The operation of steam-generating boilers and the process of removing dissolved gases from the feed water is of utmost importance.
Deaeration is essential in the boiler system process.
Deaeration involves removing oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from the water. Removing oxygen and carbon dioxide from the water before it enters the boiler system is essential. This prevents corrosion of the boiler system components and reduces costly maintenance and repairs to your system.
Oxygen and carbon dioxide can corrode and destroy metal components of the boiler system.
Corrosion can be costly to repair or replace. This is due to oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) not being removed from the water.
In order to avoid unwanted corrosion, it is necessary to treat the water before it enters the boiler system. This can be achieved through different techniques, including deaeration, chemical treatment, or mechanical filtration.
The deaeration process typically requires a deaerator. This device combines heat and vacuum to remove dissolved gases from water. The deaerator reduces the amount of dissolved solids in the water.This can improve the efficiency of the boiler system. Neglecting regular maintenance and inspection of the boiler can lead to severe corrosion damage and operational issues.
Read More
Topics:
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
feed water,
De-Aeration,
steam generating boilers,
carbon dioxide,
oxygen,
steam,
decarbonator,
boiler system
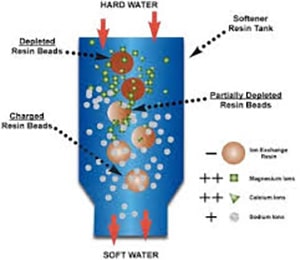
Extending the life of your ion exchange resin in boiler feed water applications
Did you know that when producing steam, it is most effectively accomplished by utilizing a decarbonation process? Decarbonation and Degasification is the most economical way to process fluent water pre-Ion exchange treatment through a vertically packed tower called a decarbonator, often called a degasifier. This is the most economical method to remove carbon dioxide (CO2) and Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) to prevent the formation of carbonic acid. Other corrosive conditions are Degasification and Decarbonation, which will extend the life of the ion exchange resin. If CO2 levels remain high in the inlet feed water to the ion exchange system, the resin beds, whether cation or anion, will require more frequent regeneration, and your chemical usage and cost will rise.
In industrial applications, it’s easy to overlook.
Often, there is insufficient focus on selecting the right decarbonation or degasification system to ensure that the process water treatment system performs at the highest optimal level. For water filtration, when the primary process is membrane filtration, often referred to as “reverse osmosis, " too little attention is given to properly removing CO2 from the process to lower the pH and adjust the alkalinity.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
scaling,
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin
The Term referred to as “Degasification” or "Decarbonation" and how they work
Relates to the process of the removal of suspended gas or solids that are converted to a gas-based upon certain criteria during water filtration, treatment, membrane filtration, or attempting to adjust pH. When removing (CO2) the process is often referred to as “Decarbonation”, when removing (H2S) the process is often referred to as “Degasification”.
Degasification is the most economical method for
the removal of Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S), Carbon Dioxide (CO2), and Oxygen (02) can all be removed by “Degasification”. The other variables are the total inlet water flow rate, the inlet feed temperature of the water, the ambient air temperature, the inlet concentrations that can be expressed as parts per billion (ppb), parts per million (ppm) or Mg/l, and the desired effluent removal levels also expressed in the same method. It is also important to fully understand the actual application and the use of the water to determine how critical maintaining critical levels are and what impact variations will create for the final use. Understanding these variables will aid you in the design of the system and any additional redundant systems needed to assure full compliance with standards.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
Decarbonation

Following NSF/ANSI 61 regulations when designing and selecting the materials for the manufacturing of water treatment equipment.
It is important to understand what regulatory standards or constructions standard may be required to be compliant. This includes the designing and fabrication of systems such as reverse osmosis utilizing membrane technology, decarbonation of Carbon Dioxide, degasification of Hydrogen Sulfide, and water filtration for the removal of micron particles from potable and nonpotable water processes.
One requirement that engineers and manufacturers often encounter is called NSF /ANSI 61. NSF is an international and nonprofit, nongovernmental organization that is focused and dedicated to public health and safety as it relates to potable water systems and their components. NSF/ANSI 61 developed and established minimum requirements for the control of potential adverse human health effects from products and their components that contact with drinking water.
DeLoach Industries Inc. manufactures multiple types of water treatment equipment and adheres to strict compliance with NSF/ANSI 61 standards with all of their manufacturing procedures and practices. This strict adherence assures owners that water treatment equipment like decarbonation and degasification towers, reverse osmosis, and ion exchange that the equipment and material are all in full compliance with the NSF/ANSI 61 requirements.
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
About DeLoach Industries,
fabrication,
contact molded process,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Decarbonation,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
decarbonator,
H2S Degasifier,
ansi61,
nsf/ansi61
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
pH levels of water,
aeration,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
fiberglass,
About DeLoach Industries,
fabrication,
biological scrubber,
Chemical Odor,
media packing,
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
De-Aeration,
decarbonator,
boiler system,
distillation,
degasifier,
RO system,
H2S Degasifier,
Fish Farming,
Aquaculture,
Pisciculture,
Biological Odor Control Scrubber,
Biological odor control,
removal of CO2 from water,
Deagasification,
decarbonation of water,
Sand filters,
Filter Media,
municipal water systems,
greensand,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Drinking Water
CO2 & pH In municipal and industrial water processes
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) in municipal and Industrial water can create problems in the water treatment process, increase operational costs of the treatment plant, and cause excessive corrosion to equipment and ancillary equipment.
In nature, one of the most natural common causes that create low pH or acidity in water is an element known as “Carbon Dioxide” (CO2). The process of how carbon dioxide enters the water in the first place is a topic worth exploring. Nature creates one of the most common causes of CO2 found in the water naturally. When the water reaches an equilibrium with our atmosphere followed by the biological degradation that is aided by the photosynthesis of organic carbon (CH2O) then carbon dioxide begins to form. Organic carbon is dissolved in water and it forms “Carbonic Acid”
(H2CO3). CO2 (g) + H2O (l) = H2CO3 (aq).
The process to form the carbonic acid is slow and only a small portion remains as an acid because proton losses occur during the process.
H2CO3 (aq) « H+ (aq) + HCO3- (aq)
CO3- (aq) « H+ (aq) + CO32- (aq)
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
water plant,
pH levels,
caustic,
Decarbonation,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
decarbonator,
gases,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier,
Co2 ph