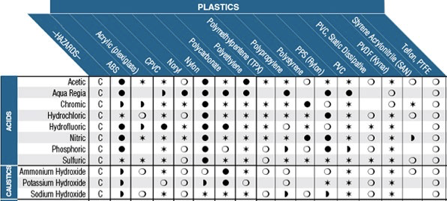
In process control systems, it is often required to handle fluids that have a harsh chemical nature. In these cases, it is necessary to be aware of material-chemical compatibility. Chemical compatibility is a general term referring to the way a specific chemical interacts with a specific material. This information is taken into consideration when selecting materials for construction for tanks, valves, pipework, tubing, and other devices that may encounter harsh chemicals. Common chemical types that are used in process systems are acids, bases, corrosives and oxidizers, and hydrocarbons. Typical chemical-resistant materials include natural and synthetic rubbers, vinyl polymers, fluoropolymers, and stainless steel. In order to determine which materials are compatible with certain chemicals, a chemical compatibility chart is often used. A chemical compatibility chart contains tabulated data about how a given material interacts with a given chemical.
Often, the manufacturer of the equipment or material in question will have their own compatibility chart for their specific goods. Most compatibility charts will have the same type of information. Materials will be categorized along one axis of the table, with fluids or gasses categorized along the other axis. At the intersection of a material with a fluid, you will find an indication of the level of compatibility. Some charts will use an A-F categorization, others may use a more graphical style. Most charts will be accompanied by a key or guide that explains how to use the table. There may also be multiple concentration levels and temperature ranges for a given fluid in cases where the distinction makes a difference with compatibility.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
caustic,
Decarbonation,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
Deagasification
The need to remove harmful water elements, such as Hydrogen Sulfide H2s and Carbon Dioxide CO2, from water in the pisciculture and aquaculture market is extremely important.
To achieve maximum results, the industry utilizes a treatment technology called “Degasification” and controls the pH precisely to maximize results. When utilizing equipment such as the DeLoach Industries degasification systems, the hydrogen sulfide, and carbon dioxide levels can be removed to 99.999% ug/l.
pH control with water degasification in water treatment is very important for aquaculture and the pisciculture market. In addition, there are a host of other organic and inorganic elements found in water, both naturally occurring and manmade, that require removal during some part of the water treatment process, and pH plays a significant role in the effectiveness of the treatment process.
Every application of degasification depends on pH adjustment to maximize results. As an example, the treatment of water may require the removal of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) to protect the species during the growth period. Hydrogen sulfide can be removed either as a “free” gas or requires the conversion of sulfides into (H2S) as a gas. You will often also see the need to adjust the pH of the water chemistry to maximize both the removal and the conversion to increase the efficiency of the equipment utilized to remove the hydrogen sulfide, such as a degasification tower or a degasifier.
Why is pH important, and what it means in water?
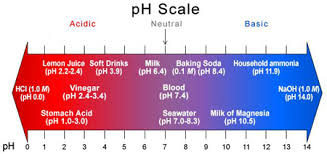
Water pH is a term used to describe whether or not the water is “acidic” or “basic.” pH ranges in water can be from 0-14. 0 is the most acidic, and 14 is at the far end and is the most basic, leaving “7” as the neutral state. A pH of 7 is neither acidic nor basic. So, what causes pH to be acidic? In nature, the most common cause of a low acidic pH in water is carbon dioxide (CO2) which occurs naturally when photosynthesis, decomposition, or respiration occurs in nature. The increase in CO2 causes an increase in ions, producing a lower pH in a simplified explanation.
How does pH play such a significant role in Aquaculture and Pisciculture?
