Would it be possible for our odor control scrubbers to communicate with us and tell us when there are problems?
Or when they need service? With the new technological revolution, we are now this is quickly becoming a reality. DeLoach Industries is rapidly changing how water treatment and odor control and air emissions are treated with new advancements in artificial intelligence and integration into proven technologies.
Most operators will tell you that to keep and maintain an odor control system whether it's Biological Vs. chemical can be quite challenging depending on the type and source of the off-gas to be treated and depending on the type of chemical reagents being utilized such as acid or caustic solutions. When odor control systems such as a biological scrubber are met with varying flow rates, corrosive gases, or spiking concentrations an odor control system can be daunting to keep in balance and operating efficiency. But what if they could think or communicate with other devices or even operators for themselves? What if they could make corrections in caustic feed rates because of ammonia (NH3) concentration spikes, order chemicals like caustic or acid for pH control, and even inform us when they anticipate a problem for either the odor control scrubber or another critical component that it depends upon? That time has now arrived that’s to DeLoach Industries' new advancements to their equipment systems.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
water distribution system,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
gases
The type of Odor Control Wet Scrubber selected for the treatment and neutralization of Ammonia (NH3) gases depends on several variables, including the type and source of the ammonia gas and whether or not it is “Free” ammonia and or unionized.
Ammonia is a very miscible and stable molecule with solid hydrogen bonds, making it very soluble in water and difficult to treat without using a properly designed and sized ammonia scrubber. The concentrations, air flow rates, temperature of the gas stream, and chemical reagents being utilized, such as caustic to remove and then treat the ammonia, all play a significant role in the removal efficiency of the ammonia gas scrubber system. Unlike other types of “odor control scrubbers,” an ammonia scrubber is much more sensitive to variables such as the gas stream temperature because of the solubility of ammonia.
Ammonia is produced from nitrogen and hydrogen
the process is called the Haber Process by combining nitrogen with air and adding pressure, you can make ammonia.
It takes about 200 atmospheres of pressure, and the process varies from refinery to refinery. Still, on average, you can only make approximately 15% of ammonia during each pass which takes multiple passes to achieve the 15%. The reaction to make ammonia is exothermic when produced in a refining process.
However, ammonia is also formed in nature in smaller quantities. Most ammonia (90%) is utilized for fertilizer production, but ammonia can be found in food, pharmaceutical products, and cleaning supplies. When ammonia gas is released into the air, it has a very noxious and pungent odor that can be dangerous to inhale, so often, odor control scrubbers are required to capture and treat the ammonia gas.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
wastewater,
degasifier,
gases,
H2S Degasifier,
Ammonia
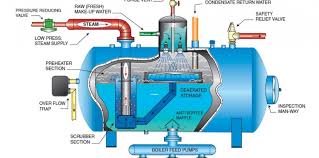
In the United States manufacturing industry, an astonishing 400 million gallons of water per day (MGD) is consumed to generate steam.
Out of this amount, approximately 60 MGD is sent to blow-down drains, while another 300 MGD is used for direct injection of steam. The common denominator in all of these processes is the need for purified and treated water. Without proper treatment, manufacturers would face frequent shutdowns and increased capital expenditure, significantly impacting their cost of goods. One effective method of water treatment to protect boilers is through degasification and deaeration.
Degasification towers play a crucial role in removing harmful gases such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S), carbon dioxide (CO2), and often dissolved oxygen (DO). The elimination of these corrosive gases is vital for enhancing the lifespan and efficiency of boiler systems. If these gases are allowed to remain in the boiler feed water, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), it can lead to disastrous consequences, including higher operating costs and reduced system longevity. Carbon dioxide (CO2) can convert into carbonic acid, creating a corrosive environment for the boiler and other critical components. In cases where an ion exchange process is implemented prior to the boiler, the presence of carbon dioxide (CO2) can drastically increase regeneration costs as the resins are consumed. By removing carbon dioxide (CO2), the life of the resin is extended, and the pH of the water is elevated, reducing the need for additional chemicals and further lowering operating costs.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
degasification,
iron oxidation,
water treatment,
water distribution system,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
feed water,
De-Aeration,
steam generation,
steam generating boilers,
carbon dioxide,
steam,
decarbonator,
boiler system,
degasifier,
gases,
RO membrane,
carbonic acid,
RO system,
H2S Degasifier,
Boiler feed water
The water treatment industry has developed and evolved over the years to continue to find new ways to produce degassed water,
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
safety,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
media packing,
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
wastewater,
Global,
carbon dioxide,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
gases,
RO membrane,
H2S Degasifier,
degassed water
Many types of water treatment systems depend on some type of media to provide the best performance required as it relates to water treatment and waste water treatment. For use in reverse osmosis there is a reliance on membranes which act as filters to separate the solids from the water. For ion exchange there are “resins” whether AION or CATION the resins works to treat hard and corrosive water. Degasification and decarbonation towers both require an internal media and sometimes this is referred to as “Random Packing” or “Loose Fill Media” and in this process the media acts like a traffic cop directing traffic.
