In modern industrial water treatment, advancements in technology and processes have revolutionized the way contaminants are removed from water.
This blog explores the integration of NSF/ANSI 61 certified systems, artificial intelligence in water treatment, and cutting-edge processes such as decarbonation and degasification. We'll also discuss the key differences between forced draft and induced draft degasification towers, helping you make informed decisions while designing your Industrial Water Treatment System.
-
NSF/ANSI 61-Certified Water Treatment Systems: To ensure the safety and quality of water treatment equipment, NSF/ANSI 61 certification has become a crucial standard. This certification verifies that materials and components used in water treatment systems comply with health and safety requirements. When selecting a water treatment solution, opting for NSF/ANSI 61 certified systems guarantees peace of mind and adherence to the highest industry standards.
-
Harnessing Artificial Intelligence in Water Treatment: Artificial intelligence (AI) has penetrated various industries, and water treatment is no exception. Integrating AI into water treatment processes allows for more efficient and optimized operations. AI-driven systems can monitor water quality in real-time, predict system failures, optimize chemical dosing, and reduce energy consumption. By leveraging AI technologies, water treatment facilities can enhance their overall performance and streamline resource utilization.
-
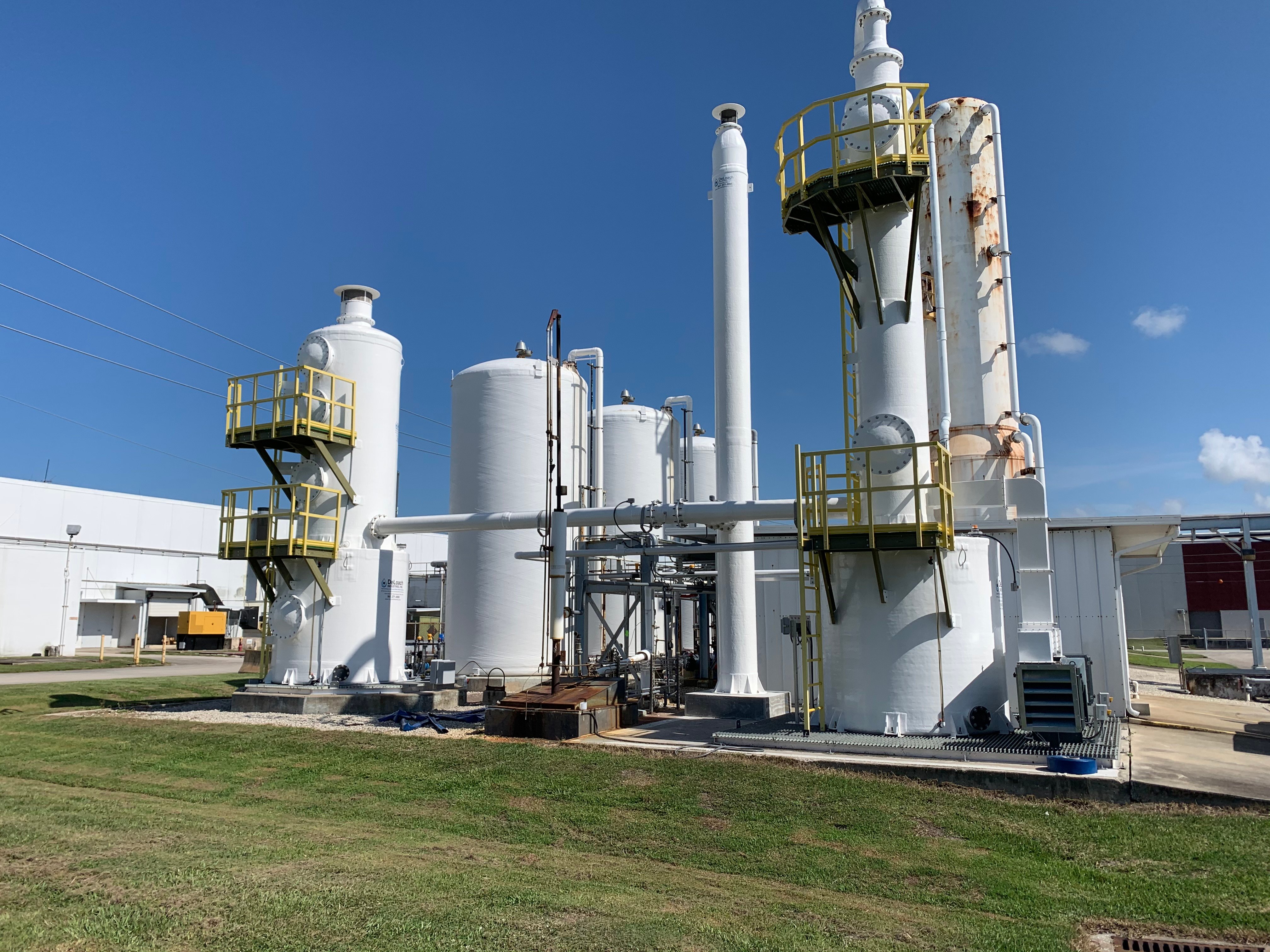
Decarbonation and Degasification Systems: Decarbonation and degasification are essential processes in industrial water treatment, particularly in pH levels in water and the ability to control removing the contaminants. These processes target the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other dissolved gases from water to improve its quality. Two key systems used for this purpose are the decarbonator and aeration system.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
NSF/ANSI 61,
Chemical Odor,
Decarbonation,
Safe drinking water,
De-Aeration,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
degassed water,
ansi61,
nsf/ansi61,
Deagasification,
decarbonation of water,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Drinking Water,
Industrial Odor Control,
DeLoach Industries,
contaminants,
process system,
safe drinking water act,
drinking water standards,
environmental safety,
air emissions,
Forced Draft,
Induced Draft
Degasification and decarbonation are essential processes in water treatment that play a crucial role in improving water quality.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
gases,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier,
co2 dissolved in water,
degassed water,
decarbonation of water,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
hydrogen sulfide molar mass,
DeLoach Industries,
carbon filters,
removing hydrogen sulfide in water,
hydrogen sulfide gas,
dissolved oxygen
Water demineralization is also called deionization and is a process known as “Ion Exchange.”