Removing certain harmful elements is typically required to safeguard the growth of most aquatic species, and elements such as sulfides, sulfates, and free H2S hydrogen sulfide gases are dangerous. They can often kill many types of aquatic life. To maximize the removal of hydrogen sulfide from water utilizing a DeLoach Industries degasification tower, it is important to maintain as close to a pH of 5 as possible. When the pH rises above 5, the ability to convert and strip the free H2S gas from the water diminishes. When a degasification tower operates within this specific range and if it has been designed with the higher efficient distribution systems such as the ones utilized by DeLoach Industries, removal efficiencies of 99.999%- 100% can be achieved. If the pH rises to 7 or above, the removal process becomes much more difficult, and typically you will have much lower results. The pH adjustment during the water treatment process is normally accomplished by adding commercially available acid, such as “Sulphuric Acid,” one of the most common within the municipal and food and beverage industry.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
carbon dioxide,
oxygen,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
H2S Degasifier,
Aqua Farming,
Fish Farming,
Aquaculture,
Pisciculture
The need for pH control with water degasification and decarbonation in water treatment includes almost every industry and includes;
The need for pH control with water degasification and decarbonation in water treatment includes almost every industry and including; Aquaculture, food, and beverage, industrial, municipal, and even pisciculture. In some water treatment applications, harmful gases such as Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) are removed, while in other applications, Carbon Dioxide (CO2) or a combination of both. In addition, there's a host of other organic and inorganic elements found in water, both naturally occurring and manmade, that require removal during some part of the water treatment process.
In almost every application of degasification or decarbonation, you will hear or see the term pH used either by need or by the result. If, as an example, the water treatment application requires the removal of Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) to be removed either as “free” gas or requires the conversion of Sulfides into (H2S) gas. You will often also see the need to adjust the pH of the water chemistry to maximize both the removal and the conversion to increase the efficiency of the equipment being utilized to remove the hydrogen sulfide, such as a degasification tower or commonly called a degasifier.
So, what is pH?
Water pH is a term used to describe whether or not the water is “acidic” or “basic.” pH ranges in water can be from 0-14. 0 is the most acidic, and 14 is at the far end and is the most basic, leaving “7” as the neutral state. A pH of 7 is neither acidic nor basic. So, what causes pH to be acidic? In nature, the most common cause of a low acidic pH in water is Carbon Dioxide (CO2) which occurs naturally when photosynthesis, decomposition, or respiration occurs in nature. The increase in CO2 causes an increase in ions, producing a lower pH in a simplified explanation.
How does pH play such a significant role in degasification and decarbonation?
As mentioned above in the example of the removal of certain harmful elements such as sulfides, sulfates, and free H2S hydrogen sulfide gases, to maximize the removal from water utilizing a degasification tower, it is essential to maintain as close to a pH of 5 as possible. When the pH rises above 5, the ability to convert and strip the free H2S gas from the water diminishes. When a degasification tower operates within this specific range and if it has been designed with the higher efficient distribution systems such as the ones utilized by DeLoach Industries, removal efficiencies of 99.999%- 100% can be achieved. If the pH rises to seven or above, the removal process becomes much more complex, and typically, you will have much lower results. The pH adjustment during the water treatment process is typically accomplished by adding commercially available acid, such as “sulphuric acid,” one of the most common in the municipal and food and beverage industry.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
odor control,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
gases,
H2S Degasifier,
Aqua Farming,
Fish Farming,
Aquaculture
Basics of water decarbonation for dissolved organic carbon.
The water treatment industry continues to develop and evolve. Over the past two decades, there have been many new developments in technology and even more refinement in existing technologies such as "Degasification". The evolution and advancement of water treatment have been driven by the constantly increasing demand from an increase in population that demand cost-effective solutions and recognition to improve safety with the implementation of NSF 61 standards.
All human cultures on our planet share a single commonality: the dependency on water to survive.
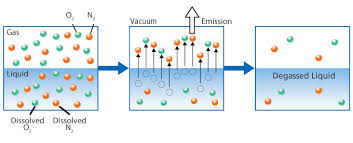
Many existing technologies, such as "Degasification," have evolved with higher efficiency to meet the demand changes and provide safety to consumers and the systems. Degasification refers to the removal of dissolved gases from liquids, and the science to degasify water is based upon a chemistry equation known as "Henry's Law". The "proportionality factor" is called Henry's law constant" and was developed by William Henry in the early 19th century. Henry's Law states that "the amount of dissolved gas is proportional to its partial pressure in the gas." The most "cost" effective method to perform degasification is with the packed vertical tower called a "Degasifier” or “Decarbonator.”