In this case it directs the water on its way down and through a towers internals where it is constantly reshaping the water droplets over and over again forcing gas molecules to come to the surface edge of the water where they are removed. Carbon filters also require a media which is of course “Carbon”. The carbon media acts like a sponge absorbing the contaminants that you wish to remove from the water until it is saturated and must be replaced or regenerated. Even sand filters or pressure filters require a media.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
water treatment,
water plant,
media packing,
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
feed water,
wastewater,
decarbonator,
gases,
RO membrane
Ten years ago if I had purposed that one day our water would have artificial intelligence I think I would have been laughed out of the industry. But now, anything you can imagine with the new electronic revolution is possible because of the current revolution referred to as “The Internet of Things” (IoT). Placing nano-size SIP (Systems in a package) into a water stream and tracking its path or location or performing inspections on critical infrastructure or equipment is now a reality.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
phosphate levels,
pH levels,
Alkalinity,
Global,
decarbonator,
degasifier
One of the largest consumers of energy in the US is water and wastewater treatment plants.
Because of the need for large horsepower pumps and blowers, a municipal water and wastewater treatment plant consumes a tremendous amount of kilowatt hours of electricity. The energy cost is factored into the “cost of production” of water or wastewater treatment, and the “rate base” charge is increased accordingly to the consumer.
Does Renewable Power Work in a Water Treatment Plant?
Because solar energy is “space intensive,” you do not see a lot of solar power being deployed across the USA at water treatment plants. In our opinion, this is a mistake, and most likely, the decision was made back when solar power output was much lower. With the increased efficiency of solar panels and decreased production cost, it makes tremendous sense to revisit the use of Solar energy to offset the operational cost of a water treatment plant or wastewater treatment plant operation.
Providing solar energy for specific pieces of process equipment is also a viable option when you consider deploying solar energy. For example, operating a Degasification tower or Decarbonator utilizing 10 350-watt solar panels will generate 3500 watts during peak daylight hours and enough to offset the cost of smaller horsepower blower motors. If the solar panels are configured as a canopy, they can also provide a nice shade or protective barrier above the piece of equipment if installed outdoors, as most packed column towers are located outside.
What about other forms of renewable energy? Do they work?
At water treatment or wastewater treatment facilities. Co-generation use has been around for many years at Wastewater plant facilities wastewater treatment plants. A cogeneration unit is a combination “Generator” to produce power and a “Thermal” energy source to produce heated water. The water can be used domestically or can be used to produce chilled water with the help of a Chiller system. The wastewater treatment plant provides a critical component by producing gases such as “Methane,” which can be used as a cogeneration unit fuel source. Water treatment plants do not produce methane or other combustible forms of gases like a cogeneration plant would produce, so you normally do not see Cogeneration system units deployed at a Water treatment facility.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
water treatment,
water distribution system,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
Decarbonation,
wastewater,
Recycling,
Global,
steam generation,
steam
Protecting Your Pharmaceutical Water: Ensuring Quality and Efficiency in Water Treatment
In the pharmaceutical industry, the removal of dissolved gases from water is a critical step in the water treatment process. However, it is essential to select the appropriate method of removing these gases, as the wrong choice can have detrimental effects on vital process water equipment such as steam boilers and distillation columns. Failure to address high levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the water can lead to the formation of carbonic acid, which corrodes and damages both the steam boiler tubes and distillation columns. To mitigate these risks, the implementation of a degasification tower or "Degasifier" is crucial, as it effectively removes dissolved gases like hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2) to acceptable levels below 7 parts per billion (ppb).
Utilizing a degasification tower offers a cost-effective solution to reduce and eliminate gases in the water stream. In comparison, alternative methods such as reverse osmosis (RO) membranes require additional steps, including pH adjustment, to achieve similar results. The conversion of carbon dioxide (CO2) into carbonates can result in increased membrane fouling and elevated capital costs for the RO system. By implementing a degasification system, businesses can achieve optimal performance, minimize membrane fouling, and benefit from cost savings in both capital and operational expenses.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
water treatment,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
dissolved gases,
pharmaceutical water,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
gases,
RO membrane,
carbonic acid,
RO system
The importance of removing Carbon Dioxide in the water!
Carbon dioxide exists naturally in nature as free CO2 and can be found in many water sources from lakes, streams, or other surface water bodies. Carbon dioxide occurs naturally in small amounts (about 0.04 percent) in the Earth's atmosphere. Monitoring CO2 levels in your water can be done through test kits or monitoring systems. When monitoring CO2 levels, it is important to note the concentration at which the monitoring needs to occur. Industrial level ion exchange systems should be monitored at a concentration typically 15–20 times greater than required for drinking water quality. Ion exchange systems used for high purity water production should be monitored at a concentration typically 40–50 times greater than what is required for drinking water quality. Due to carbon dioxide’s abundance and its role as the primary driver of climate change, there are concerns about increasing concentrations of this gas in the atmosphere. To reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, people can reduce the amount of carbon dioxide released during energy production by using renewable energy sources and energy efficiency. Carbon dioxide can be captured and stored underground with carbon sequestration technologies.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
carbon dioxide,
CO2 in water,
excess co2,
hydrogen ion
Saving Steam with Degasification: Optimizing Water Treatment for Cost Efficiency and Enhanced Performance.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
Decarbonation,
steam generation,
carbon dioxide,
steam,
decarbonator,
distillation