manmade, that require removal during some part of the water treatment process.
In almost every application of degasification or decarbonation, you will hear or see the term pH used either by need or by the result. If, as an example, the water treatment application requires the removal of Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) to be removed either as “free” gas or requires the conversion of Sulfides into (H2S) gas. You will often also see the need to adjust the pH of the water chemistry to maximize both the removal and the conversion to increase the efficiency of the equipment being utilized to remove the hydrogen sulfide, such as a degasification tower or commonly called a degasifier.
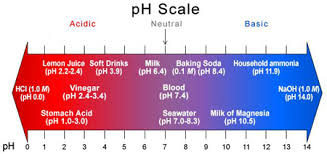
So, what is pH?
Water pH is a term used to describe whether or not the water is “acidic” or “basic.” pH ranges in water can be from 0-14. 0 is the most acidic, and 14 is at the far end and is the most basic, leaving “7” as the neutral state. A pH of 7 is neither acidic nor basic. So, what causes pH to be acidic? In nature, the most common cause of a low acidic pH in water is Carbon Dioxide (CO2) which occurs naturally when photosynthesis, decomposition, or respiration occurs in nature. The increase in CO2 causes an increase in ions, producing a lower pH in a simplified explanation.
How does pH play such a significant role in degasification and decarbonation?
As mentioned above in the example of the removal of certain harmful elements such as sulfides, sulfates, and free H2S hydrogen sulfide gases, to maximize the removal from water utilizing a degasification tower, it is essential to maintain as close to a pH of 5 as possible. When the pH rises above 5, the ability to convert and strip the free H2S gas from the water diminishes. When a degasification tower operates within this specific range and if it has been designed with the higher efficient distribution systems such as the ones utilized by DeLoach Industries, removal efficiencies of 99.999%- 100% can be achieved. If the pH rises to seven or above, the removal process becomes much more complex, and typically, you will have much lower results. The pH adjustment during the water treatment process is typically accomplished by adding commercially available acid, such as “sulphuric acid,” one of the most common in the municipal and food and beverage industry.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
gases,
H2S Degasifier,
Aqua Farming,
Fish Farming,
Aquaculture
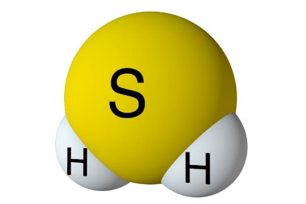
Hydrogen Sulfide Chemical Formula and the Molar Mass of H2S.
H2S is a naturally occurring chemical compound created in nature with the decay of organic material. Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with a molecular formula comprised of (2) hydrogen atoms and (1) one sulfur atom. The formula is displayed as H2S. The gas is a colorless hydride, often known as the “Rotten egg gas.” This gas is very dangerous as it is poisonous and toxic to all life forms. It is also very corrosive and flammable. The H2S molar mass is 34.1 g/mol, with a melting point of -76 F (-60 C) and a melting point of –115.6F or (-82C).
Hydrogen sulfide gas is also created more often from a byproduct of a manufacturing process or the removal of water or wastewater treatment systems. In wastewater, as organic material decays, H2S is released, captured, and treated to protect human lives, reduce corrosion, H2S gas exposure, and H2S gas poisoning, H2S presence and reduce odor complaints. H2S gas is produced during manufacturing operations at refineries, pulp mills, and mining. These high levels of H2S are released during manufacturing. They must be captured and neutralized to protect human life from unwanted health effects such as pulmonary edemaand prevent excessive corrosion to your system. You cannot even smell gas at higher concentrations, and it is not distinguishable as “rotten egg gas,” which makes it even more dangerous and drives the need for hydrogen sulfide scrubbers equipment, fume scrubbers, or odor control scrubbers.