The key words in this previous sentence for owners, operators, and engineers to focus on is "the most cost-effective" as there is no other process more cost-effective at removing dissolved gases at the lowest cost than using a Degasifier or decarbonator. The process of degasification is simple enough to understand. Water is pumped to the top of a vertically constructed tower, where it first enters the tower through some type of distribution system at the same time, there is a cross-current air flowing up from the bottom by a blower located at the bottom of the tower, and the air encounters the water and is exhausted at the top of the tower through an exhaust port. There are various types of distribution systems, and we will explore these in later discussions. Once the water enters the top of the tower and passes through the distribution system, it then travels by gravity downward. The next thing the water encounters is some type of media packing. There are various forms of media packing offered in the degasification industry, and each type can offer higher performance or have the ability to deter fouling. The selection of the type, size, and volume is where the “experience, engineering, and understanding of each application” comes into play.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
About DeLoach Industries,
water plant,
NSF/ANSI 61,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
media packing,
pH levels,
scaling,
caustic,
Decarbonation,
Safe drinking water,
dissolved gases,
carbon dioxide,
decarbonator,
boiler system,
degasifier,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier,
Dissolved organic Carbon,
co2 dissolved in water
In the production and purification of water for industry
there are many types of different processes available to remove harmful minerals and gases from the water stream but the most effective process and most cost-effective from both a capital investment and operational cost is a “Forced Draft Degasification System” (Degasifier).
Degasification is used in a wide range of water processes for industrial and municipal applications which extend from the production of chemicals to the production of semiconductors and in all applications the need to remove contaminants from the water and dissolved gases is key to achieving the end results needed in the industrial water process. Water from the ground often contains elements such as calcium carbonate, manganese, iron, salts, hydrogen sulfide, and sulfur just to name a few of the basic contaminants and these naturally occurring elements can cause serious damage and consequences to process equipment such as boiler systems, piping, membranes, and cation and anion exchange resins used in the demineralization process.
Calcium carbonate can dissolve in water under certain pH ranges forming carbonic acid and releasing carbon dioxide (CO2) gases. These gases are not only very corrosive to equipment like boiler feed systems and boiler tubes but also attack the actual resin beds found in cation and anion softening and demineralization system causing an increase in regeneration and chemical consumption and resin bed replacement.
By incorporating a Force Draft Degasification system you can remove dissolved gasses
like CO2 and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) to as low as 99.999% and improve the cation and anion system performance, extend the resin bed life, and lower the operating cost of the water treatment process.
Quite often Forced Draft Degasification is utilized “post” treatment to also remove newly formed dissolved gases prior to entering the boiler feed system to prevent corrosion damage within the tubes and feed system and pumps. These gases are easily removed with the forced draft degasifier at a much lower cost than chemical additives or liquid cell degasification that requires higher capital cost and much higher operating cost.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
iron oxidation,
water treatment,
water distribution system,
aluminum,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
calcium carbonate,
media packing,
pH levels,
Langilier index (LSI),
Decarbonation,
ION Exchange Resin,
dissolved gases,
feed water,
De-Aeration,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier
To enhance and control the production and quality of seafood grown and harvested.
The industry increasingly focuses on constructing in-house aquaculture fish farms, commonly called aqua farming. The most popular species of aqua farming continue to be salmon, tilapia, catfish, and carp. Increased interest in the United States has developed aqua farming facilities in southern Florida with favorable climate and water conditions.
When considering several types of fish species to grow for harvest, it is important to remember the need to control the water quality. If the aqua farm is intended to utilize man-made tanks, they will depend upon a constant flow of incoming water. If the aqua farm focuses on salmon, the water quality and temperature play a major role in the operation's mortality rates and production yields.
Having water with too high of hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide, total Organic carbons, and even turbidity can increase mortality rates among the younger fish species and is especially critical to salmon.
Having high levels of metals
Such as Iron that is identified as either “ferric” (Fe-) or “ferrous” (FE+2) and is naturally occurring within the Florida waters and other parts of the US will cause significant damage to young salmon species because the metal accumulates within the gills of the fish causing suffocation. Other metals are also detrimental to fish, including copper, aluminum, arsenic, cadmium, chromium, Lead, manganese, and mercury, to name a few, and the water quality must be evaluated and tested in the early stages of design to anticipate the required types of process systems needed.
Read More
Topics:
water treatment issues,
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
Alkalinity,
Decarbonation,
carbon dioxide,
oxygen,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier,
Aqua Farming,
Fish Farming,
Aquaculture,
Pisciculture
Water Treatment
When planning and designing a man made on land aquaculture or pisciculture facility.
The most important key element is the quality of the water. For operations developing in Florida or the Caribbean it is important to remember that water quality varies in Florida and other states in the US and typically requires some type of water treatment. For fresh and salt water land based farms that utilize tanks located inside of a building the water needs to be treated and pure from any naturally occurring contaminants such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S), iron (Fe+), and even carbon dioxide (CO2).
The most cost effective way to treat incoming water for aquaculture farming and remove hydrogen sulfide, iron, and lower carbon dioxide is the use of a “degasification” tower. A degasification tower or degasifier is a piece of process equipment. Degasifiers can also be referred to as a “decarbonator” or “air stripper” or even “aeration tower”. The degasification tower is a vertical column designed to remove certain types of contaminants by “stripping” the molecules of converted gases and expelling them from the water as a gas. The science is based upon “Henry’s Law” and it relies upon the disproportionate varying vapor pressures of gases.
If the incoming raw water contains levels of sulfides or hydrogen sulfide gases it is recommended to remove the hydrogen sulfide to improve the water quality and reduce the risk of the development and formation of bacteria that can thrive on the Sulfur. In addition hydrogen sulfide is corrosive and will cause harm to other components within the process if left untreated. It is important to adjust the pH of the raw feed water prior to degasification to ensure full conversion of the sulfides into hydrogen sulfide gas (H2S) to enable the degasification process to perform and remove up to 99.99% of the harmful contaminants without adding additional chemicals. This saves money and improves quality of the product!
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
degasification,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
Alkalinity,
Decarbonation,
Caribbean,
carbon dioxide,
decarbonator,
degasifier,
gases,
carbonic acid,
H2S Degasifier,
Aqua Farming,
Fish Farming,
Aquaculture,
Pisciculture
Treating Hydrogen Sulfide for Environmental Safety
Read More
Topics:
odor control,
aeration,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
pH levels,
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
gases,
Amine,
H2S Degasifier
DeLoach Industries made history in 1977 at the City of Cape Coral Florida water treatment plant with its large scale “degasification towers” connected to what was to become the first municipal water treatment facility in the United States to deploy the use of reverse osmosis on a large-scale production municipal treatment plant.
The Cape Coral water treatment plant for came online in 1977 and produced 3 million gallons of water per day (GPD) or 11.35 liters of purified and treated water utilizing the “reverse osmosis” process. By 1985 the plant had expanded as it kept up with growth to produce 15 million gallons per day making it at the time the world’s largest “reverse osmosis” water treatment plant facility.
Read More
Topics:
water quality,
pH levels of water,
water treatment,
advanced treatment solutions,
water plant,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
pH levels,
Alkalinity,
scaling,
chlorine,
caustic,
Decarbonation,
wastewater,
carbon dioxide,
degasifier,
RO membrane,
RO system,
H2S Degasifier
Would it be possible for our odor control scrubbers to communicate with us and tell us when there are problems?
Or when they need service? With the new technological revolution, we are now this is quickly becoming a reality. DeLoach Industries is rapidly changing how water treatment and odor control and air emissions are treated with new advancements in artificial intelligence and integration into proven technologies.
Most operators will tell you that to keep and maintain an odor control system whether it's Biological Vs. chemical can be quite challenging depending on the type and source of the off-gas to be treated and depending on the type of chemical reagents being utilized such as acid or caustic solutions. When odor control systems such as a biological scrubber are met with varying flow rates, corrosive gases, or spiking concentrations an odor control system can be daunting to keep in balance and operating efficiency. But what if they could think or communicate with other devices or even operators for themselves? What if they could make corrections in caustic feed rates because of ammonia (NH3) concentration spikes, order chemicals like caustic or acid for pH control, and even inform us when they anticipate a problem for either the odor control scrubber or another critical component that it depends upon? That time has now arrived that’s to DeLoach Industries' new advancements to their equipment systems.
Read More
Topics:
degasification,
water distribution system,
advanced treatment solutions,
biological scrubber,
water plant,
odor control scrubber,
hydrogen sulfide (H2S),
Chemical Odor,
Decarbonation,
dissolved gases,
gases