Do you think all distribution systems are made equal?
if you do you may be surprised that there is a lot of variation in manufacturing protocols for aerators, degasifiers, and decarbonators. Aerators are often found in use at Industrial Water Treatment and municipal water treatment facilities around the globe.
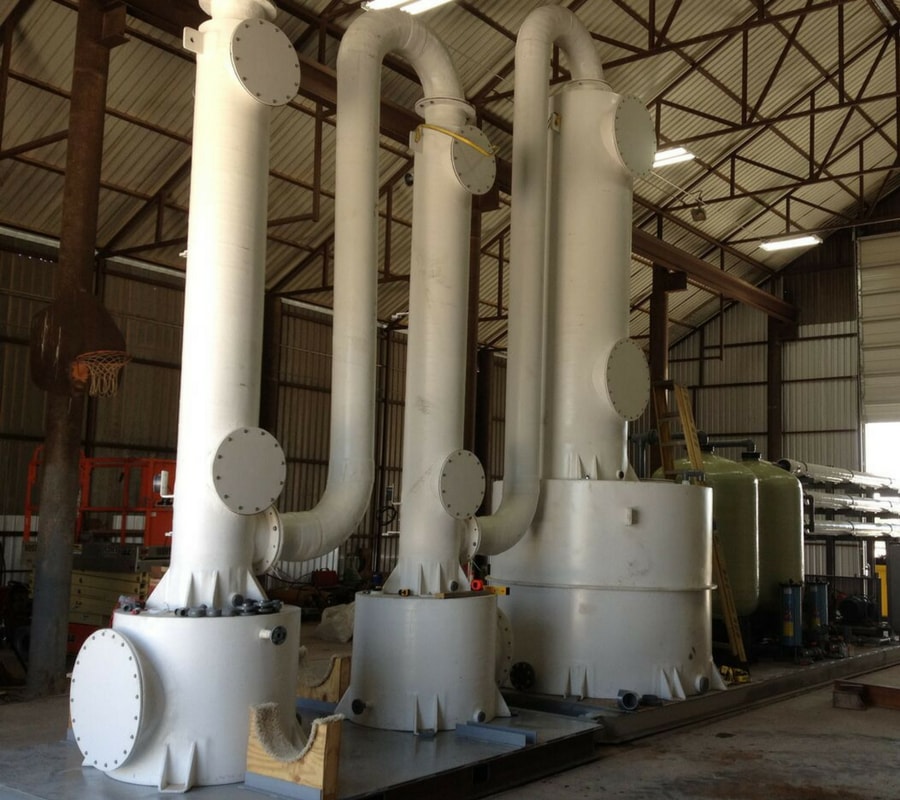
For water treatment, you may be surprised to learn that one of the key items that separate different types of aerators and decarbonators for water treatment is the type of distribution system it utilizes. To improve Carbon Dioxide (CO2) or Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) removal you need to select the best distribution system for the tower and make sure it's maintained. Now, there are many types of aerators in general and the term is used broadly. From floating pond aerators to wastewater aerators, to vertical tower aerators, decarbonators, and degasifiers for industrial water treatment aerators. We will focus on vertical tower aerators for industrial water treatment. All types of Aerators and even degasifiers and even decarbonators and Odor Control Scrubbers require some type of distribution system to begin the process of gas transfer and to remove Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) from water or Carbon Dioxide (CO2). It is important to evenly distribute the water or chemical solution across the media bed.
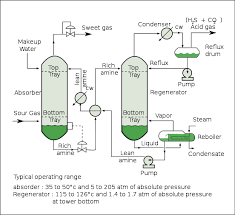
There are several types of distribution systems available and the three most common ones you will see on the marketplace are the “Tray” type, Weir, or the header lateral utilizing gas release “Nozzles”.
The selection of what type of distribution system is typically driven by the marketing side of who is selling you the tower. But in terms of real performance a distribution system utilizing a nozzle system will outperform a tray-type distributor. All packed towers are designed utilizing Henry’s Law Constant” theory of chemistry and what all towers rely upon is some type of method to break the surface tension of the water and expose the molecules of gases so that they either can escape or can be introduced to a reaction agent.
When towers are designed it is important to properly hydraulically load the top of the media bed. This is considered " Degasification Basics". This is important for many reasons and we will address these points in future updates. When using a properly designed nozzle distribution system such as a DeLoach Industries header lateral system then you get the benefit of both proper hydraulic load across the bed and you also gain anywhere from 4-10% removal efficiency depending upon the application. When looking at a chemical scrubber versus a biological scrubber you will notice they too have very different distribution systems. DeLoach Industries, Inc. has learned over its 60 years in business how to maximize gas transfer release. If designed and built properly the gas release process or interaction process (if designing a scrubber) has already begun “before” it enters the media bed.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
aeration,
Decarbonation,
De-Aeration,
decarbonator,
degasifier
Ammonia (AM) is a common water pollutant that significantly impacts the water process industry.