According to the “Agency for Toxic Substance & Disease Registry,” those who work within certain industries are exposed daily to higher levels of hydrogen sulfide gas than the normal public. Because the gas is also heavier than air, it will settle into lower places like manholes, tanks, and basements, and it will travel across the ground filling in low-level areas. To protect the public, OSHA (occupational safety and health administration) has set guidelines and rules known as “Permissible Exposure Limits” (PEL). A PEL is a legal limit a worker may be exposed to a chemical substance. The PEL limit for hydrogen sulfide is ten parts per million (10 ppm) over eight hours.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
degasification,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
dissolved gases,
wastewater,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
gases,
H2S Degasifier,
Hydrogen Sulfide Chemical Formula,
Molar mass,
Hydrogen Sulfide formula,
molar mass h2s,
hydrogen sulfide molar mass,
hydrogen sulfide gas
Treating Hydrogen Sulfide for Environmental Safety
Read More
Topics:
odor control,
aeration,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
gases,
Amine,
H2S Degasifier
Caustic solution for Sodium hydroxide water treatment of Sodium Hydroxide
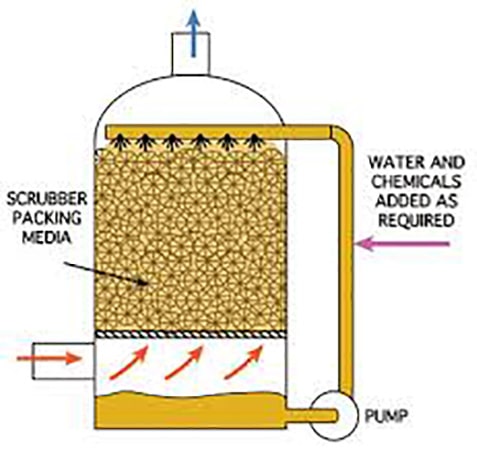
There are many industries that require the use of a caustic scrubber which is considered a chemical scrubber and they range from the municipal industry, mining, semiconductor markets, pulp and paper, and chemical refining. There is a wide variety of industrial processes that generate noxious or corrosive off gases that require treatment and a comparison is made between biological Vs. chemical. Often biological scrubbers have limitations due to concentrations, composition, or temperature of the contaminants and if the gas stream contains acid fumes then a biological scrubber is quickly ruled out.
The odor control selection is often fraught with choices of capital cost over operational cost and quite often comes down to familiarity from the designer or purchaser. It is always a good idea to freshen up the industrial odor control the do’s and don’t’s before selecting the final solution. If the off-gas source that needs to be treated is hydrogen sulfide (H2S) or some other type of gas stream produced by an acid or ammonia it will often require neutralization for human health reasons and to protect equipment or may be required to meet regulatory compliance. Caustic scrubbers may be either vertical or horizontal by design, but both utilize a packed media bed of either random packing or trays to allow the gas fumes to meet the recirculating caustic solution which then forces the reaction to occur.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
pH levels,
caustic,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
gases,
caustic solution,
sodium hydroxide water treatment
What type of Odor Control Scrubber do I select?
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
degasifier,
gases
A Biological Scrubber is a wet odor control scrubber that treats and removes contaminants from an air stream.
It utilizes caustic typically to control the pH of the re-circulation solution. There are several types of odor control and chemical fume scrubbers on the market today. Each plays a role in treating noxious or corrosive gases in the industry.
Biological scrubbers are used in municipal applications to treat low and high hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gas levels. This colorless gas is removed from the water or wastewater treatment process.
Water treatment equipment such as “degasification” or “decarbonation” towers.
Strips the hydrogen sulfide gas from the treated wastewater and exhausts the gas from an exhaust port. These gases are captured and sent to the biological scrubber via an air duct system. The health effects of hydrogen sulfide can cause eye irritation, loss of appetite, and fluid in the lungs. Hydrogen gases are captured at a wastewater treatment process, including treatment facilities, lift stations, or head-works facilities. The PVC or FRP duct system sends the gases to the biological scrubber.
How does a Biological Scrubber work?
A biological scrubber utilizes tiny microorganisms (bacteria) to break down and digest contaminants. The bacteria feed on the contaminants and utilize this as a feed source to live and grow. When utilizing a biological scrubber for hydrogen sulfide (H2S) treatment, the by-product waste is acid from the digested H2S. This lowers the pH and requires the use of caustic to buffer the water and nutrient solution that is recirculated within the scrubber to maintain a neutral pH. The captured gas containing contaminants enters the bottom of a vertical biological scrubber. Similar to how the gas enters any other type of chemical scrubber or single or dual pass odor control scrubber.
The gas stream travels upward. Passes over a media bed that has been cultured to grow live microorganisms. A biological odor control scrubber already has “artificial intelligence” because of the millions of microbes colonies it supports.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
odor control,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
dissolved gases,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
gases,
RO system,
H2S Degasifier,
what is a scrubber