Basics of water decarbonation for dissolved organic carbon.
The water treatment industry continues to develop and evolve. Over the past two decades, there have been many new developments in technology and even more refinement in existing technologies such as "Degasification". The evolution and advancement of water treatment have been driven by the constantly increasing demand from an increase in population that demand cost-effective solutions and recognition to improve safety with the implementation of NSF 61 standards.
All human cultures on our planet share a single commonality: the dependency on water to survive.
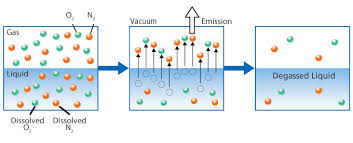
Many existing technologies, such as "Degasification," have evolved with higher efficiency to meet the demand changes and provide safety to consumers and the systems. Degasification refers to the removal of dissolved gases from liquids, and the science to degasify water is based upon a chemistry equation known as "Henry's Law". The "proportionality factor" is called Henry's law constant" and was developed by William Henry in the early 19th century. Henry's Law states that "the amount of dissolved gas is proportional to its partial pressure in the gas." The most "cost" effective method to perform degasification is with the packed vertical tower called a "Degasifier” or “Decarbonator.”
The key words in this previous sentence for owners, operators, and engineers to focus on is "the most cost-effective" as there is no other process more cost-effective at removing dissolved gases at the lowest cost than using a Degasifier or decarbonator. The process of degasification is simple enough to understand. Water is pumped to the top of a vertically constructed tower, where it first enters the tower through some type of distribution system at the same time, there is a cross-current air flowing up from the bottom by a blower located at the bottom of the tower, and the air encounters the water and is exhausted at the top of the tower through an exhaust port. There are various types of distribution systems, and we will explore these in later discussions. Once the water enters the top of the tower and passes through the distribution system, it then travels by gravity downward. The next thing the water encounters is some type of media packing. There are various forms of media packing offered in the degasification industry, and each type can offer higher performance or have the ability to deter fouling. The selection of the type, size, and volume is where the “experience, engineering, and understanding of each application” comes into play.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
About DeLoach Industries,
water plant,
NSF/ANSI 61,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
media packing,
pH levels,
scaling,
caustic,
Decarbonation,
Safe drinking water,
dissolved gases,
carbon dioxide,
decarbonator,
boiler system,
degasifier,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier,
Dissolved organic Carbon,
co2 dissolved in water
In the production and purification of water for industry
there are many types of different processes available to remove harmful minerals and gases from the water stream but the most effective process and most cost-effective from both a capital investment and operational cost is a “Forced Draft Degasification System” (Degasifier).
Degasification is used in a wide range of water processes for industrial and municipal applications which extend from the production of chemicals to the production of semiconductors and in all applications the need to remove contaminants from the water and dissolved gases is key to achieving the end results needed in the industrial water process. Water from the ground often contains elements such as calcium carbonate, manganese, iron, salts, hydrogen sulfide, and sulfur just to name a few of the basic contaminants and these naturally occurring elements can cause serious damage and consequences to process equipment such as boiler systems, piping, membranes, and cation and anion exchange resins used in the demineralization process.
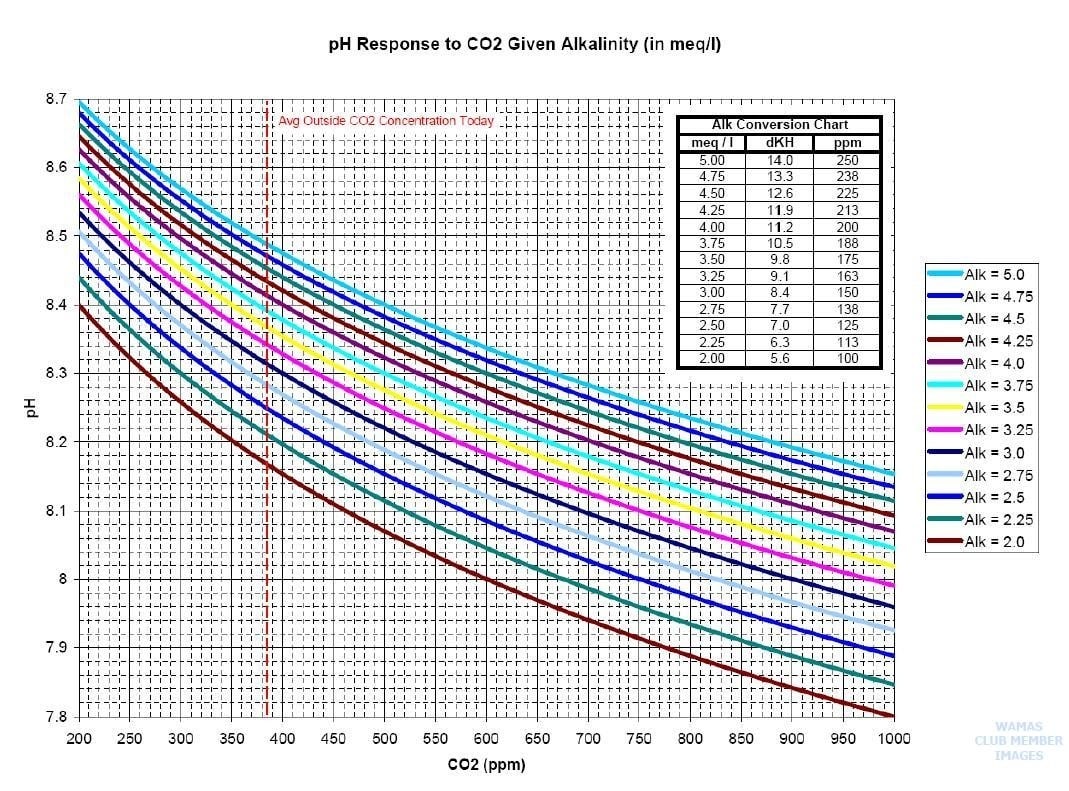
Calcium carbonate can dissolve in water under certain pH ranges forming carbonic acid and releasing carbon dioxide (CO2) gases. These gases are not only very corrosive to equipment like boiler feed systems and boiler tubes but also attack the actual resin beds found in cation and anion softening and demineralization system causing an increase in regeneration and chemical consumption and resin bed replacement.