In simple terms, water demineralization is “Water Purification.” The process involves removing dissolved ionic mineral solids from a feed-water process, typically for “Industrial” water applications. Still, it can also be utilized to remove dissolved solids from a water process for “Aquaculture,” “Food and Beverage,” and the “Municipal” markets.
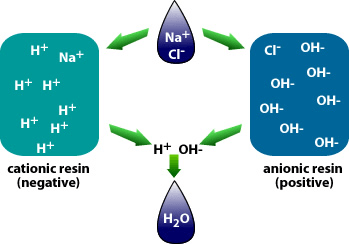
Why is demineralization utilized? It can remove dissolved solids to near distilled water quality at a much lower capital and operational cost than other treatment processes such as membrane softening (Reverse Osmosis). Demineralization applies the science known as “Ion Exchange,” which attracts negative and positive charged ions and allows either to attach themselves to a negative ion depending on their respective current negative or positive charge during what is known as a resin cycle. In other technical articles, we will explore and go into more specific details on the science of the ion exchange process. Water that has dissolved salts and minerals has ions, either negatively charged ions known as “Anions” or positively charged ions known as “Cations.” To treat the water and remove these contaminants, the ions in the water are attracted to counter-ions, which have a negative charge. In a demineralization treatment process, there are pressure vessels that hold resin beads which are typically made of plastic. The beads are made from a plastic material with an ionic functional group that allows them to hold and maintain an electrostatic electrical charge. Some of these resin groups are negatively charged, referred to as “Anion” resins, while others hold a positive charge and are called “Cations” resins.
There are different applications to apply Ion exchange technologies, which is why you will often hear different terminology interchanged like deionization and demineralization. The raw water quality and the specific application will dictate the type of ion exchange process needed. For example, if the water contains a high level of hardness, the water will most likely contain Ca2+ or Mg2+ dissolved solids possessing a positive charge. To replace these hard ions, it is typical to utilize a resin bed with a salt ion like Na+. As the water passes over the resin bead material within the pressure vessel. The hard ions are replaced with the salt ion; therefore, all the hardness within the water is removed. However, the water will now contain a higher concentration of sodium ions, and this must be considered during the evaluation and selection process of the type of resin material to utilize for the specific application. If the water application requires high purity and the removal of as many solids as possible, then the term or process selected is referred to as demineralization.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
water distribution system,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
media packing,
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
RO system,
H2S Degasifier,
Aquaculture,
degassed water,
Co2 ph,
removal of CO2 from water,
Deagasification,
decarbonation of water,
hydrogen ion,
particulate matter,
municipal water systems,
industrial facilities,
automated control systems,
Ion exchange,
cations,
anions
The water treatment industry has developed and evolved over the years to continue to find new ways to produce degassed water,
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
safety,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
media packing,
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
wastewater,
Global,
carbon dioxide,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
gases,
RO membrane,
H2S Degasifier,
degassed water
Industrial water treatment systems play a crucial role in maintaining the quality and sustainability of water used in various industrial processes. One of the key challenges faced by industries is the presence of dissolved gases, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), and corrosive gases like hydrogen sulfide (H2S) in the water. These gases can have detrimental effects on equipment, cause pH imbalances, and even compromise the overall efficiency of industrial processes.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
water treatment,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
degassed water,
Deagasification,
decarbonation of water,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Drinking Water,
DeLoach Industries,
water process system