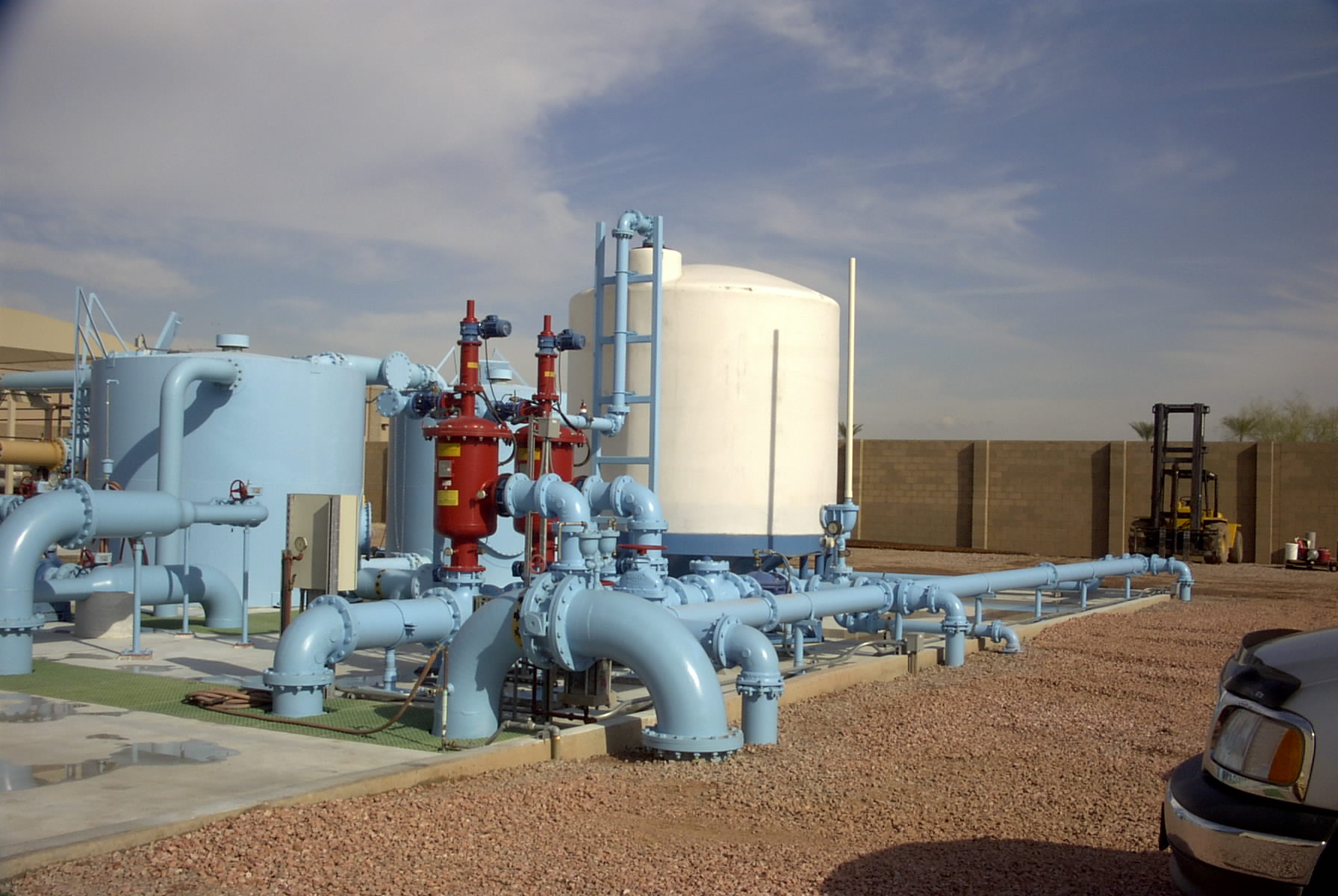
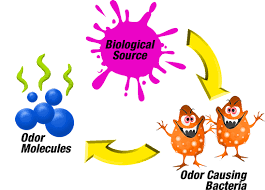
A Biological Scrubber is a wet odor control scrubber that treats and removes contaminants from an air stream.
It utilizes caustic typically to control the pH of the re-circulation solution. There are several types of odor control and chemical fume scrubbers on the market today. Each plays a role in treating noxious or corrosive gases in the industry.
Biological scrubbers are used in municipal applications to treat low and high hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gas levels. This colorless gas is removed from the water or wastewater treatment process.
Water treatment equipment such as “degasification” or “decarbonation” towers.
Strips the hydrogen sulfide gas from the treated wastewater and exhausts the gas from an exhaust port. These gases are captured and sent to the biological scrubber via an air duct system. The health effects of hydrogen sulfide can cause eye irritation, loss of appetite, and fluid in the lungs. Hydrogen gases are captured at a wastewater treatment process, including treatment facilities, lift stations, or head-works facilities. The PVC or FRP duct system sends the gases to the biological scrubber.