By incorporating a Force Draft Degasification system you can remove dissolved gasses
like CO2 and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) to as low as 99.999% and improve the cation and anion system performance, extend the resin bed life, and lower the operating cost of the water treatment process.
Quite often Forced Draft Degasification is utilized “post” treatment to also remove newly formed dissolved gases prior to entering the boiler feed system to prevent corrosion damage within the tubes and feed system and pumps. These gases are easily removed with the forced draft degasifier at a much lower cost than chemical additives or liquid cell degasification that requires higher capital cost and much higher operating cost.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
iron oxidation,
water treatment,
water distribution system,
aluminum,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
calcium carbonate,
media packing,
pH levels,
Langilier index (LSI),
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
dissolved gases,
feed water,
De-Aeration,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier
To enhance and control the production and quality of seafood grown and harvested.
The industry increasingly focuses on constructing in-house aquaculture fish farms, commonly called aqua farming. The most popular species of aqua farming continue to be salmon, tilapia, catfish, and carp. Increased interest in the United States has developed aqua farming facilities in southern Florida with favorable climate and water conditions.
When considering several types of fish species to grow for harvest, it is important to remember the need to control the water quality. If the aqua farm is intended to utilize man-made tanks, they will depend upon a constant flow of incoming water. If the aqua farm focuses on salmon, the water quality and temperature play a major role in the operation's mortality rates and production yields.
Having water with too high of hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide, total Organic carbons, and even turbidity can increase mortality rates among the younger fish species and is especially critical to salmon.
Having high levels of metals
Such as Iron that is identified as either “ferric” (Fe-) or “ferrous” (FE+2) and is naturally occurring within the Florida waters and other parts of the US will cause significant damage to young salmon species because the metal accumulates within the gills of the fish causing suffocation. Other metals are also detrimental to fish, including copper, aluminum, arsenic, cadmium, chromium, Lead, manganese, and mercury, to name a few, and the water quality must be evaluated and tested in the early stages of design to anticipate the required types of process systems needed.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
Alkalinity,
Decarbonation,
carbon dioxide,
oxygen,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier,
Aqua Farming,
Fish Farming,
Aquaculture,
Pisciculture
Water Treatment
When planning and designing a man made on land aquaculture or pisciculture facility.
The most important key element is the quality of the water. For operations developing in Florida or the Caribbean it is important to remember that water quality varies in Florida and other states in the US and typically requires some type of water treatment. For fresh and salt water land based farms that utilize tanks located inside of a building the water needs to be treated and pure from any naturally occurring contaminants such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S), iron (Fe+), and even carbon dioxide (CO2).
The most cost effective way to treat incoming water for aquaculture farming and remove hydrogen sulfide, iron, and lower carbon dioxide is the use of a “degasification” tower. A degasification tower or degasifier is a piece of process equipment. Degasifiers can also be referred to as a “decarbonator” or “air stripper” or even “aeration tower”. The degasification tower is a vertical column designed to remove certain types of contaminants by “stripping” the molecules of converted gases and expelling them from the water as a gas. The science is based upon “Henry’s Law” and it relies upon the disproportionate varying vapor pressures of gases.
If the incoming raw water contains levels of sulfides or hydrogen sulfide gases it is recommended to remove the hydrogen sulfide to improve the water quality and reduce the risk of the development and formation of bacteria that can thrive on the Sulfur. In addition hydrogen sulfide is corrosive and will cause harm to other components within the process if left untreated. It is important to adjust the pH of the raw feed water prior to degasification to ensure full conversion of the sulfides into hydrogen sulfide gas (H2S) to enable the degasification process to perform and remove up to 99.99% of the harmful contaminants without adding additional chemicals. This saves money and improves quality of the product!