It is not just polluting water bodies but also aqua wells and humidifiers. Generally, AM is produced from human sweat and urine and created from synthetic ammonia in industrial processes.
Ammonia has three types of amines – primary, secondary, and tertiary – all are toxic for humans and aquatic life.
- Primary Amine has two carbon and one nitrogen atom, also called methylamine or CHNH2.
- Secondary Amine has two nitrogen atoms with no carbon atom between them, also called Dimethylamine or CH2(NH)CH3.
- Tertiary Amine has three nitrogen atoms with no carbon atoms between them; thus, it’s called Trimethylamine or CH3C(NH)CH3.
In natural conditions, primary Amide bacteria produce Amide under high-temperature conditions. In an aqueous solution and soil environments with high pH levels (>6).
Primary amide can form by the dehydrogenation of nitriles, such as acetonitrile, which are further oxidized to form acetic acid.
Primary amide form by alkaline hydrolysis of nitro compounds such as 2-nitrophenol.
Process systems often need to recognize when the Degasification or Decarbonation system is failing or underperforming.
Read More
Topics:
Decarbonation,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
Amine,
Ammonia,
Deagasification,
Filter Media,
distribution system,
blower motor,
process system,
frequent inspections
Understanding De-Aeration and Decarbonation in Water Treatment Systems
De-Aeration and decarbonation are two essential processes used to remove carbon dioxide (CO2) and dissolved oxygen (O2) from water streams, particularly in boiler-feed water systems. While both processes share the goal of eliminating CO2, they differ in their approach to removing oxygen. A De-Aeration system focuses on removing both CO2 and O2, while a decarbonation system primarily targets the removal of CO2. Let's delve deeper into these processes to understand their mechanisms and benefits.
In a De-Aeration system, steam is introduced at the bottom of the tower. The inlet feed water is heated to near saturation temperature, minimizing pressure drop and venting limits. This ensures optimal thermal operating efficiency of the tower. The steam acts as a carrier gas, stripping both CO2 and O2 from the water as it rises through the tower. The tower is equipped with an internal distribution system and media packing to enhance the removal of dissolved gases. By the time the water reaches the top of the tower, it has undergone significant de-aeration, resulting in reduced CO2 and O2 levels. This purified water is then ready for entry into the boiler, ensuring efficient and reliable steam generation.
Read More
Topics:
media packing,
Decarbonation,
De-Aeration,
carbon dioxide,
oxygen,
steam,
decarbonator
Protecting Your Pharmaceutical Water: Ensuring Quality and Efficiency in Water Treatment
In the pharmaceutical industry, the removal of dissolved gases from water is a critical step in the water treatment process. However, it is essential to select the appropriate method of removing these gases, as the wrong choice can have detrimental effects on vital process water equipment such as steam boilers and distillation columns. Failure to address high levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the water can lead to the formation of carbonic acid, which corrodes and damages both the steam boiler tubes and distillation columns. To mitigate these risks, the implementation of a degasification tower or "Degasifier" is crucial, as it effectively removes dissolved gases like hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2) to acceptable levels below 7 parts per billion (ppb).
Utilizing a degasification tower offers a cost-effective solution to reduce and eliminate gases in the water stream. In comparison, alternative methods such as reverse osmosis (RO) membranes require additional steps, including pH adjustment, to achieve similar results. The conversion of carbon dioxide (CO2) into carbonates can result in increased membrane fouling and elevated capital costs for the RO system. By implementing a degasification system, businesses can achieve optimal performance, minimize membrane fouling, and benefit from cost savings in both capital and operational expenses.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
water treatment,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
dissolved gases,
pharmaceutical water,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
gases,
RO membrane,
carbonic acid,
RO system
The importance of removing Carbon Dioxide in the water!
Carbon dioxide exists naturally in nature as free CO2 and can be found in many water sources from lakes, streams, or other surface water bodies. Carbon dioxide occurs naturally in small amounts (about 0.04 percent) in the Earth's atmosphere. Monitoring CO2 levels in your water can be done through test kits or monitoring systems. When monitoring CO2 levels, it is important to note the concentration at which the monitoring needs to occur. Industrial level ion exchange systems should be monitored at a concentration typically 15–20 times greater than required for drinking water quality. Ion exchange systems used for high purity water production should be monitored at a concentration typically 40–50 times greater than what is required for drinking water quality. Due to carbon dioxide’s abundance and its role as the primary driver of climate change, there are concerns about increasing concentrations of this gas in the atmosphere. To reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, people can reduce the amount of carbon dioxide released during energy production by using renewable energy sources and energy efficiency. Carbon dioxide can be captured and stored underground with carbon sequestration technologies.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
carbon dioxide,
CO2 in water,
excess co2,
hydrogen ion
Saving Steam with Degasification: Optimizing Water Treatment for Cost Efficiency and Enhanced Performance.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
Decarbonation,
steam generation,
carbon dioxide,
steam,
decarbonator,
distillation
The operation of steam-generating boilers and the process of removing dissolved gases from the feed water is of utmost importance.