How does a Biological Scrubber work?
A biological scrubber utilizes tiny microorganisms (bacteria) to break down and digest contaminants. The bacteria feed on the contaminants and utilize this as a feed source to live and grow. When utilizing a biological scrubber for hydrogen sulfide (H2S) treatment, the by-product waste is acid from the digested H2S. This lowers the pH and requires the use of caustic to buffer the water and nutrient solution that is recirculated within the scrubber to maintain a neutral pH. The captured gas containing contaminants enters the bottom of a vertical biological scrubber. Similar to how the gas enters any other type of chemical scrubber or single or dual pass odor control scrubber.
The gas stream travels upward. Passes over a media bed that has been cultured to grow live microorganisms. A biological odor control scrubber already has “artificial intelligence” because of the millions of microbes colonies it supports.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
odor control,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
dissolved gases,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
gases,
RO system,
H2S Degasifier,
what is a scrubber
Odor control and acid scrubbers are both popular in many industries.
Read More
Topics:
odor control,
water treatment,
biological scrubber,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
dissolved gases,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
gases,
H2S Degasifier
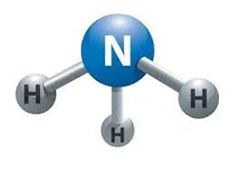
The type of Odor Control Wet Scrubber selected for the treatment and neutralization of Ammonia (NH3) gases depends on several variables, including the type and source of the ammonia gas and whether or not it is “Free” ammonia and or unionized.
Ammonia is a very miscible and stable molecule with solid hydrogen bonds, making it very soluble in water and difficult to treat without using a properly designed and sized ammonia scrubber. The concentrations, air flow rates, temperature of the gas stream, and chemical reagents being utilized, such as caustic to remove and then treat the ammonia, all play a significant role in the removal efficiency of the ammonia gas scrubber system. Unlike other types of “odor control scrubbers,” an ammonia scrubber is much more sensitive to variables such as the gas stream temperature because of the solubility of ammonia.
Ammonia is produced from nitrogen and hydrogen
the process is called the Haber Process by combining nitrogen with air and adding pressure, you can make ammonia.
It takes about 200 atmospheres of pressure, and the process varies from refinery to refinery. Still, on average, you can only make approximately 15% of ammonia during each pass which takes multiple passes to achieve the 15%. The reaction to make ammonia is exothermic when produced in a refining process.
However, ammonia is also formed in nature in smaller quantities. Most ammonia (90%) is utilized for fertilizer production, but ammonia can be found in food, pharmaceutical products, and cleaning supplies. When ammonia gas is released into the air, it has a very noxious and pungent odor that can be dangerous to inhale, so often, odor control scrubbers are required to capture and treat the ammonia gas.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
wastewater,
degasifier,
gases,
H2S Degasifier,
Ammonia
Avoid problems with calcium chlorite and corrosive gasses with your odor control scrubber.
When planning or designing an odor control system, one should pay close attention to several key variables that can cause havoc on a chemical odor control scrubber when trying to treat hydrogen sulfide or ammonia gases. The need for odor control occurs in many different forms. It is essential to understand the process that is creating the odorous or corrosive gas and the need for odor control & air emissions treatment.
First, begin to identify
all the potential obstacles that may creep up later after the chemical odor or corrosive gas control system goes online, like acid or caustic consumption. For example, chemical odor control systems designed for water treatment for the municipal industry are typically needed and attached to a degasification or decarbonation process, often needed to treat hydrogen sulfide (H2S). However, designers often may not pay close enough attention to the type of water process available for “make-up” water for the chemical scrubber. The addition of caustic can create scaling or fouling. This unknown variable of the makeup water quality can lead to a complete tower shutdown if the chemical scrubber distribution and media bed scales or fouls. The most commonly used chemicals for a hydrogen sulfide (H2S) scrubber are either chlorine in the form of sodium hypochlorite or caustic in the form of caustic soda. Both of these chemicals are common to a water treatment facility and are already in place to adjust and control pH.
The makeup water plays a significant role in the operation of a chemical scrubber.
When water containing high hardness levels is used as the source for the makeup water, your chemical scrubber can become fouled, and scaling can occur in a matter of hours, depending on the alkalinity and salts within the water. Solidification can occur from the scaling when combining sodium hypochlorite and raw feed water at specific pH ranges and these ranges are usually the range needed to achieve peak performance. Calcium chloride will form, and your chemical odor control scrubber will become a solid chunk of calcium chlorite making, making the ability for water or air to pass freely through the media packing next to impossible. No matter what type of media packing is utilized in the odor control or gas scrubber, it can foul and scale if the water chemistry is incorrect. Trust me when I say “been there and done that”! I have seen operators who have allowed a chemical scrubber to become out of balance with pH control and completely solidify the tower column to the degree that neither air nor water passage is possible. The problem can still occur with ammonia scrubbers but are different with different sets of parameters.