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
Alkalinity,
Decarbonation,
Caribbean,
carbon dioxide,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
gases,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier,
Aqua Farming,
Fish Farming,
Aquaculture,
Pisciculture
Treating Hydrogen Sulfide for Environmental Safety
Read More
Topics:
odor control,
aeration,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
gases,
Amine,
H2S Degasifier
DeLoach Industries made history in 1977 at the City of Cape Coral Florida water treatment plant with its large scale “degasification towers” connected to what was to become the first municipal water treatment facility in the United States to deploy the use of reverse osmosis on a large-scale production municipal treatment plant.
The Cape Coral water treatment plant for came online in 1977 and produced 3 million gallons of water per day (GPD) or 11.35 liters of purified and treated water utilizing the “reverse osmosis” process. By 1985 the plant had expanded as it kept up with growth to produce 15 million gallons per day making it at the time the world’s largest “reverse osmosis” water treatment plant facility.
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
Alkalinity,
scaling,
chlorine,
caustic,
Decarbonation,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
RO membrane,
RO system,
H2S Degasifier
Caustic solution for Sodium hydroxide water treatment of Sodium Hydroxide
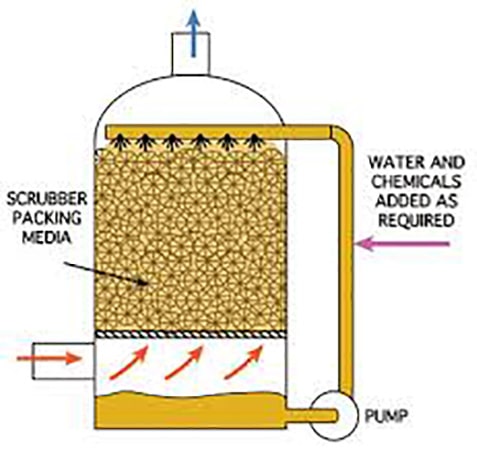
There are many industries that require the use of a caustic scrubber which is considered a chemical scrubber and they range from the municipal industry, mining, semiconductor markets, pulp and paper, and chemical refining. There is a wide variety of industrial processes that generate noxious or corrosive off gases that require treatment and a comparison is made between biological Vs. chemical. Often biological scrubbers have limitations due to concentrations, composition, or temperature of the contaminants and if the gas stream contains acid fumes then a biological scrubber is quickly ruled out.
The odor control selection is often fraught with choices of capital cost over operational cost and quite often comes down to familiarity from the designer or purchaser. It is always a good idea to freshen up the industrial odor control the do’s and don’t’s before selecting the final solution. If the off-gas source that needs to be treated is hydrogen sulfide (H2S) or some other type of gas stream produced by an acid or ammonia it will often require neutralization for human health reasons and to protect equipment or may be required to meet regulatory compliance. Caustic scrubbers may be either vertical or horizontal by design, but both utilize a packed media bed of either random packing or trays to allow the gas fumes to meet the recirculating caustic solution which then forces the reaction to occur.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
pH levels,
caustic,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
gases,
caustic solution,
sodium hydroxide water treatment
What type of Odor Control Scrubber do I select?
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
degasifier,
gases
Odor control and acid scrubbers are both popular in many industries.
Read More
Topics:
odor control,
water treatment,
biological scrubber,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
dissolved gases,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
gases,
H2S Degasifier
The type of Odor Control Wet Scrubber selected for the treatment and neutralization of Ammonia (NH3) gases depends on several variables, including the type and source of the ammonia gas and whether or not it is “Free” ammonia and or unionized.
Ammonia is a very miscible and stable molecule with solid hydrogen bonds, making it very soluble in water and difficult to treat without using a properly designed and sized ammonia scrubber. The concentrations, air flow rates, temperature of the gas stream, and chemical reagents being utilized, such as caustic to remove and then treat the ammonia, all play a significant role in the removal efficiency of the ammonia gas scrubber system. Unlike other types of “odor control scrubbers,” an ammonia scrubber is much more sensitive to variables such as the gas stream temperature because of the solubility of ammonia.
Ammonia is produced from nitrogen and hydrogen
the process is called the Haber Process by combining nitrogen with air and adding pressure, you can make ammonia.
It takes about 200 atmospheres of pressure, and the process varies from refinery to refinery. Still, on average, you can only make approximately 15% of ammonia during each pass which takes multiple passes to achieve the 15%. The reaction to make ammonia is exothermic when produced in a refining process.
However, ammonia is also formed in nature in smaller quantities. Most ammonia (90%) is utilized for fertilizer production, but ammonia can be found in food, pharmaceutical products, and cleaning supplies. When ammonia gas is released into the air, it has a very noxious and pungent odor that can be dangerous to inhale, so often, odor control scrubbers are required to capture and treat the ammonia gas.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
wastewater,
degasifier,
gases,
H2S Degasifier,
Ammonia