Deaeration is essential in the boiler system process.
Deaeration involves removing oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from the water. Removing oxygen and carbon dioxide from the water before it enters the boiler system is essential. This prevents corrosion of the boiler system components and reduces costly maintenance and repairs to your system.
Oxygen and carbon dioxide can corrode and destroy metal components of the boiler system.
Corrosion can be costly to repair or replace. This is due to oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) not being removed from the water.
In order to avoid unwanted corrosion, it is necessary to treat the water before it enters the boiler system. This can be achieved through different techniques, including deaeration, chemical treatment, or mechanical filtration.
The deaeration process typically requires a deaerator. This device combines heat and vacuum to remove dissolved gases from water. The deaerator reduces the amount of dissolved solids in the water.This can improve the efficiency of the boiler system. Neglecting regular maintenance and inspection of the boiler can lead to severe corrosion damage and operational issues.
Read More
Topics:
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
feed water,
De-Aeration,
steam generating boilers,
carbon dioxide,
oxygen,
steam,
decarbonator,
boiler system
In the past two decades, there has been a remarkable development and improvement in wastewater technologies, driven by both necessity and stringent governmental regulations.
Today, municipalities and countries worldwide are recognizing the vital importance of recycling wastewater into clean drinking water. In certain regions like the Caribbean and other foreign nations, the wastewater to the drinking water industry is not merely a choice but a necessity.
To address our global needs and challenges, the recycling of wastewater to produce safe drinking water has become an everyday practice, empowered by cutting-edge technologies such as "Ultra-Filtration" and "Membrane Bio-Reactors" (MBR). These technologies continue to advance, offering much-needed solutions to the world's water scarcity issues. Moreover, due to stricter governmental requirements for wastewater recycling, the purity standards achieved through this process often surpass those of conventional water treatment methods. To foster global growth, it is crucial for professionals and consumers alike to acknowledge and embrace wastewater recycling whenever and wherever it is applicable to meet our evolving needs.
One of the key elements in the wastewater recycling process is the removal of contaminants, such as hydrogen sulfide gas, through advanced treatment methods. Hydrogen sulfide gas, a common byproduct of various industrial processes, can pose significant risks to water quality. Through technologies like Ultra-Filtration, this harmful gas can be effectively eliminated, ensuring the production of safe drinking water.
Another crucial aspect of wastewater treatment is addressing water turbidity. Turbidity refers to the cloudiness or haziness of water caused by the presence of suspended particles. By employing techniques like Membrane Bio-Reactors (MBR), wastewater can undergo thorough filtration, effectively removing suspended solids and improving water clarity. This ensures that the recycled water meets stringent purity standards and is suitable for drinking.
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
advanced treatment solutions,
Safe drinking water,
wastewater,
Recycling,
Caribbean,
Global
Water treatment in the Caribbean poses unique challenges due to the specific characteristics of the region.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
pH levels,
Alkalinity,
Recycling,
Caribbean,
Global
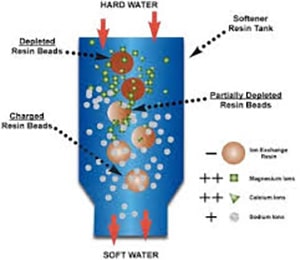
Extending the life of your ion exchange resin in boiler feed water applications
Did you know that when producing steam, it is most effectively accomplished by utilizing a decarbonation process? Decarbonation and Degasification is the most economical way to process fluent water pre-Ion exchange treatment through a vertically packed tower called a decarbonator, often called a degasifier. This is the most economical method to remove carbon dioxide (CO2) and Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) to prevent the formation of carbonic acid. Other corrosive conditions are Degasification and Decarbonation, which will extend the life of the ion exchange resin. If CO2 levels remain high in the inlet feed water to the ion exchange system, the resin beds, whether cation or anion, will require more frequent regeneration, and your chemical usage and cost will rise.
In industrial applications, it’s easy to overlook.
Often, there is insufficient focus on selecting the right decarbonation or degasification system to ensure that the process water treatment system performs at the highest optimal level. For water filtration, when the primary process is membrane filtration, often referred to as “reverse osmosis, " too little attention is given to properly removing CO2 from the process to lower the pH and adjust the alkalinity.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
scaling,
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin