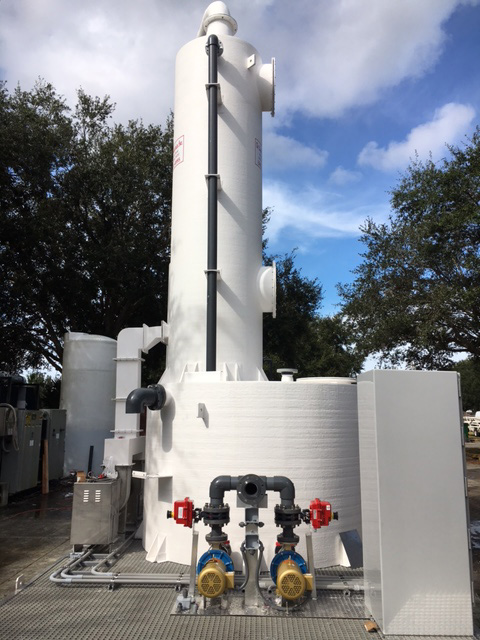
A Biological Odor Control Scrubber Is Just One Of Many Different Types Of Available Technologies to treat air emissions that may contain harmful gases.
This class of equipment commonly falls into a category referred to as “Odor Control Scrubbers” and they are utilized to remove dangerous or noxious odors from an air stream. The Biological Odor Control System has gained popularity among many end users such as municipal operators due to the reduced operating cost and more simplistic operating requirements. A typical chemical odor control scrubber often requires two or more chemical additives and more instrumentation is required to maintain system performance. With the additional chemicals required and instrumentation comes the need for more hands-on maintenance, calibration, and safety requirements which increases the operating costs and workload of the operator.
A Biological Odor Control System relies on active bacteria cultures that recirculate within a water stream and flow across a random packed media bed that is beneficial to the bacteria culture.
During the process of metabolizing harmful gases such as Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) the biological odor control system requires only the addition of Caustic to control and balance the pH and additional water makeup to replace what has been consumed through evaporation or during the blowdown process to eliminate solids. There are several different types of odor control and chemical wet scrubbers, industrial air scrubbers on the market today and each provides a solution for the treatment of noxious or corrosive gases and odors in the industry. And even though Biological scrubbers are commonly utilized in municipal applications for the treatment of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gases that were produced by a water or wastewater treatment process there are times when a Biological Scrubber does not provide the best solution for treatment. When there are wide or rapidly changing concentrations in the ppm (parts per million) level then a Biological Scrubber will have difficulties balancing and acclimating fast enough to prevent a breakthrough. As an example, In water treatment, there is a treatment process referred to as “degasification” which strips the hydrogen sulfide gas from the water, and then the concentrated H2S gas is exhausted from the tower through an exhaust port. When the concentration rises above 1 ppm for hydrogen sulfide gas then the levels become both noxious to the surroundings as well as corrosive. Many times, the levels range from 3-7 PPM in concentration with Hydrogen Sulfide and pose a serious health threat, noxious odor, and corrosive environment demanding capture and treatment. When utilizing an Odor Control Scrubber such as a Biological Scrubber the gases are pulled or pushed through an air duct system that is connected to the Biological Scrubber inlet or suction side of the blower. The same process is utilized when treating Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) gases that were captured at a wastewater treatment process. These gases may have been generated from a source such as the wastewater treatment plant, lift station, or master head-works facility. When captured the gases are also conveyed in a similar manner to the Biological Odor Control Tower for treatment.