Read More
Topics:
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
calcium carbonate,
media packing,
pH levels,
Alkalinity,
Langilier index (LSI),
scaling,
chlorine,
caustic,
ION Exchange Resin,
Safe drinking water,
dissolved gases,
De-Aeration,
carbon dioxide,
oxygen,
degasifier,
gases,
H2S Degasifier,
calcium chlorite
The water treatment industry has developed and evolved over the years to continue to find new ways to produce degassed water,
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
safety,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
media packing,
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
wastewater,
Global,
carbon dioxide,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
gases,
RO membrane,
H2S Degasifier,
degassed water
Protecting Your Pharmaceutical Water: Ensuring Quality and Efficiency in Water Treatment
In the pharmaceutical industry, the removal of dissolved gases from water is a critical step in the water treatment process. However, it is essential to select the appropriate method of removing these gases, as the wrong choice can have detrimental effects on vital process water equipment such as steam boilers and distillation columns. Failure to address high levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the water can lead to the formation of carbonic acid, which corrodes and damages both the steam boiler tubes and distillation columns. To mitigate these risks, the implementation of a degasification tower or "Degasifier" is crucial, as it effectively removes dissolved gases like hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2) to acceptable levels below 7 parts per billion (ppb).
Utilizing a degasification tower offers a cost-effective solution to reduce and eliminate gases in the water stream. In comparison, alternative methods such as reverse osmosis (RO) membranes require additional steps, including pH adjustment, to achieve similar results. The conversion of carbon dioxide (CO2) into carbonates can result in increased membrane fouling and elevated capital costs for the RO system. By implementing a degasification system, businesses can achieve optimal performance, minimize membrane fouling, and benefit from cost savings in both capital and operational expenses.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
water treatment,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
dissolved gases,
pharmaceutical water,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
gases,
RO membrane,
carbonic acid,
RO system
The operation of steam-generating boilers and the process of removing dissolved gases from the feed water is of utmost importance.
Deaeration is essential in the boiler system process.
Deaeration involves removing oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from the water. Removing oxygen and carbon dioxide from the water before it enters the boiler system is essential. This prevents corrosion of the boiler system components and reduces costly maintenance and repairs to your system.
Oxygen and carbon dioxide can corrode and destroy metal components of the boiler system.
Corrosion can be costly to repair or replace. This is due to oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) not being removed from the water.
In order to avoid unwanted corrosion, it is necessary to treat the water before it enters the boiler system. This can be achieved through different techniques, including deaeration, chemical treatment, or mechanical filtration.
The deaeration process typically requires a deaerator. This device combines heat and vacuum to remove dissolved gases from water. The deaerator reduces the amount of dissolved solids in the water.This can improve the efficiency of the boiler system. Neglecting regular maintenance and inspection of the boiler can lead to severe corrosion damage and operational issues.
Read More
Topics:
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
feed water,
De-Aeration,
steam generating boilers,
carbon dioxide,
oxygen,
steam,
decarbonator,
boiler system
Water treatment towers and storage tanks are high places that require special precautions when entering. While the majority of people who enter these locations for work can be trusted, there are some hazards that make it more important than usual to follow safety procedures.
These locations can get very hot and humid, and can also be filled with harmful chemicals and microorganisms that can cause serious health issues if inhaled or absorbed through the skin. Therefore, the general standard for workplace safety is much higher when entering locations like these.
Make sure you have read and understood the following information about safety when entering a water treatment plant. It will help you understand how to stay safe and protect yourself from harm when entering a water treatment plant. normal installation, maintenance, or even emergency repairs, it is often required to enter into a water treatment tower (degasifier, air stripper, decarbonator, or clear well/ storage tank). When this occurs, full safety protocols should be followed at all times, in accordance with OSHA regulations. A tower or tank B classification is a "Confined Space" location. For more information visit the OSHA confined space regulations page.
In addition, there are other safety risks that an operator or technician can be exposed to while inside these types of closed locations. The risk can come from fumes of hydrogen sulfide (H2S), chlorine from an injection line, or a lack of oxygen O2. A proper confined space permit should be prepared and only technicians with proper training and certifications should enter into these types of confined spaces.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
safety,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
media packing,
scaling,
caustic,
Safe drinking water,
dissolved gases,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
gases,
Ammonia,
what is a scrubber,
Hydrogen Sulfide formula,
Deagasification,
Filter Media,
DeLoach Industries, Inc.,
Drinking Water,
Clean Water,
Contaminated Water,
OSHA